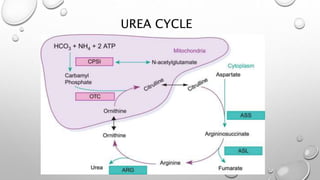
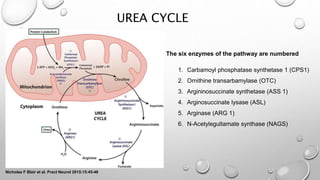
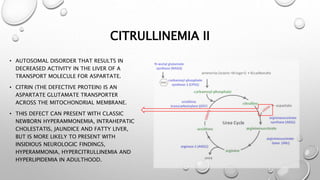
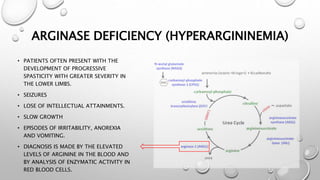
The urea cycle disorders result from genetic mutations causing defects in the metabolism of extra nitrogen from protein breakdown. There are six enzymes in the urea cycle that convert ammonia into urea for excretion. Deficiencies in the first three enzymes (CPS1, OTC, ASS) or the cofactor NAGS cause severe hyperammonemia in newborns. Symptoms include irritability, lethargy, coma, hypothermia, and seizures. Treatment involves removing protein, giving nitrogen-scavenging drugs like sodium benzoate and sodium phenylacetate, arginine supplementation, and supportive care. Long-term management includes a low-protein diet and monitoring for complications.