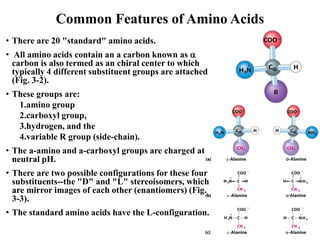
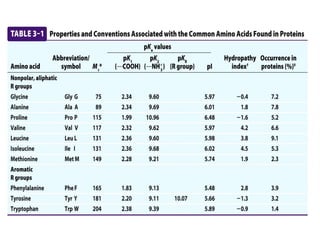
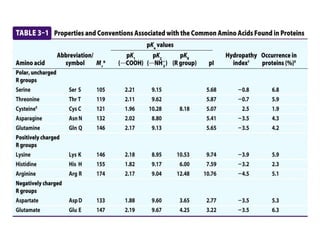
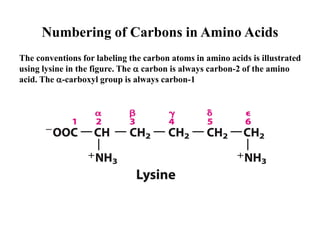
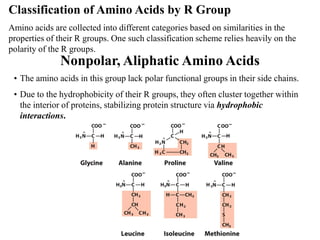
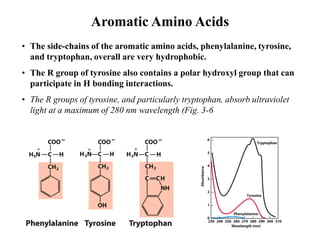
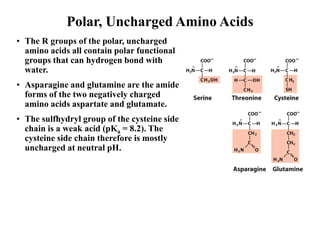
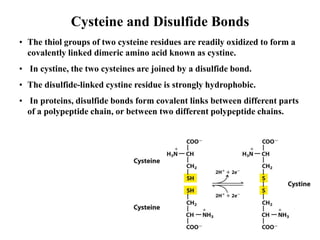
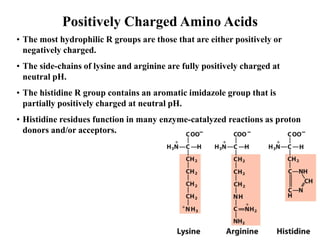
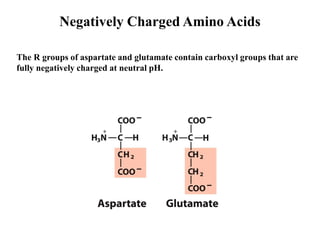
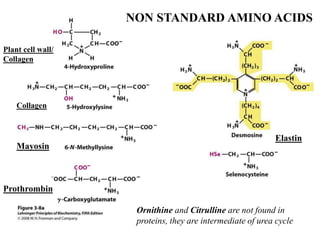
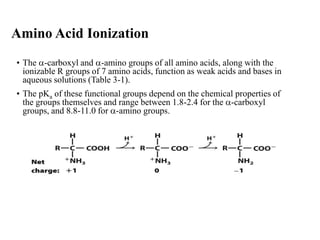
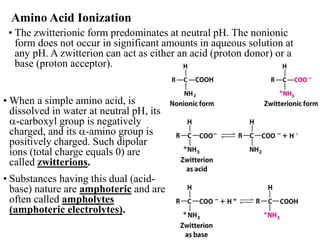
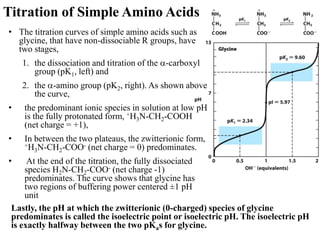
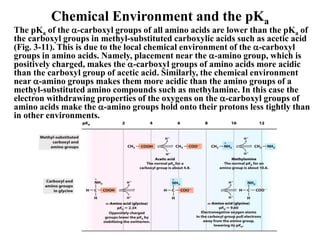
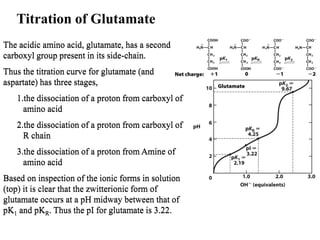
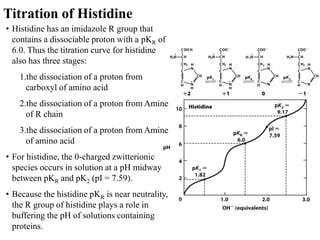
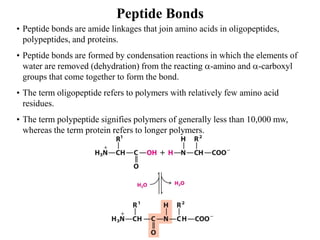
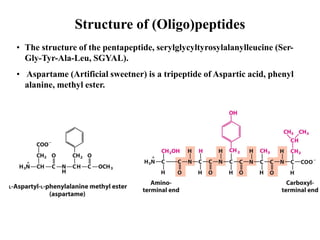
All proteins are composed of the same set of 20 amino acids that are linked together via peptide bonds. There are two main categories of amino acids - nonpolar amino acids that cluster in the interior of proteins, and polar amino acids that are charged or contain functional groups that allow hydrogen bonding. Key properties of amino acids include their ionization states, which depend on pH, and their ability to participate in covalent bonds like disulfide bridges that help determine protein structure. Amino acid sequences ultimately define the diverse functions that proteins perform in biological processes.