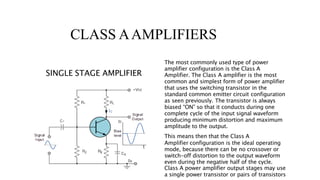
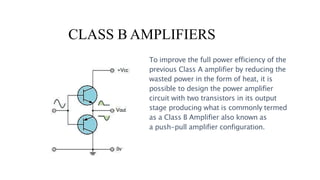
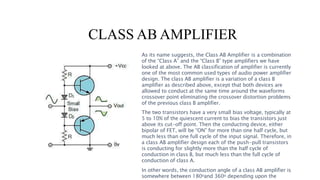
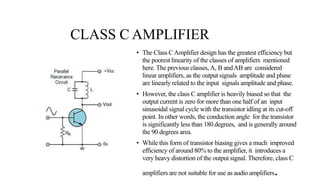
The document discusses different classes of amplifiers - Class A, B, AB, and C. Class A amplifiers have the transistor always conducting, providing minimal distortion but low efficiency. Class B amplifiers use two transistors in a push-pull configuration, improving efficiency but introducing crossover distortion. Class AB amplifiers provide a compromise between Class A and B by allowing both transistors to conduct around the crossover point, eliminating distortion while gaining efficiency. Class C amplifiers have the highest efficiency but also the poorest linearity, as the output is zero for over half the input cycle, making them unsuitable for audio but used in RF amplifiers.