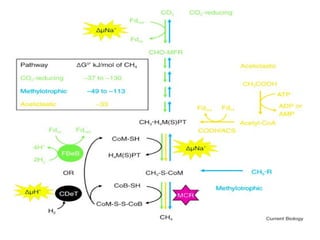
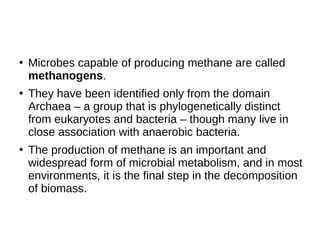
Methanogenesis is an anaerobic respiration process that utilizes carbon as an electron acceptor to produce methane, primarily from low molecular weight organic compounds. It involves three main steps: hydrolysis, acidification, and methane formation, facilitated by different types of bacteria, including hydrogenotrophic, aceticlastic, and methylotrophic methanogens. Methane production plays a significant role in global methane emissions, with wetlands and certain human activities being major sources.