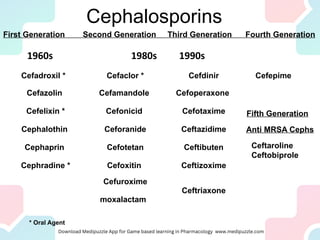
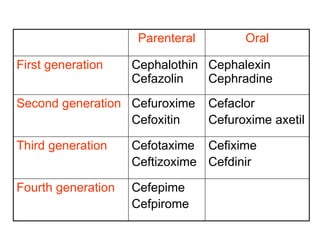
Cephalosporins are a class of beta-lactam antibiotics that are structurally similar to penicillins. They are divided into generations based on their antimicrobial spectrum and resistance to beta-lactamases. Earlier generations are effective against gram-positive bacteria while later generations have activity against more gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas. Common side effects include diarrhea, hypersensitivity reactions, and drug interactions with aminoglycosides which have synergistic activity against Klebsiella. Cephalosporins are used to treat a variety of bacterial infections depending on the generation, including pneumonia, meningitis, skin infections, and UTIs.