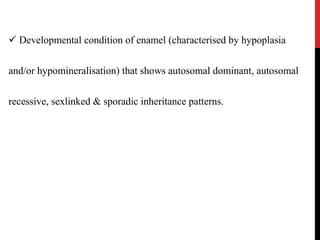
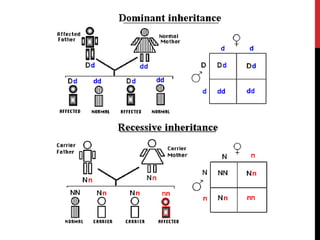
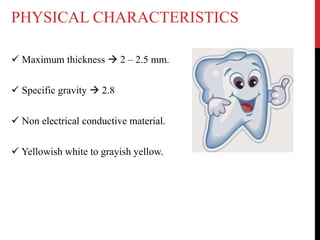
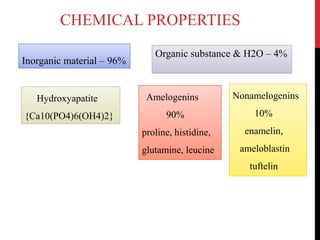
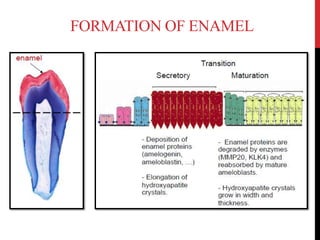
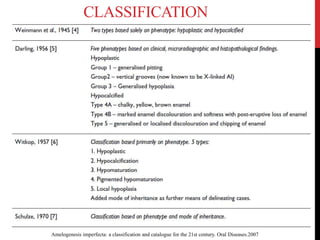
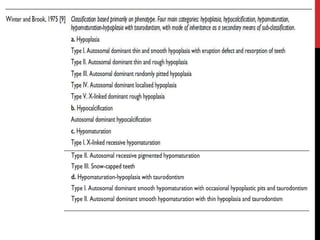
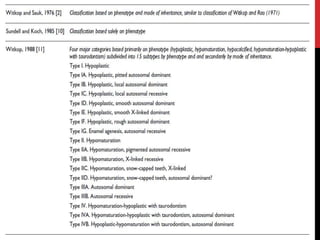
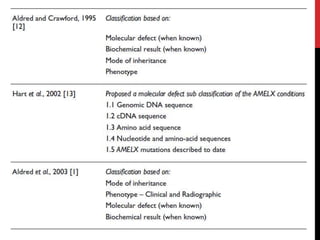
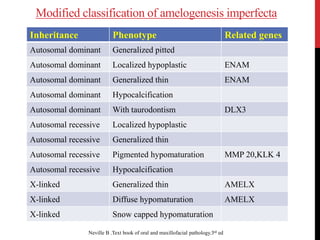
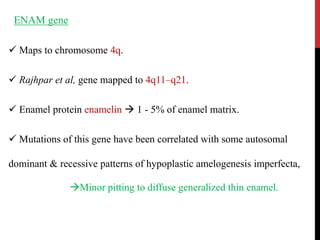
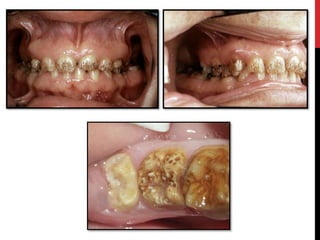
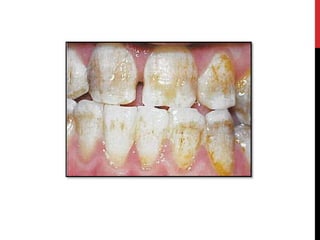
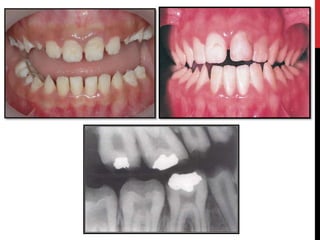
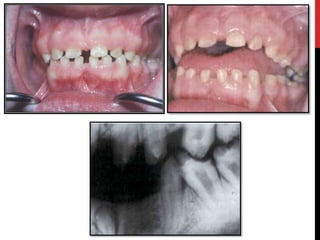
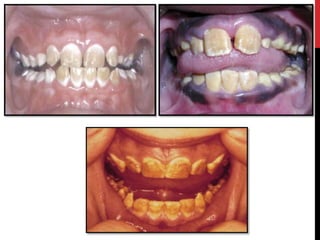
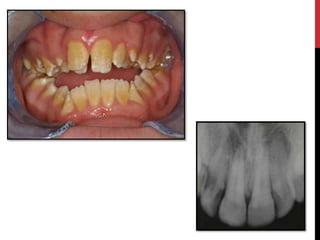
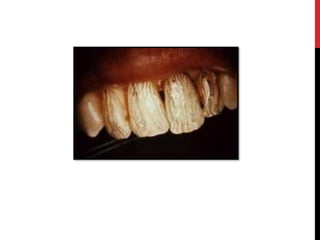
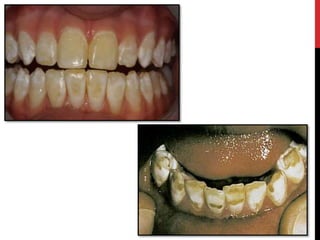
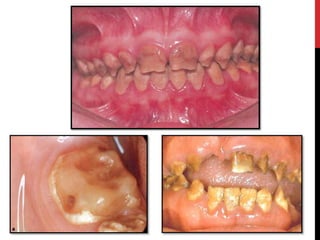
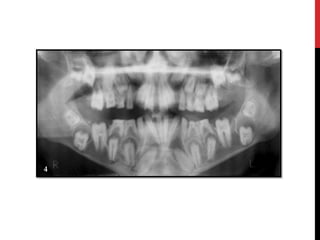
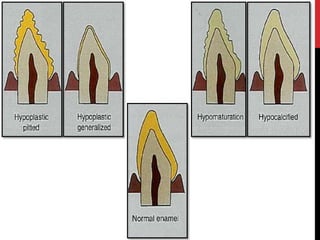
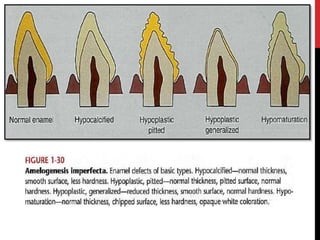
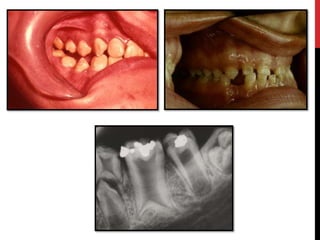
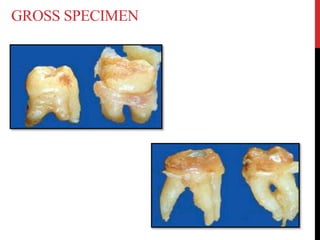
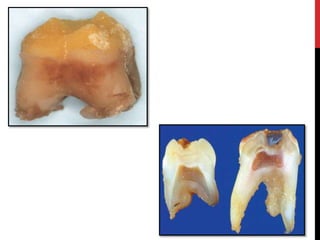
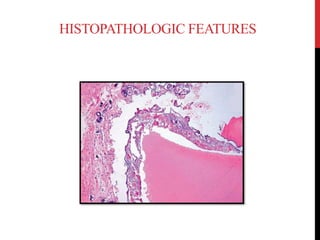
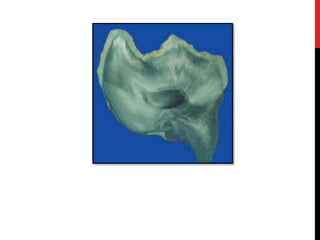
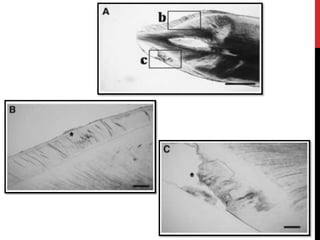
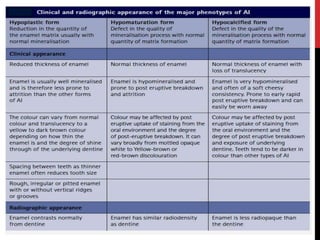
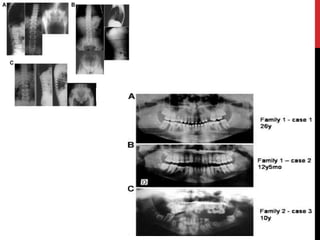
This document provides an overview of amelogenesis imperfecta (AI), a hereditary condition affecting the enamel of teeth. It discusses the classification, pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis and treatment of AI. AI results from genetic mutations that disrupt enamel formation and can be autosomal dominant, recessive or X-linked. Clinically, AI presents with hypoplastic, hypomineralised or hypocalcified enamel. Treatment involves restoring aesthetic and functional deficits through methods like crowns, composites or prosthetics.