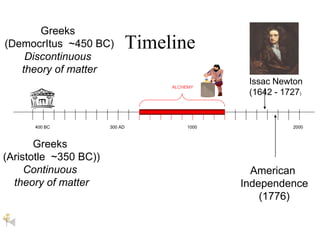
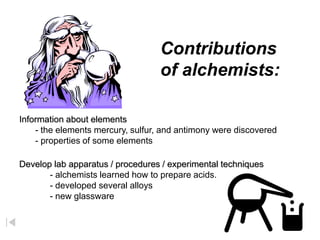
Alchemy originated in ancient Egypt and was focused on attempts to transform cheap metals like lead into gold through mysterious elixirs or powders. While alchemists made some discoveries about elements and compounds, their work was not truly scientific. Chemistry emerged in the 17th century through the scientific work of scientists like Robert Boyle, who established criteria for what constitutes a chemical element. Modern chemistry evolved from the more mystical practices of alchemy as scientists applied rigorous experimentation and analysis to the study of matter.