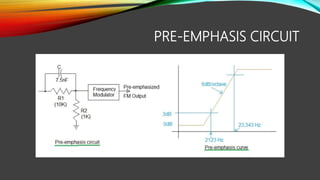
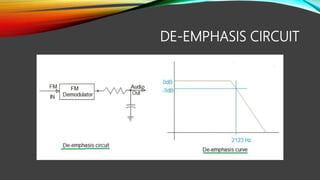
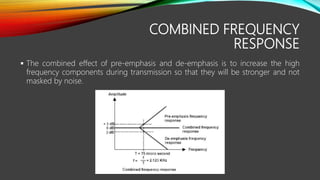
The document discusses pre-emphasis and de-emphasis in communication systems, which enhance signal quality by boosting high-frequency signals to improve the signal-to-noise ratio during transmission. Pre-emphasis circuits amplify high-frequency components at the transmitter, while de-emphasis circuits attenuate these signals at the receiver to restore the original characteristics. Both processes involve simple filter designs and have benefits and risks, including the potential for over-modulation.