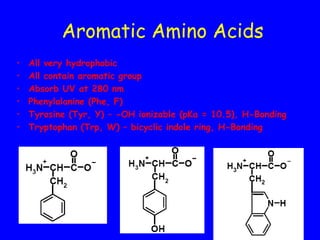
This document discusses the key properties and structures of amino acids, peptides, and proteins. It covers the basic structure of amino acids including common classifications like aliphatic, aromatic, and acidic/basic amino acids. It also describes how amino acids polymerize to form peptides and proteins through peptide bond formation and discusses factors that determine protein structure and stability like pKa, isoelectric point, and pH.