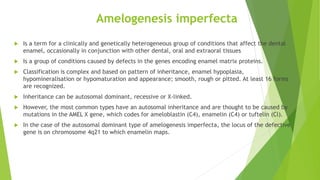
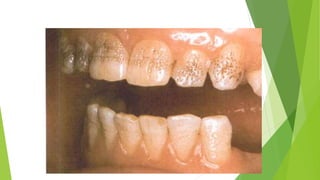
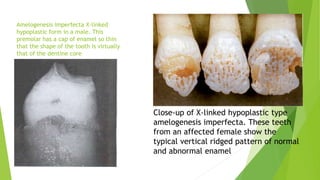
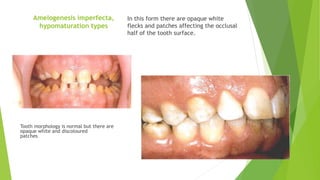
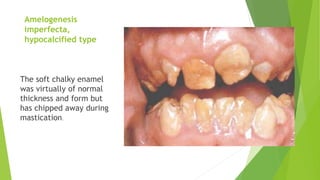
Amelogenesis imperfecta is a genetically diverse condition affecting dental enamel, with its patterns of inheritance classified as autosomal dominant, recessive, or X-linked. The disorder is caused by defects in genes that encode enamel matrix proteins, resulting in various forms including hypoplastic, hypomineralised, and hypomaturated enamel. Specific genetic mutations, particularly in the amel x gene, contribute to the severity of the condition, impacting the quality and appearance of the enamel across all teeth.