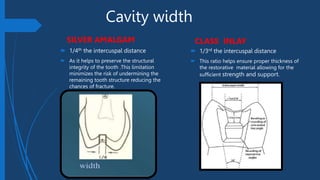
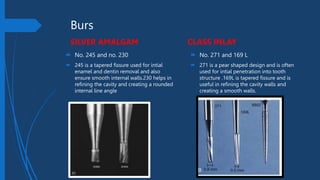
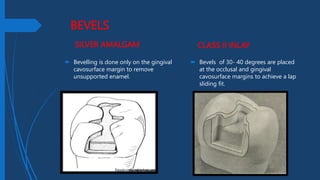
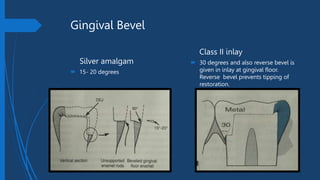
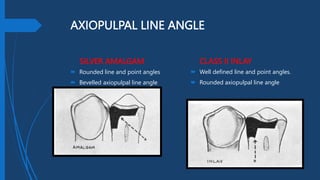
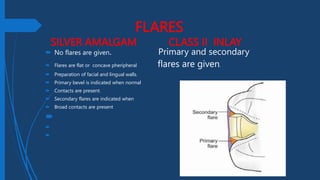
This document compares Class II silver amalgam restorations and Class II inlays in dental procedures. It outlines the differences in application, technique, material properties, and patient considerations, emphasizing that amalgam is a direct procedure while inlay requires indirect procedures. The document also details specific technical aspects such as outline forms, cavity preparation, and edge strength, noting the advantages and disadvantages of each restoration type.