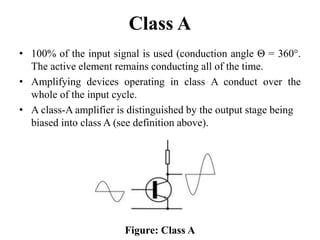
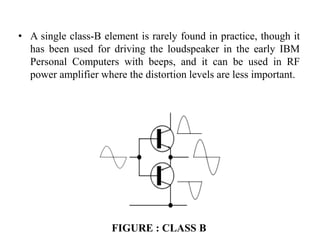
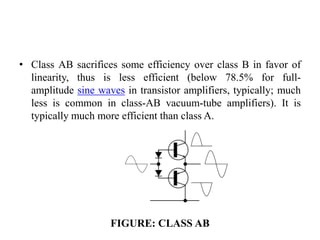
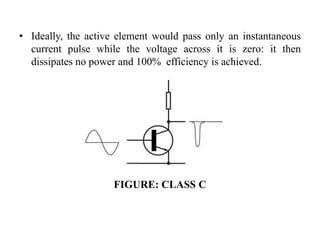
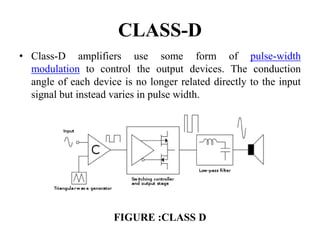
A power amplifier is the last amplifier stage that delivers power to the load. Power amplifiers are classified based on the proportion of the input cycle during which the amplifying device conducts current. Class A amplifiers conduct over the entire input cycle but have low efficiency. Class B amplifiers only amplify half of the cycle, improving efficiency but introducing distortion. Class AB is a compromise with better linearity than B. Class C has very high efficiency but is used for RF where distortion is controlled by a tuned load. Class D amplifiers use pulse-width modulation for very high efficiency.