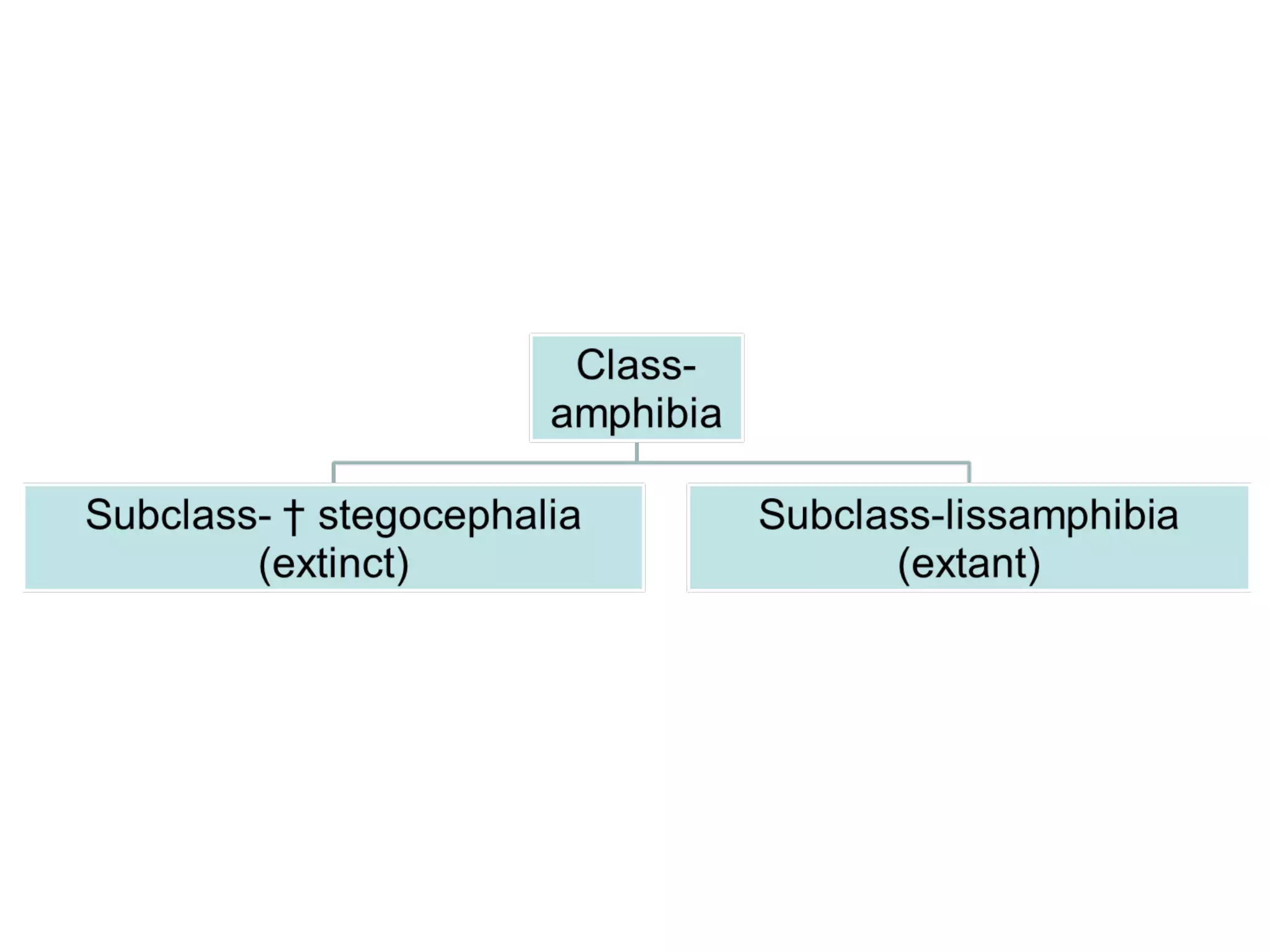
This document discusses the classification and characteristics of amphibians. It covers the major orders of amphibians including Labyrinthodontia, Phyllospondyli, Lepospondyli, Apoda, Urodela, and Anura. Key characteristics like larval development, parental care strategies, and reproductive modes are described. Examples are provided to illustrate different amphibian groups and parental care behaviors like nest building, egg guarding, carrying eggs attached to the body, and ovoviviparity.