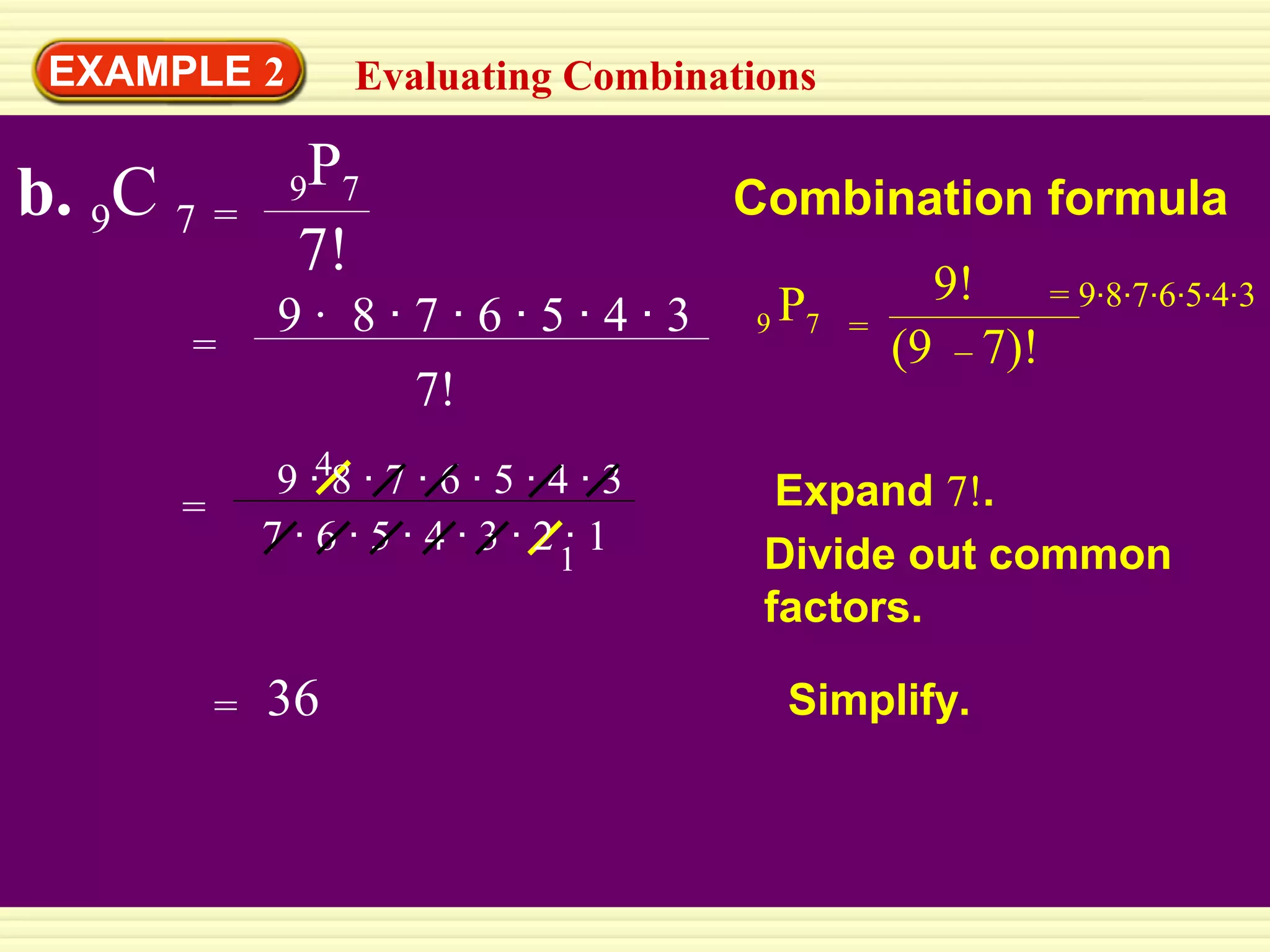
This document provides instruction on combinations and permutations. It begins with examples of evaluating combinations and permutations, such as finding the number of combinations when choosing 3 items from a group of 8 items (8C3) or the number of permutations when selecting a preferred and substitute color from 12 color options (12P2). It then provides practice problems for students to determine whether a scenario involves combinations or permutations and write the appropriate expression to calculate the number of possibilities. The document aims to teach students the differences between combinations and permutations and how to set up and evaluate expressions to solve combinatorial problems.