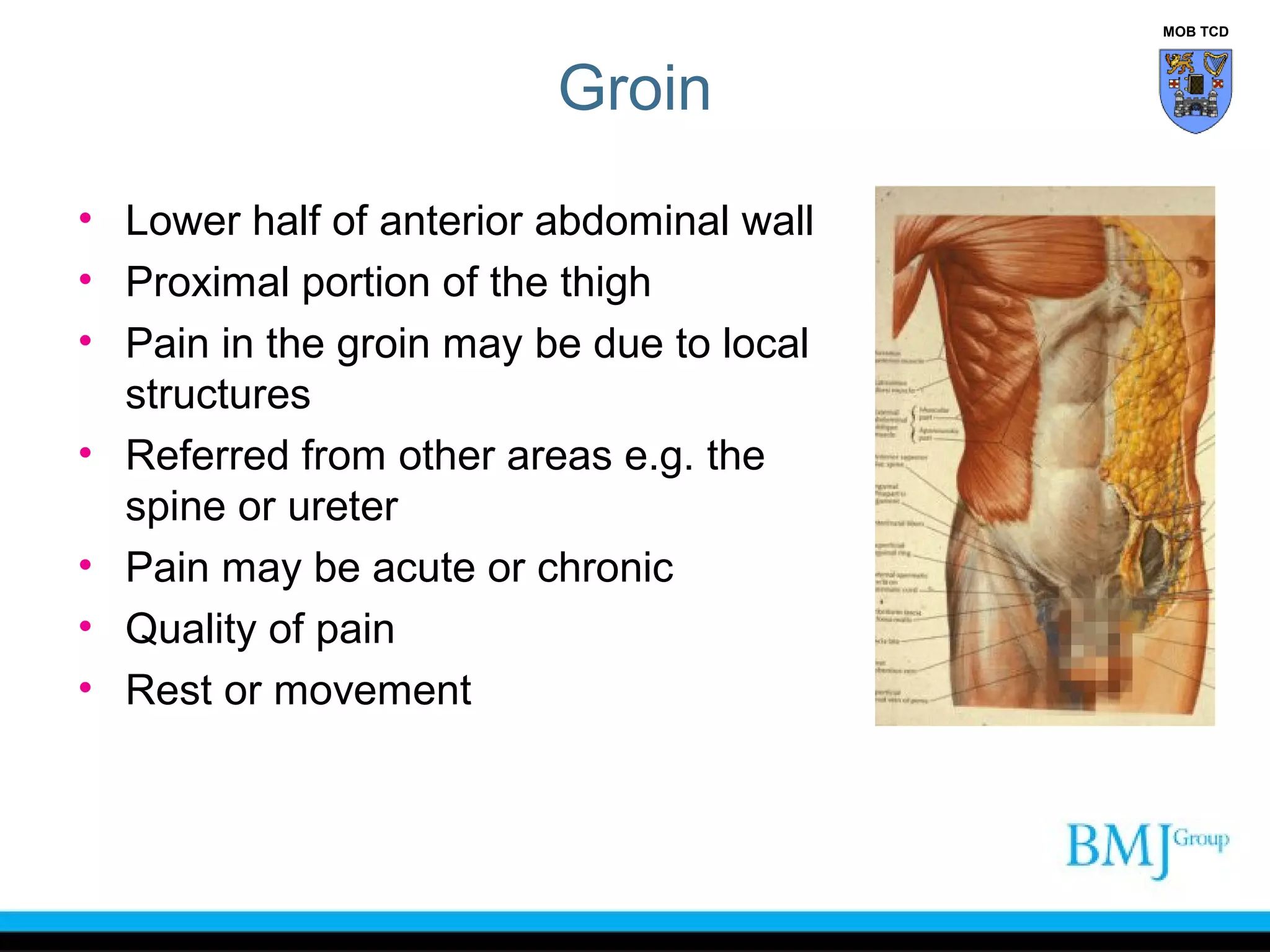
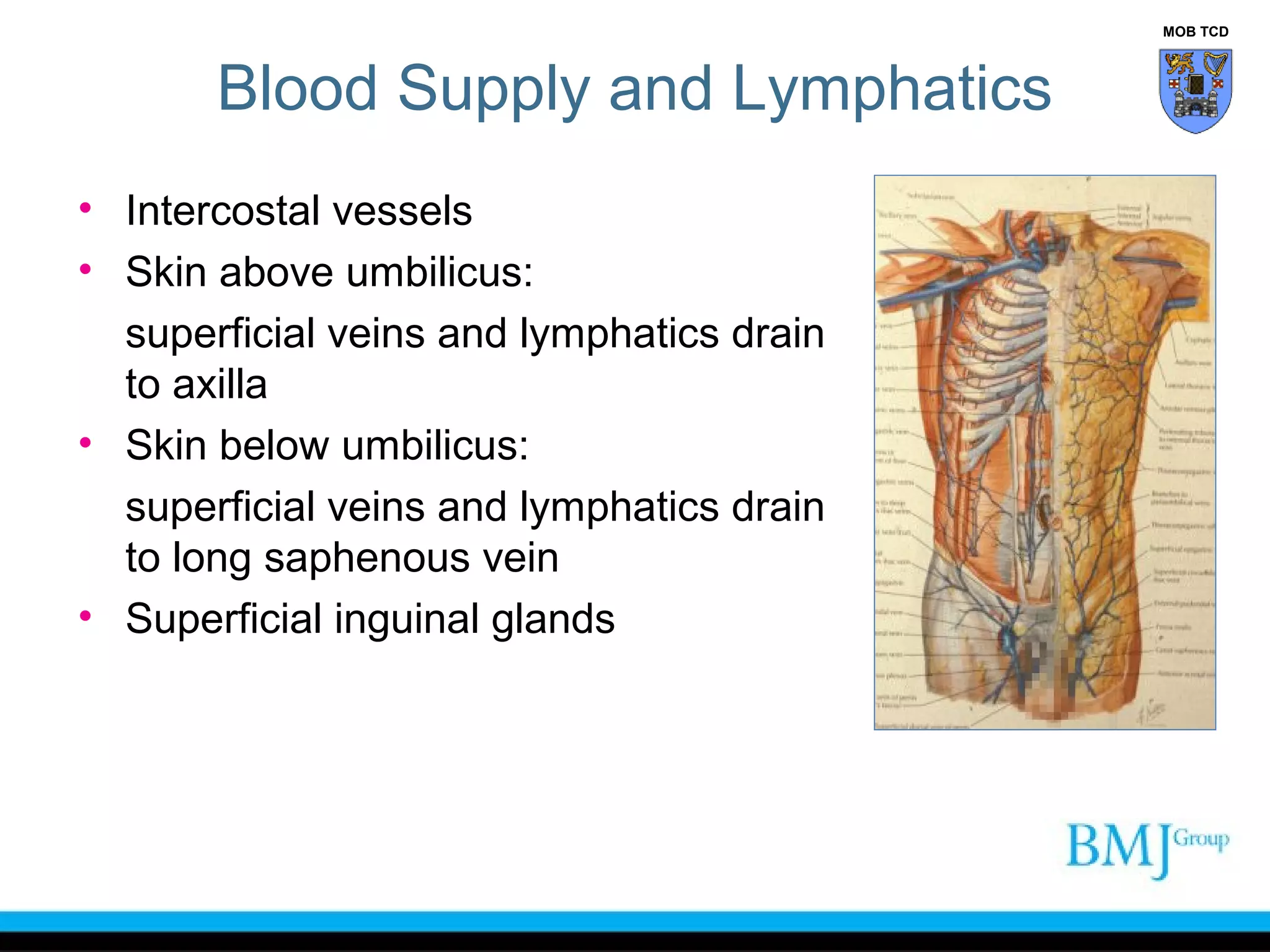
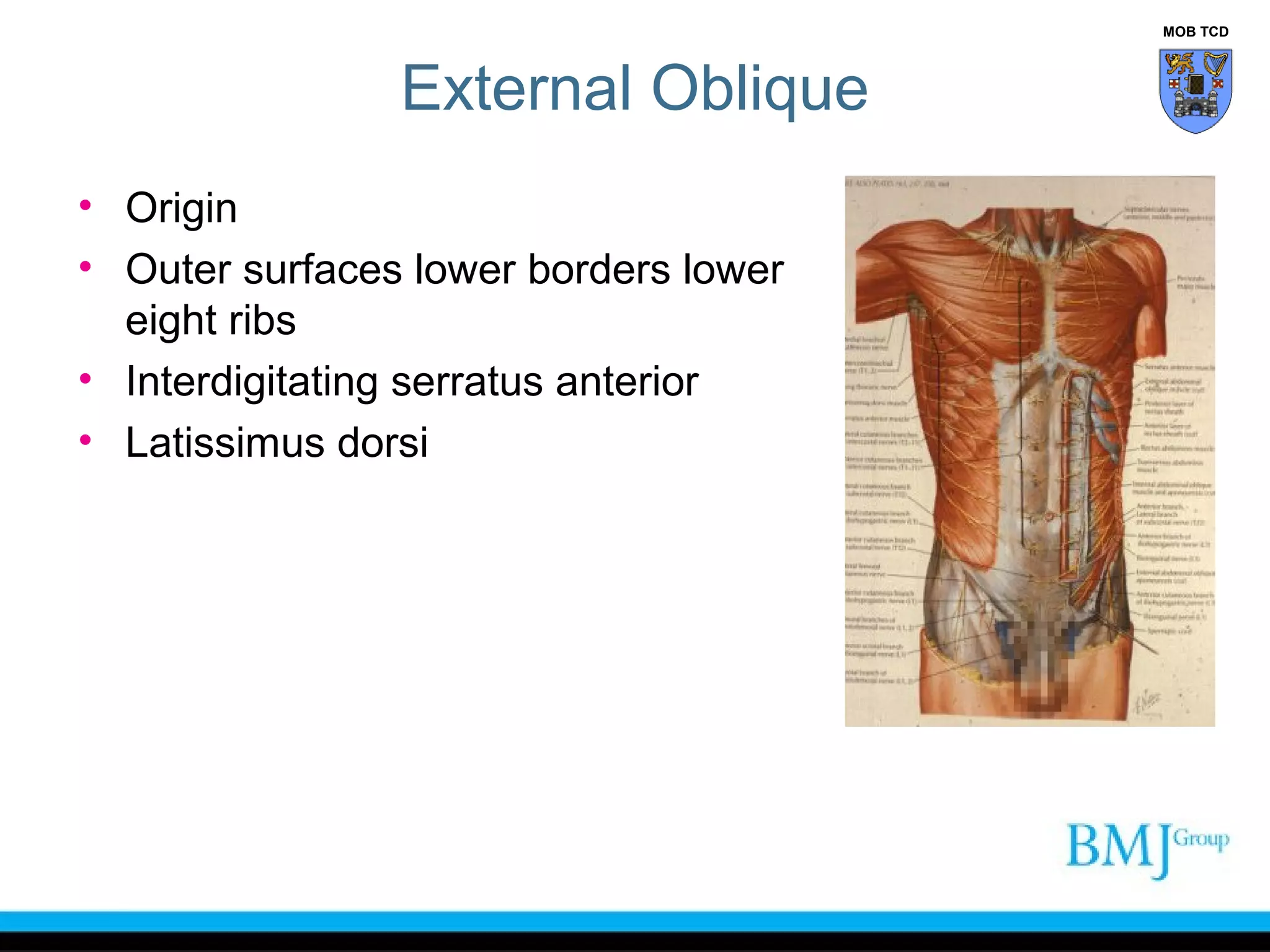
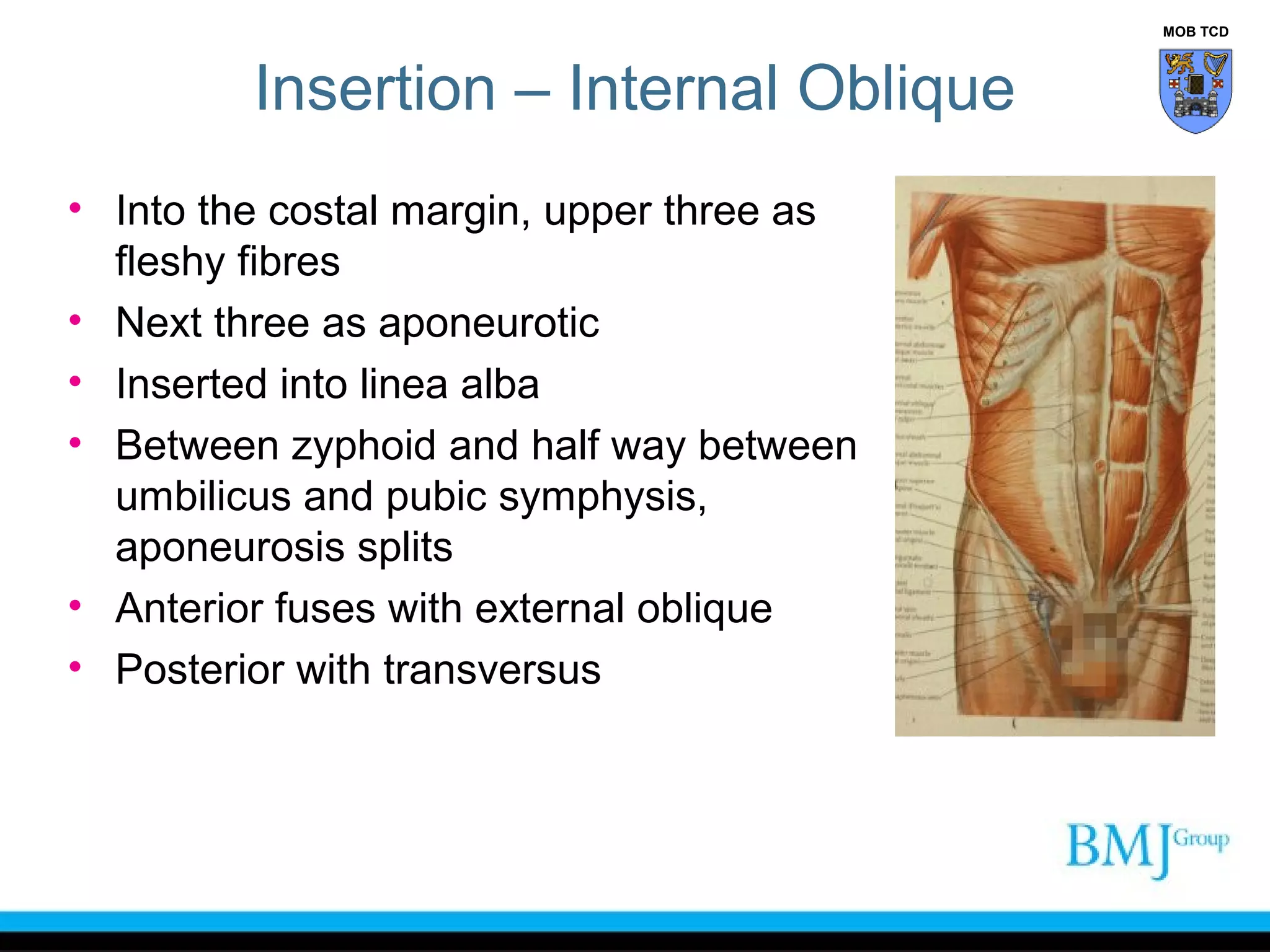
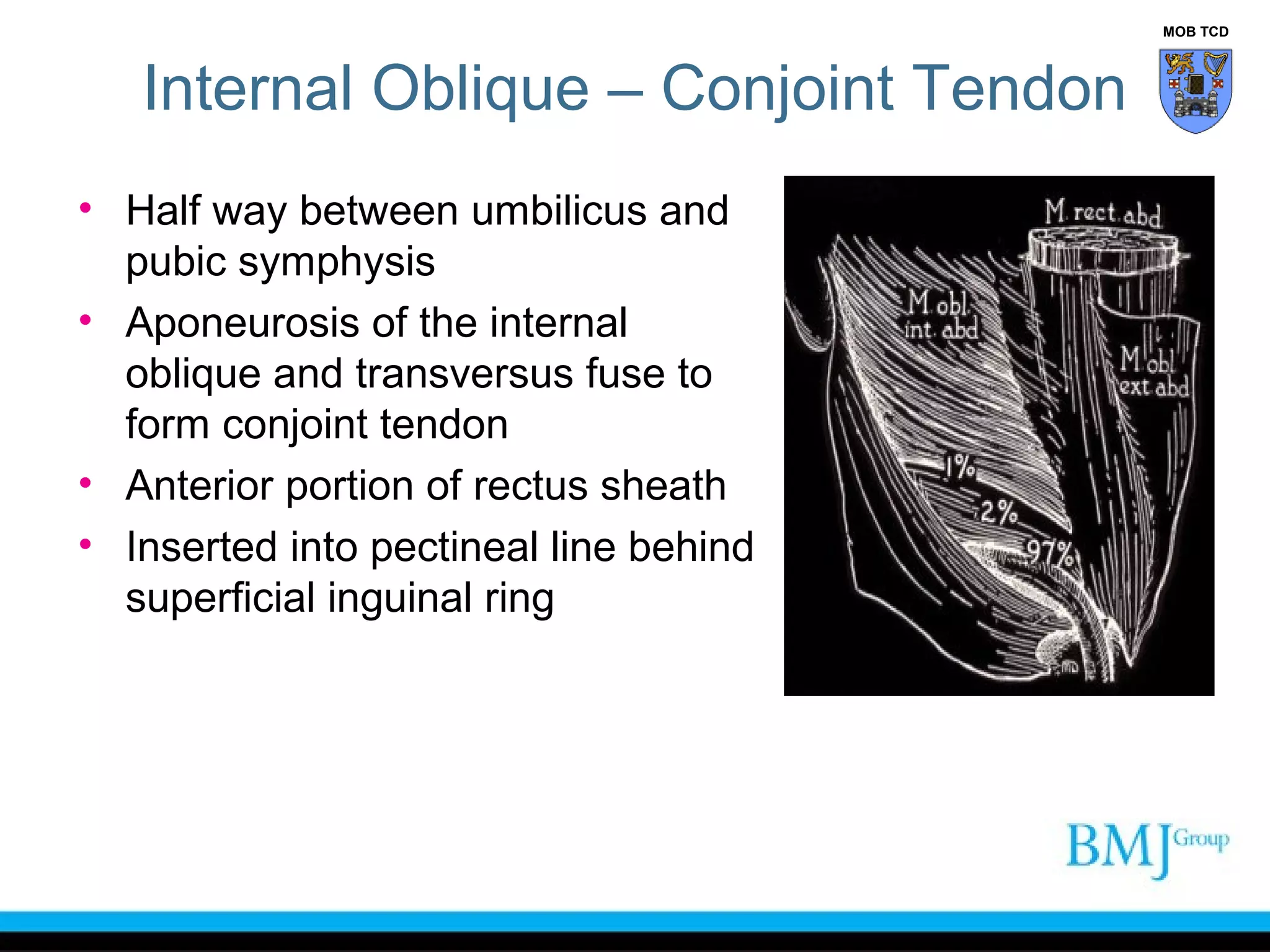
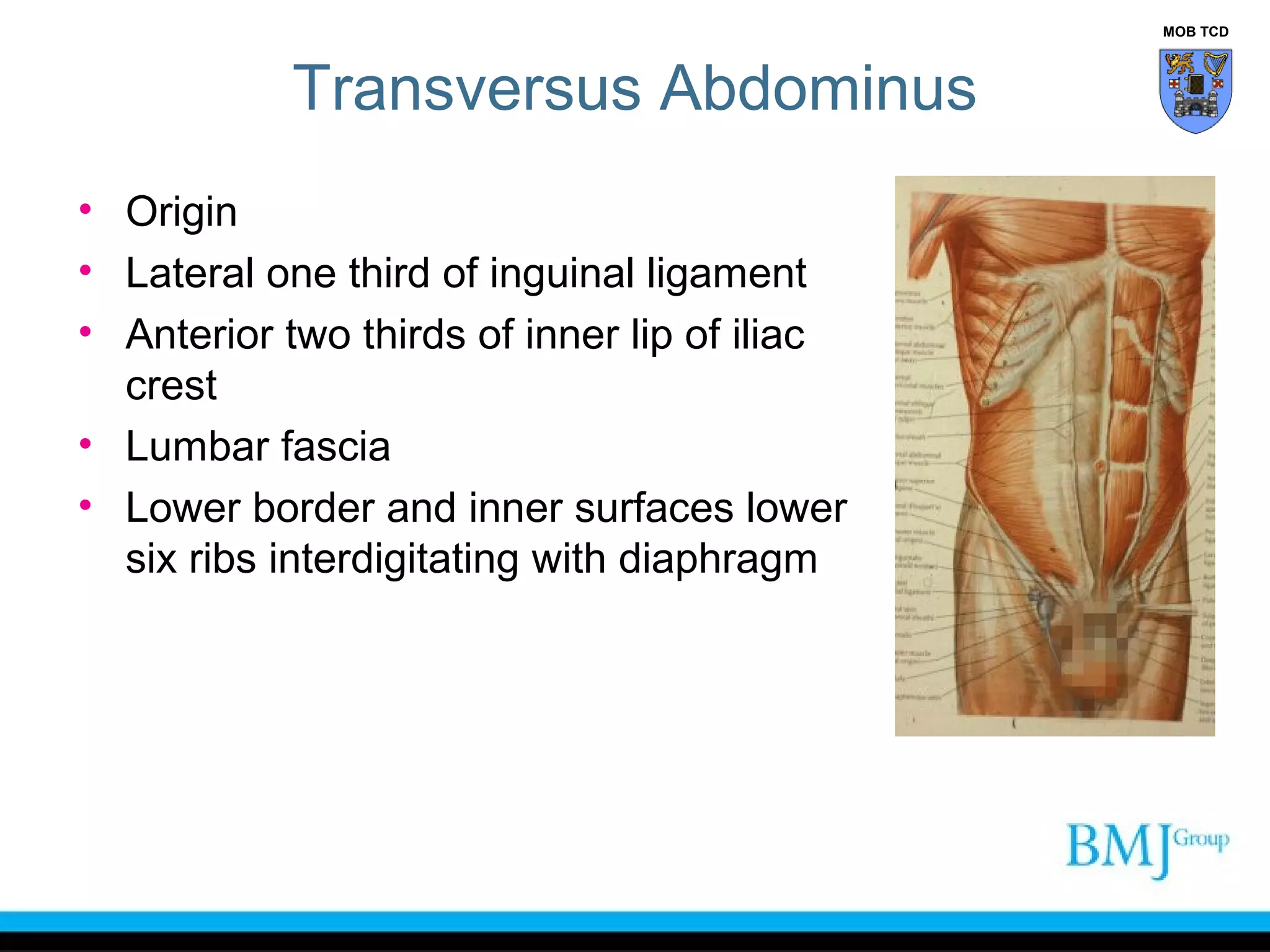
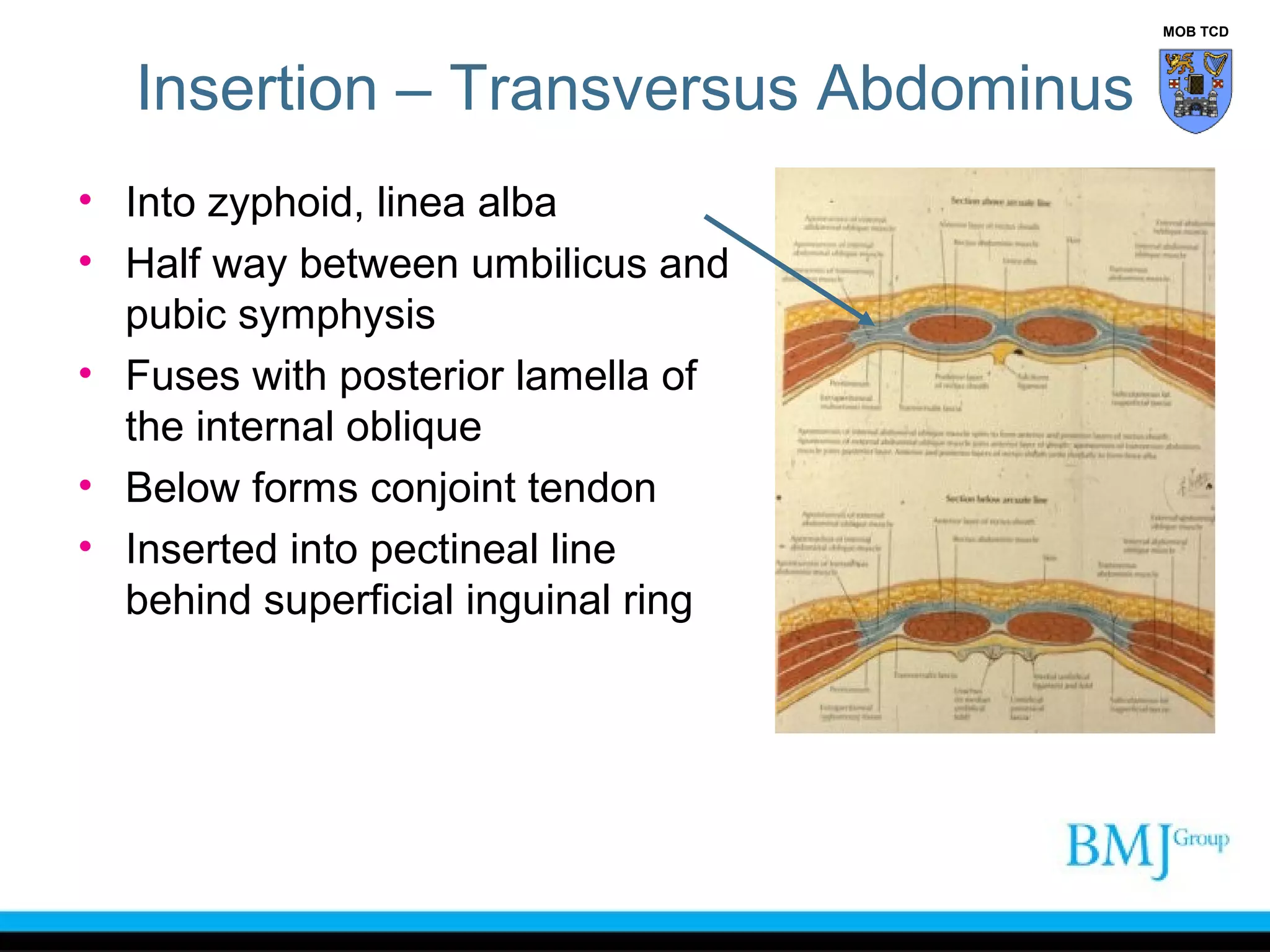
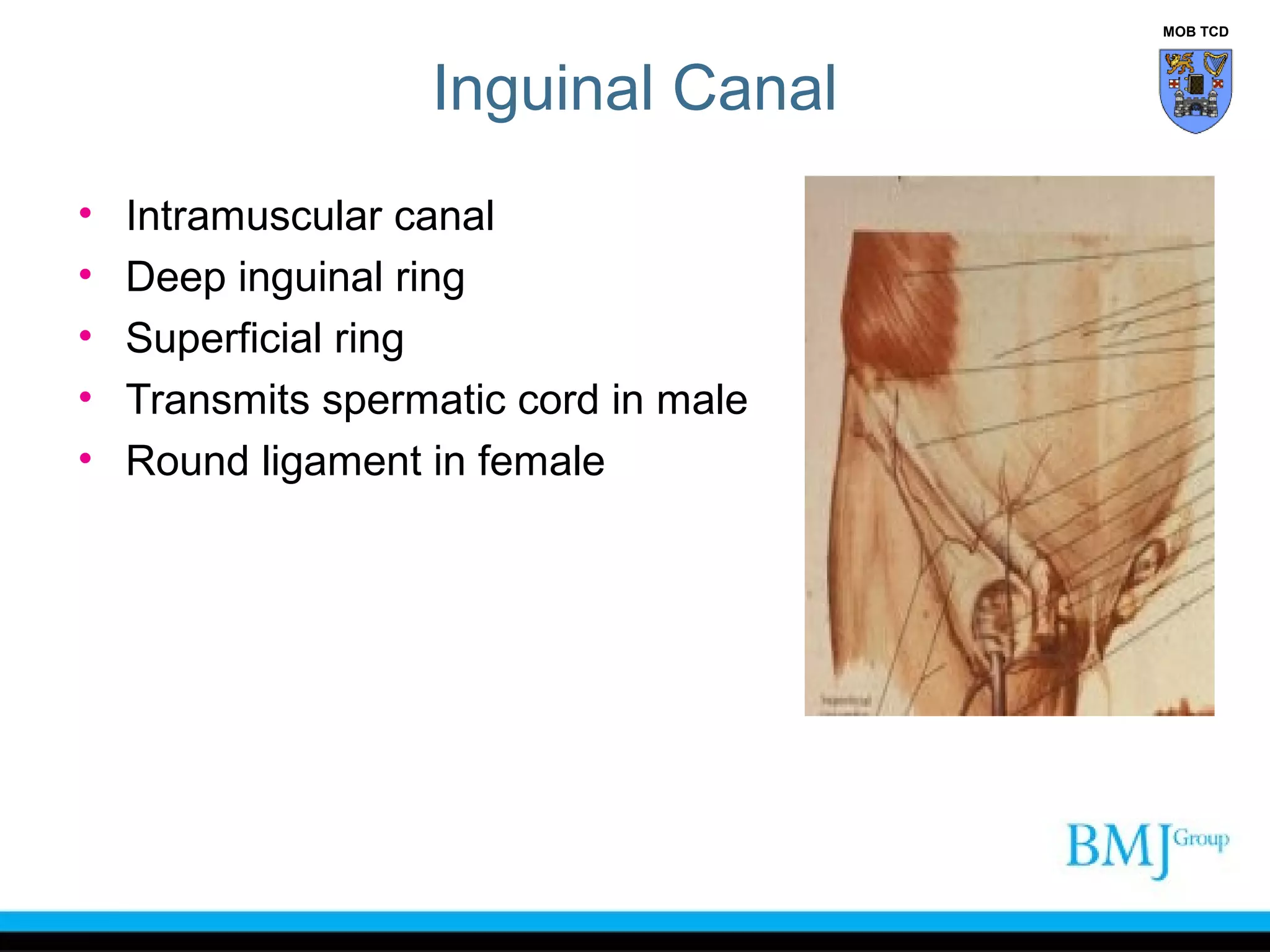
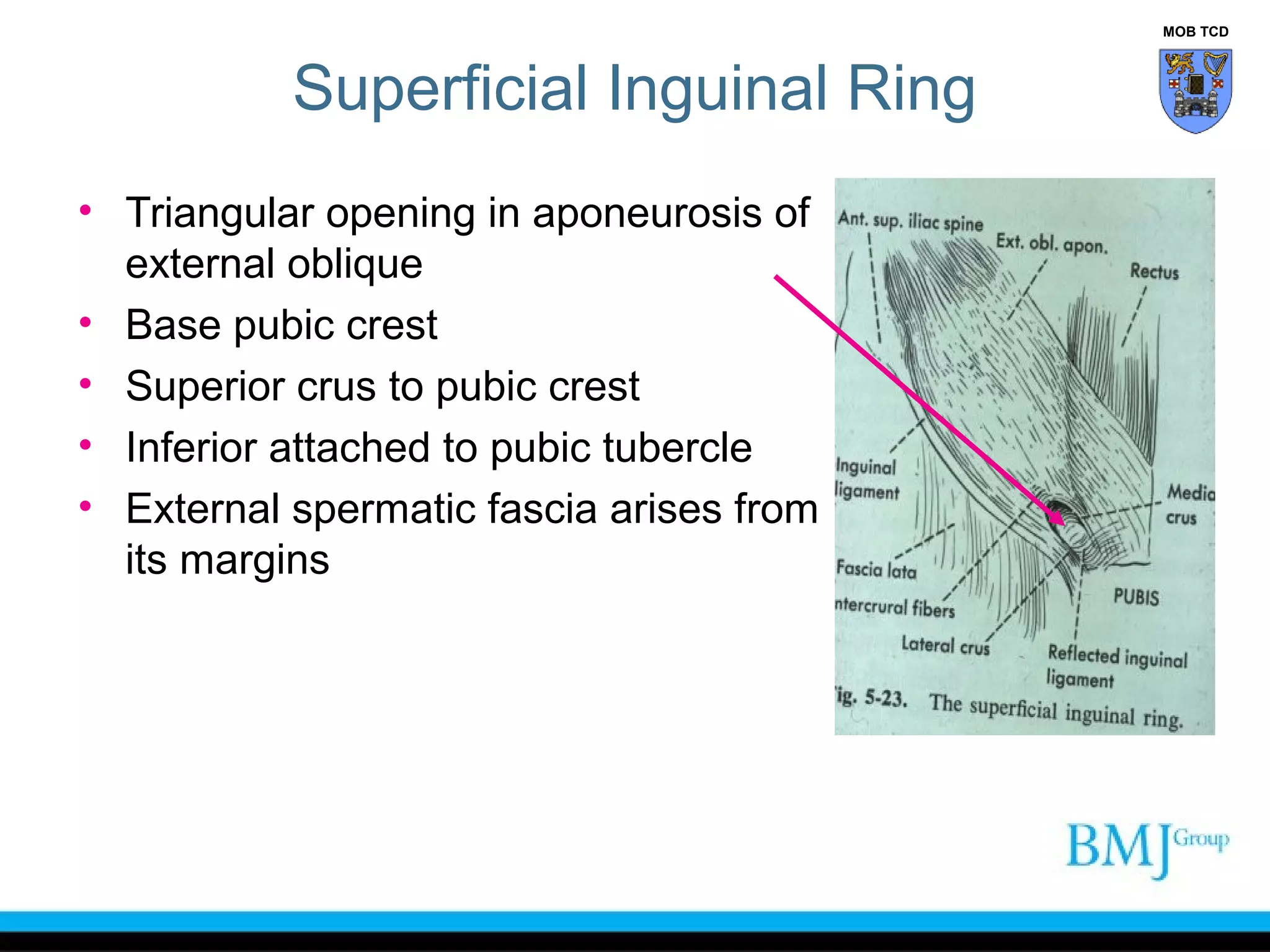
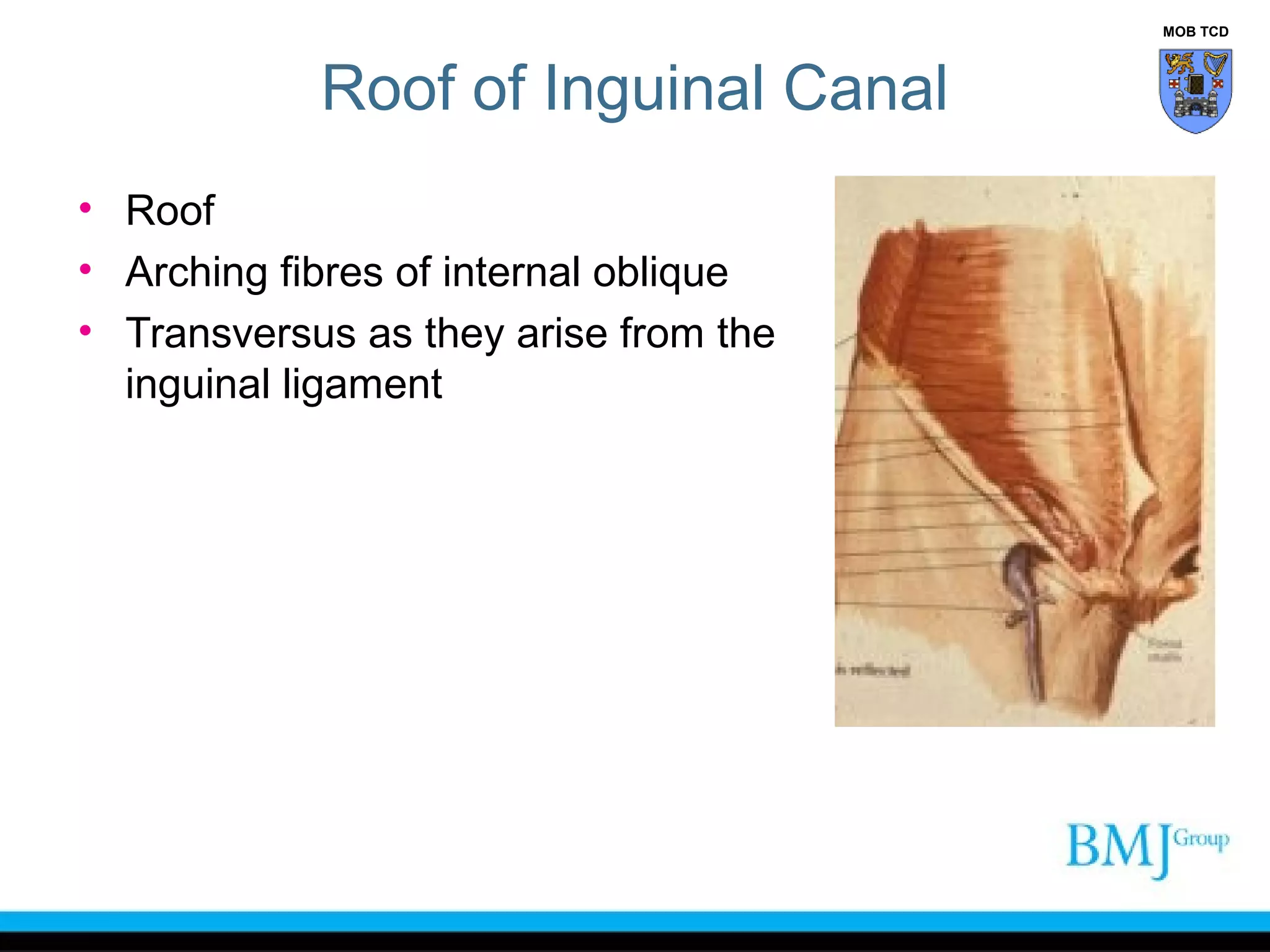
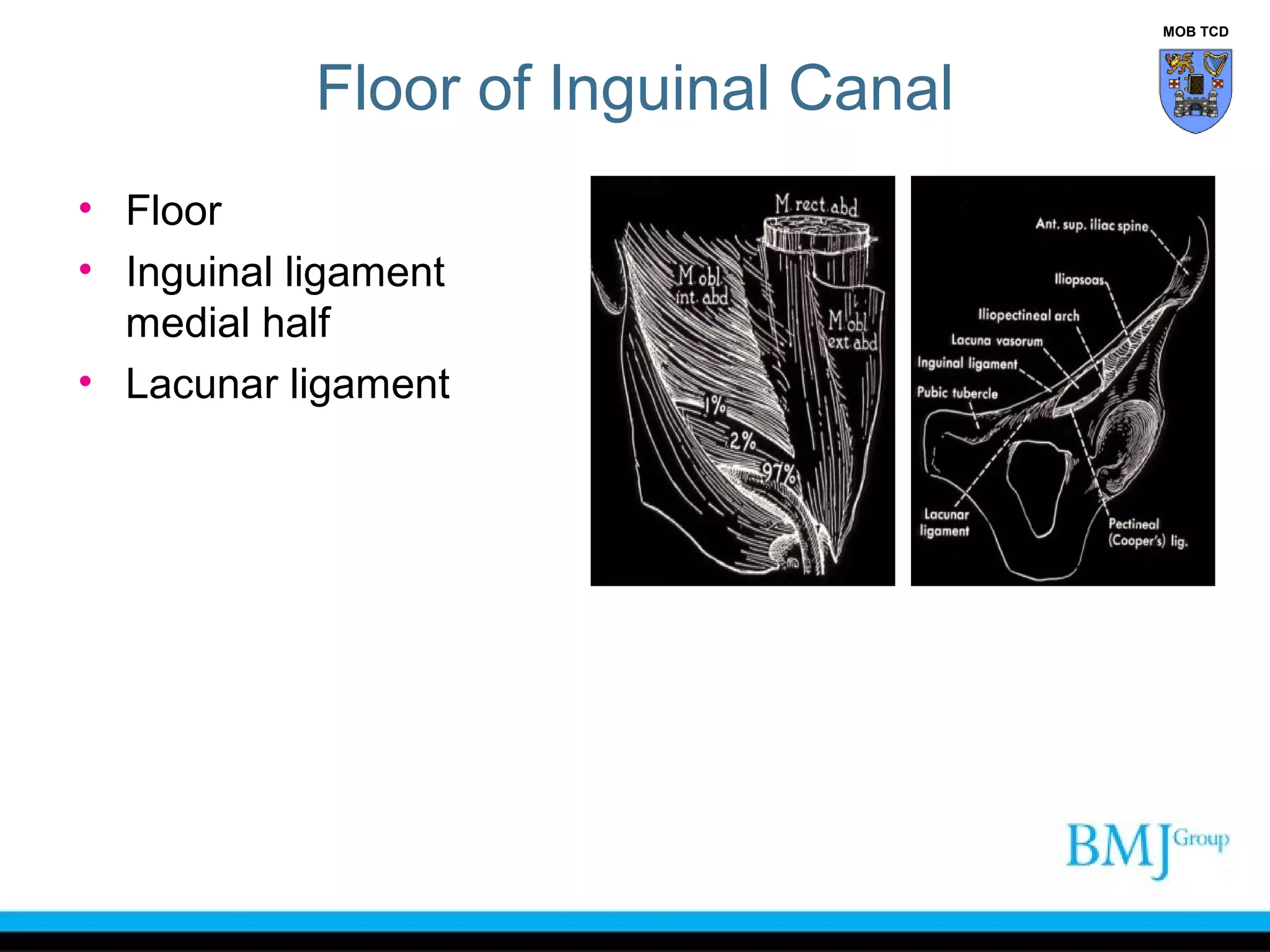
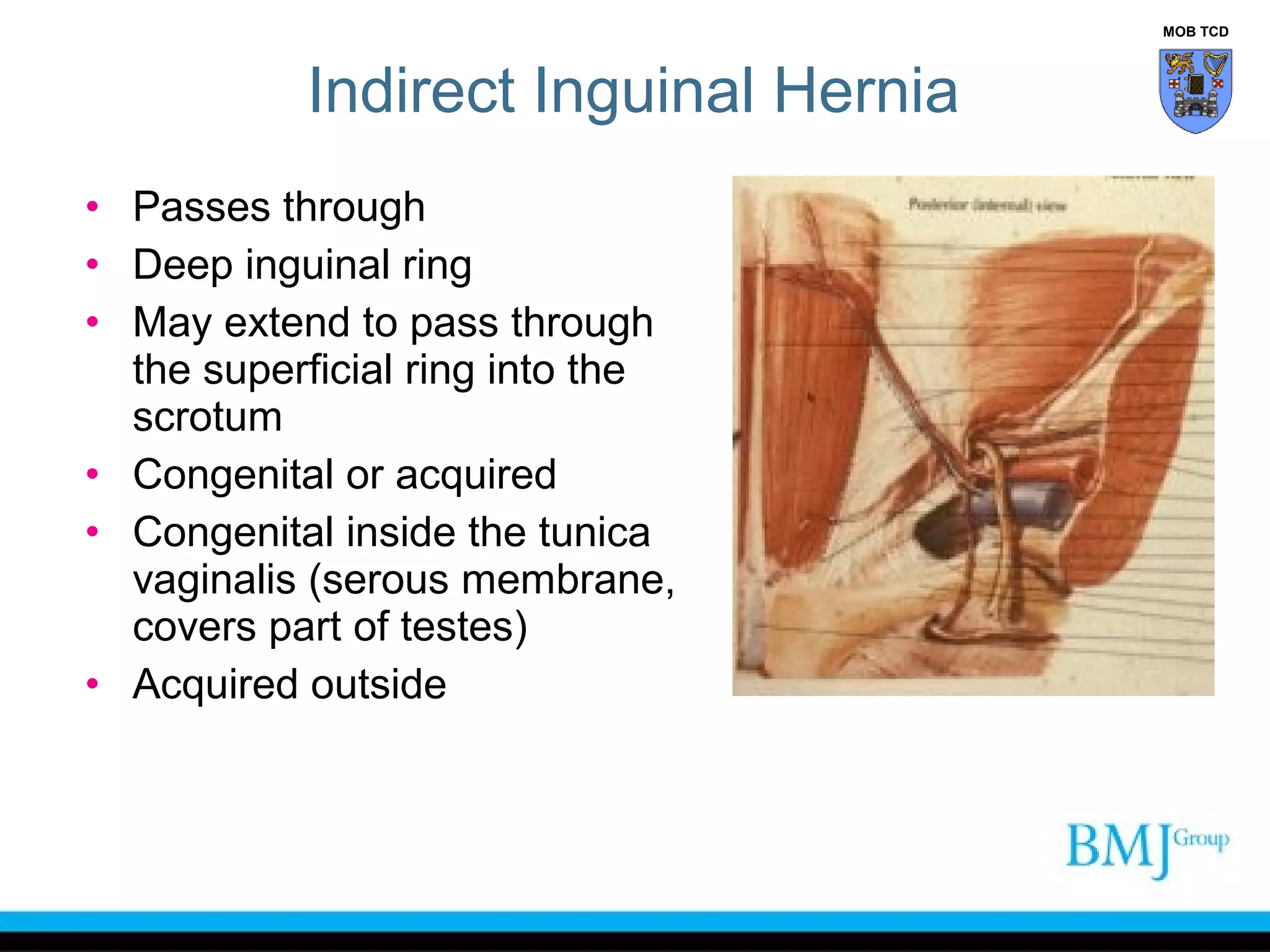
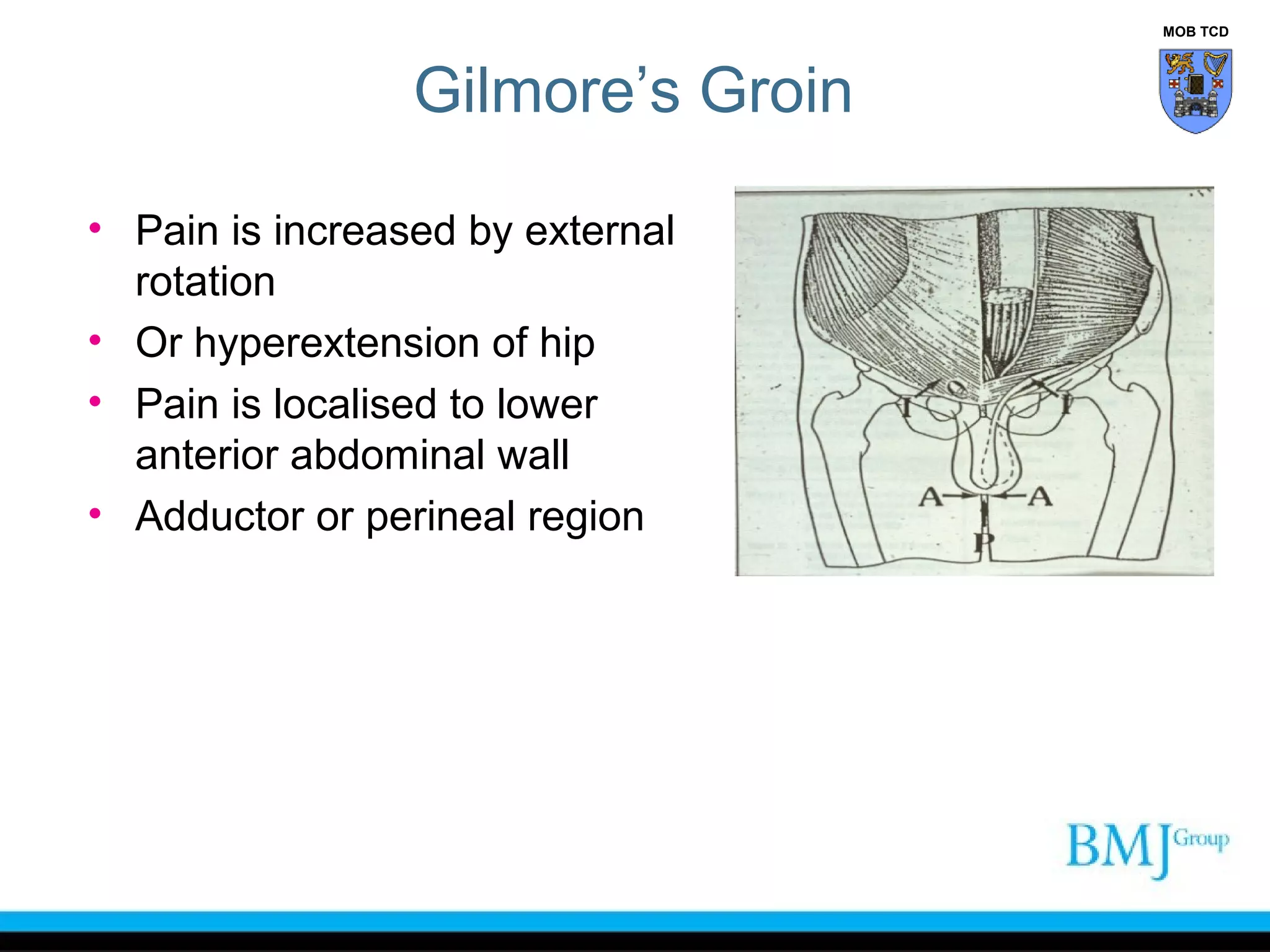
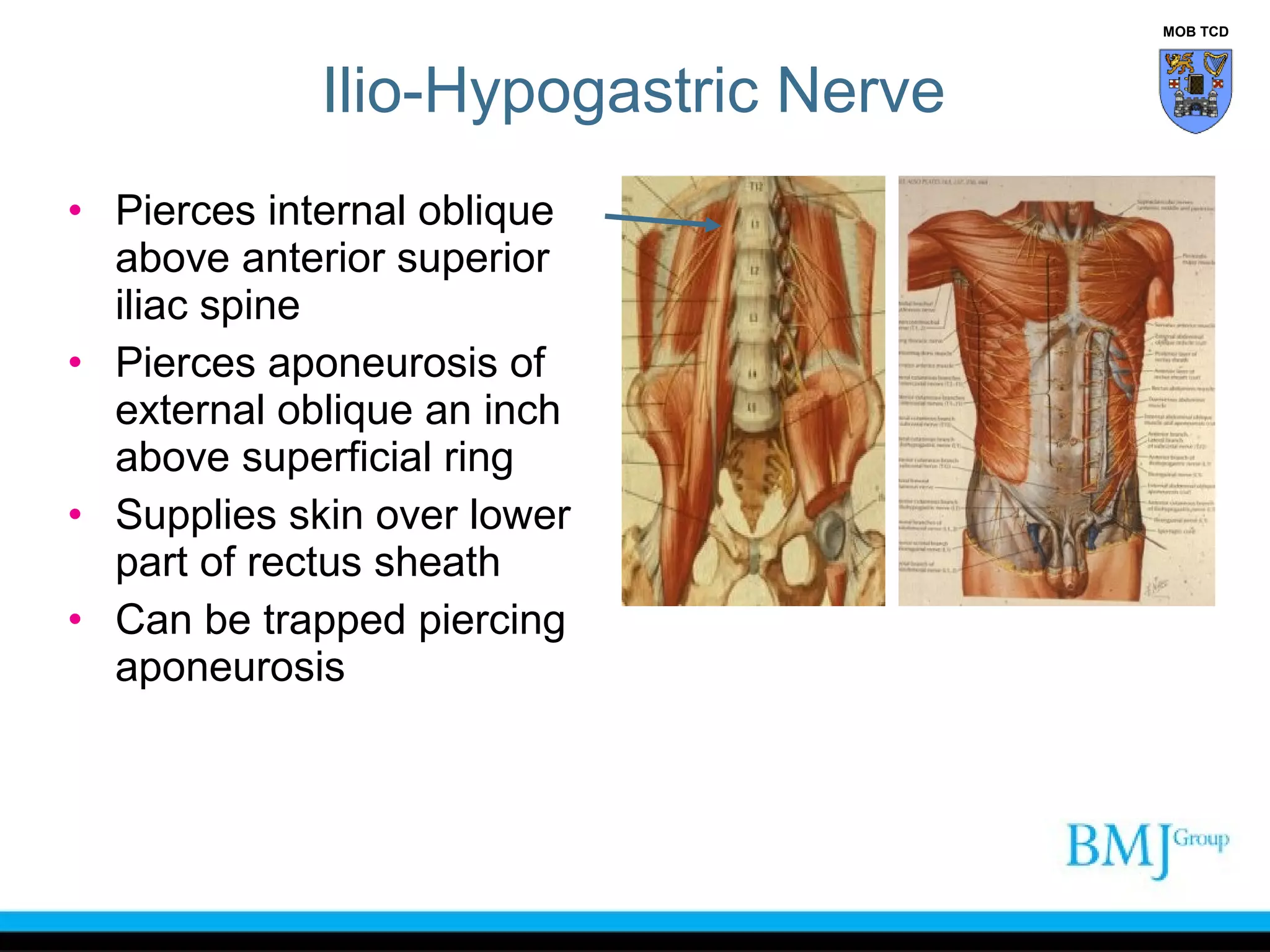
This document provides an overview of anatomy related to the groin region. It describes the structures in the groin including bones, muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and fascia. It discusses conditions that can cause groin or hip pain such as hernias, nerve entrapment, and Gilmore's groin. It also outlines the course of cutaneous nerves that innervate the groin and thigh including the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves which are susceptible to entrapment.