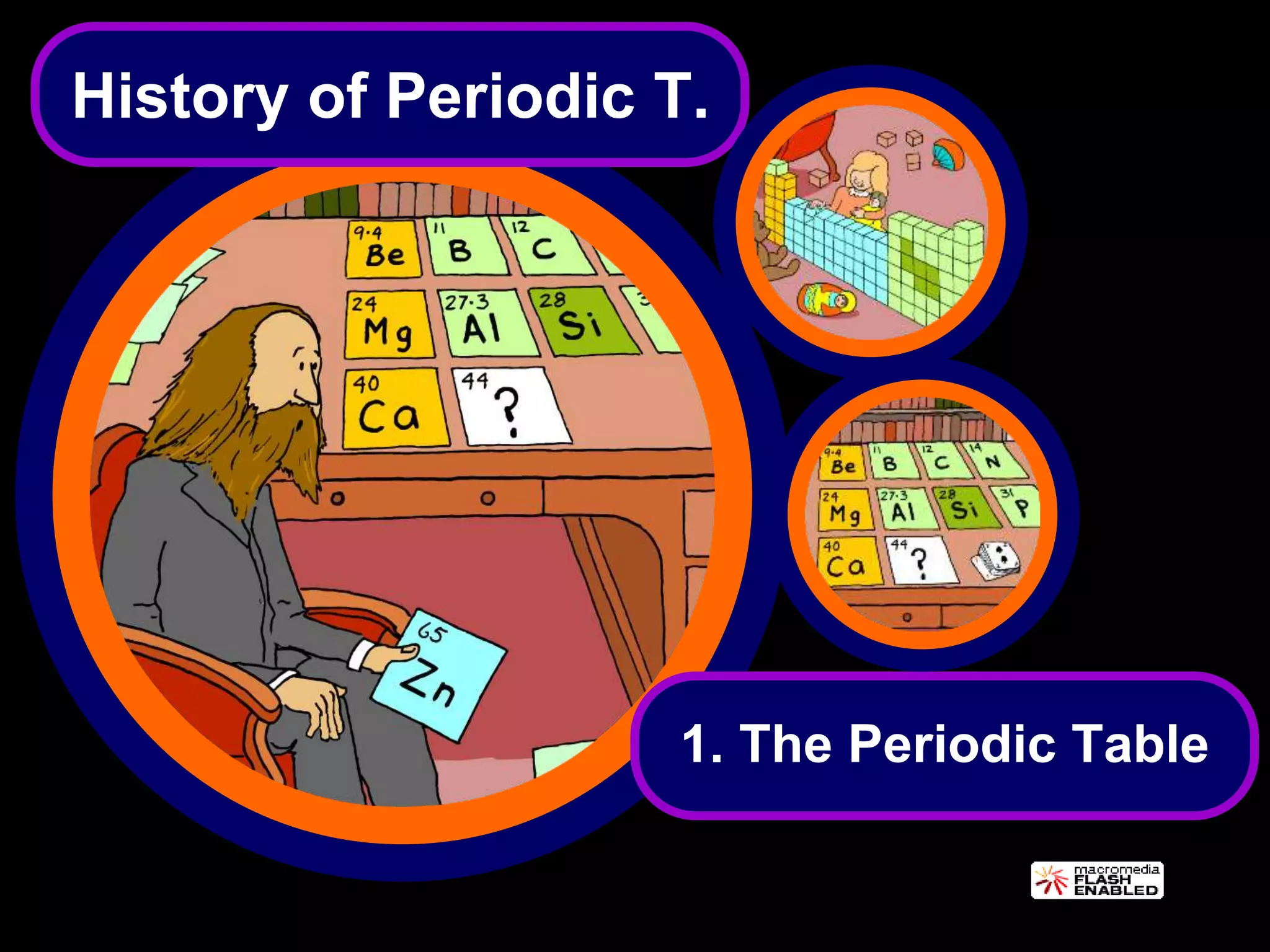
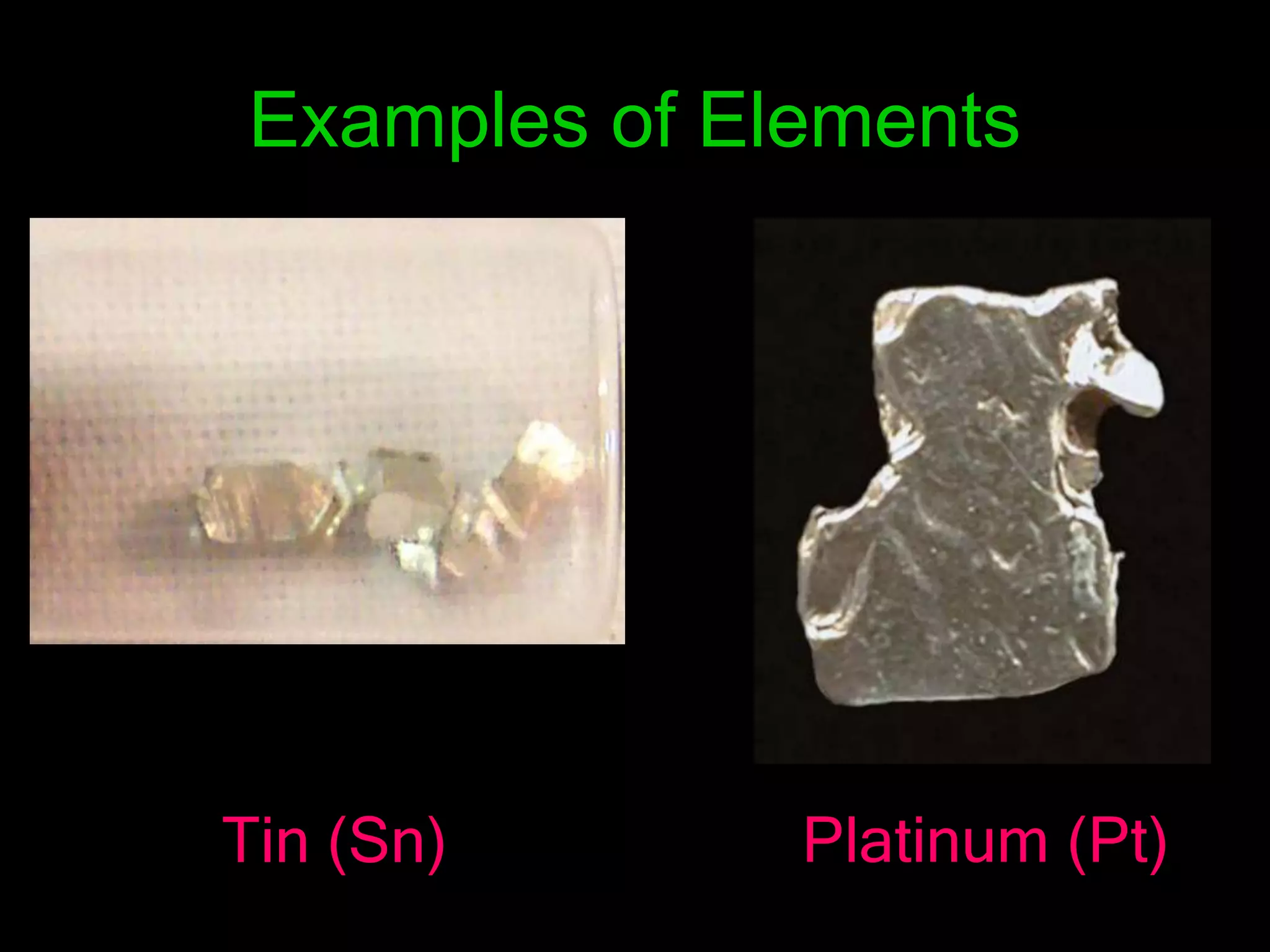
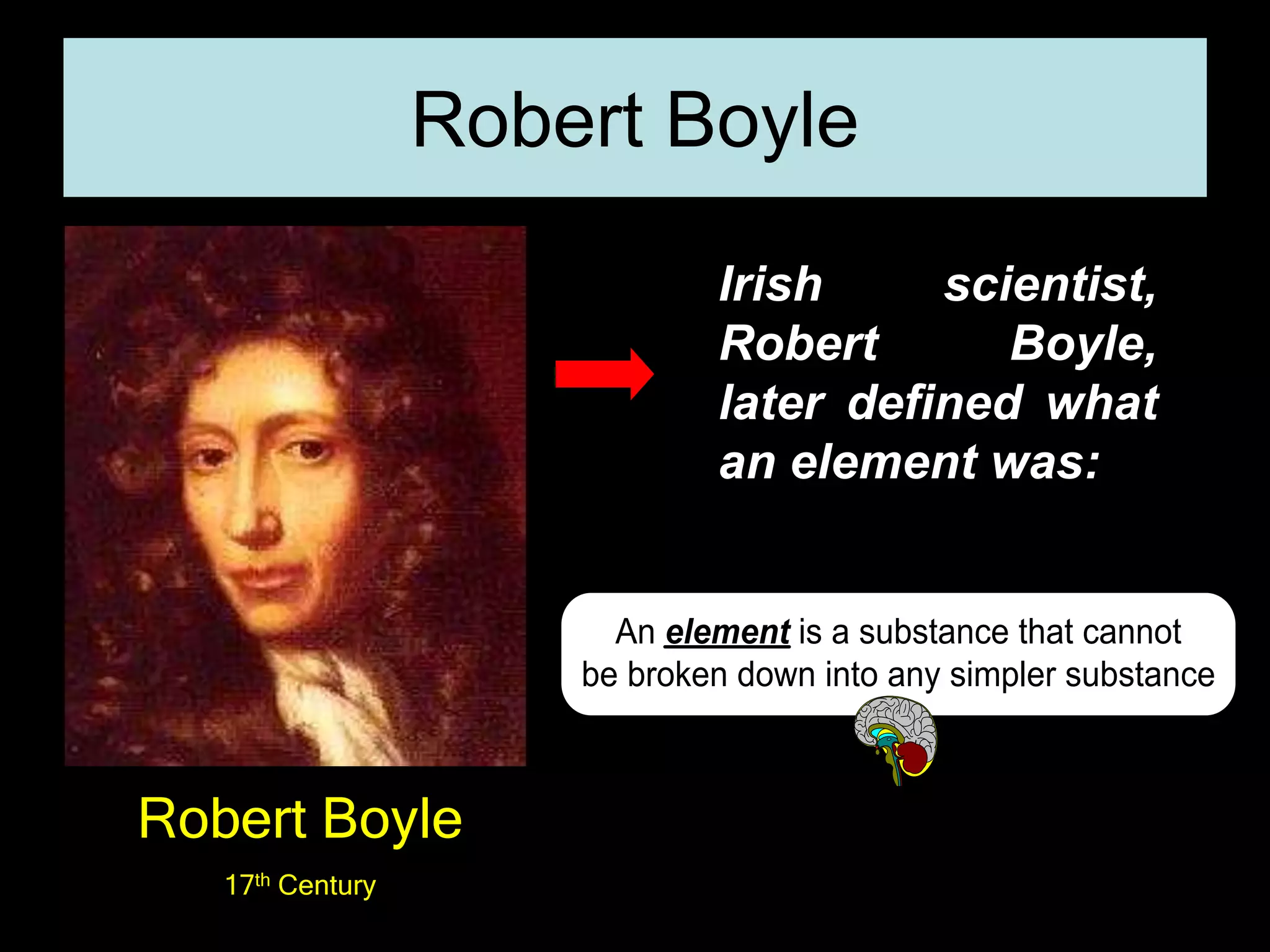
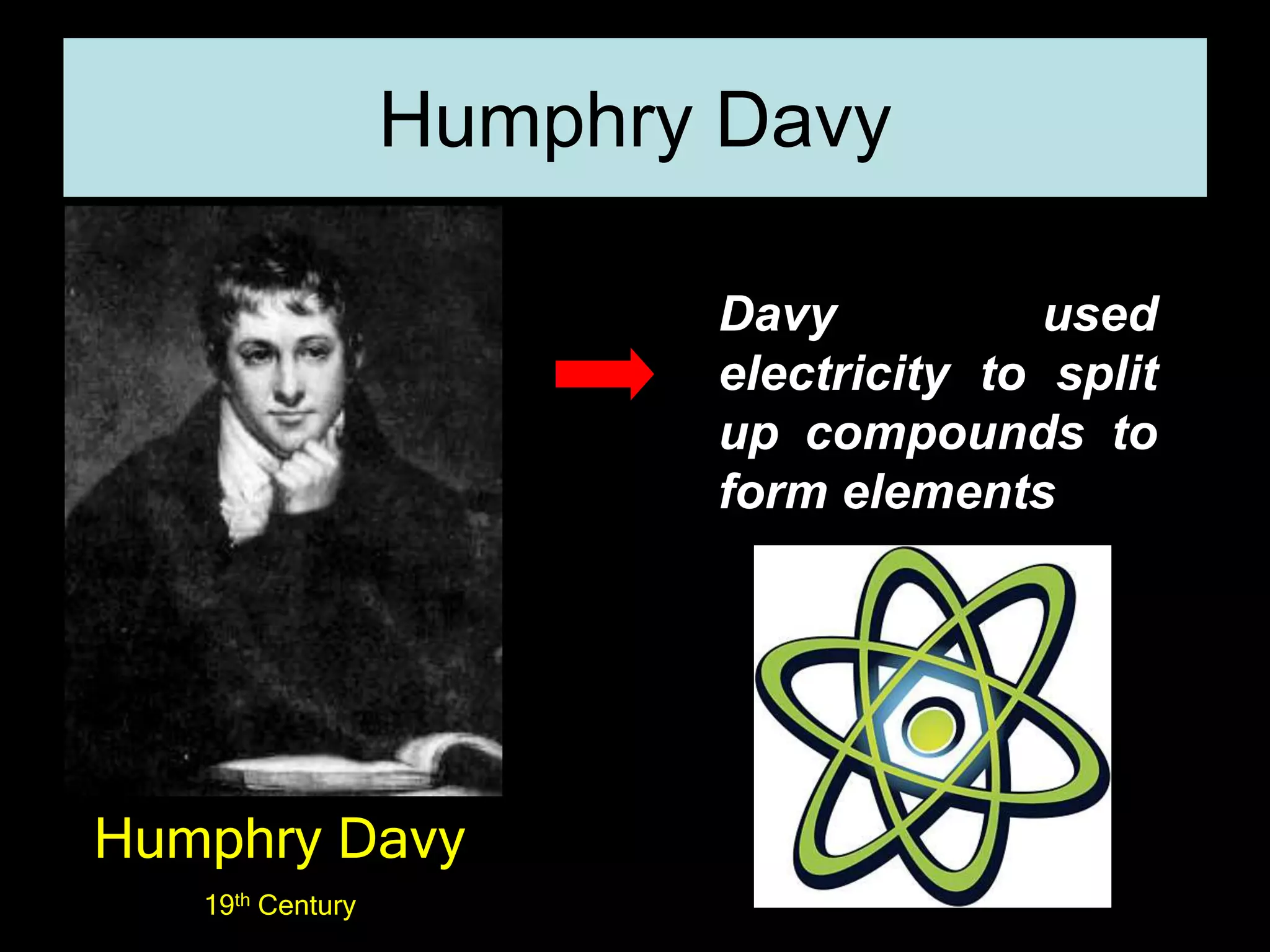
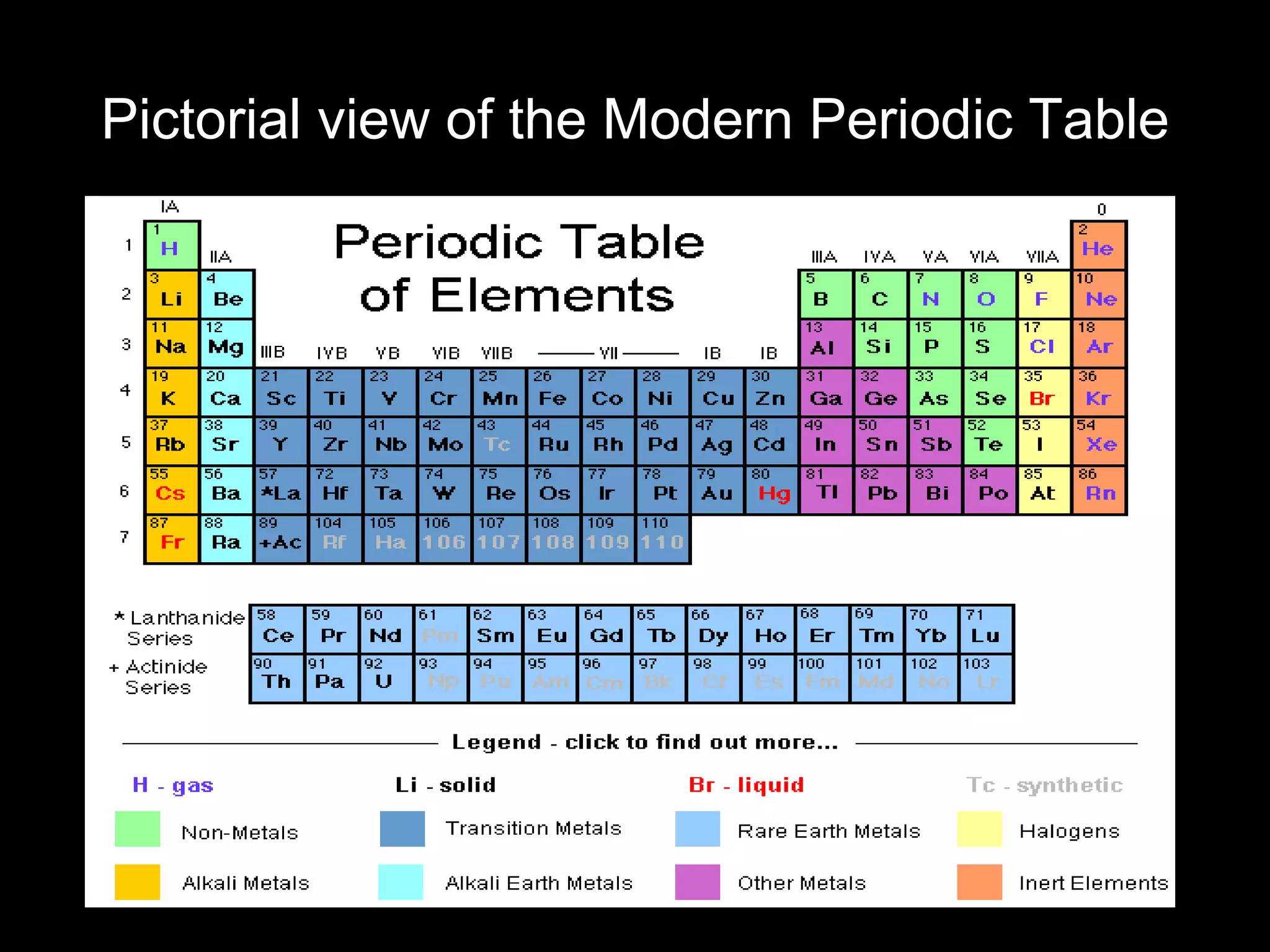
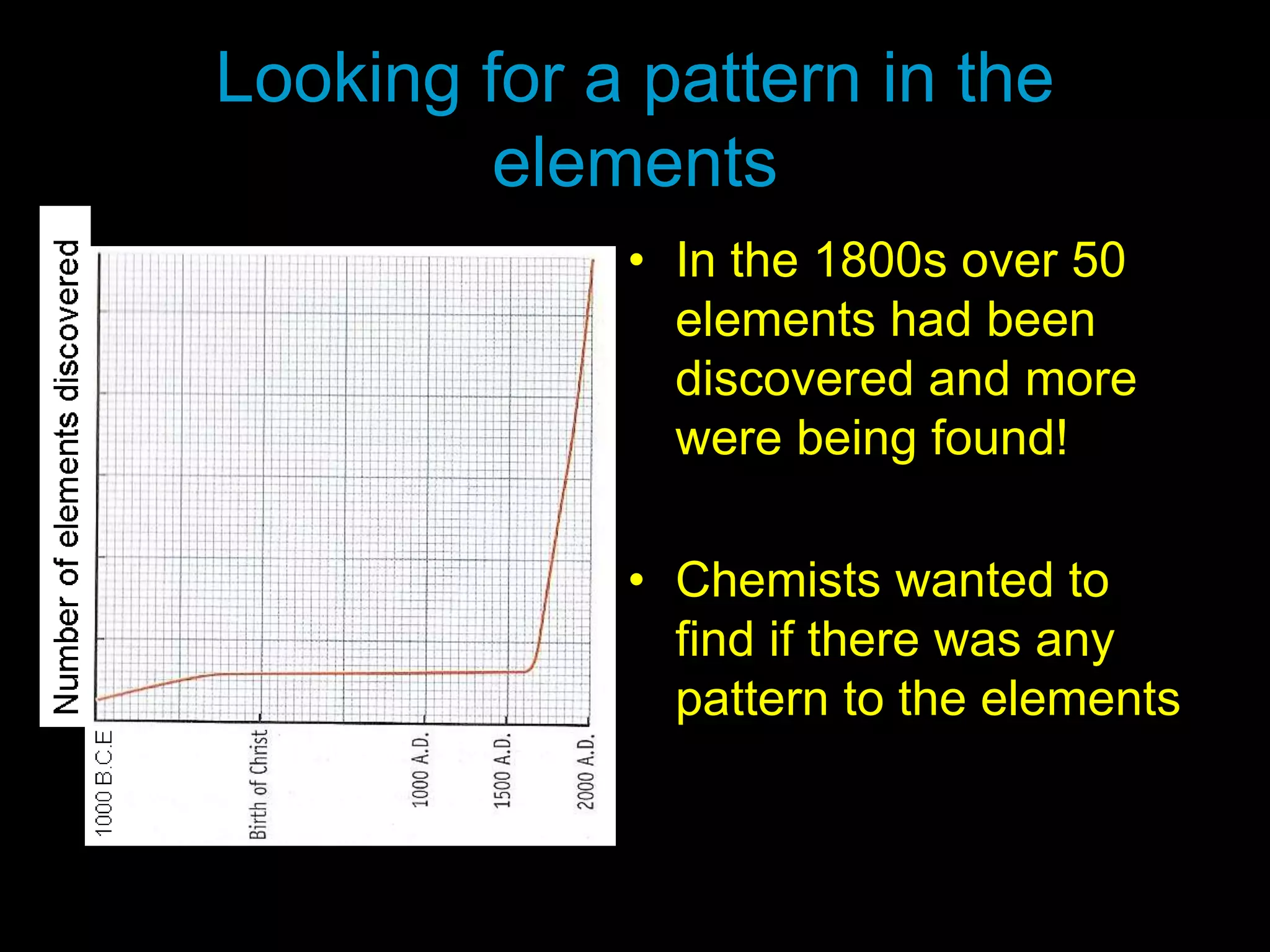
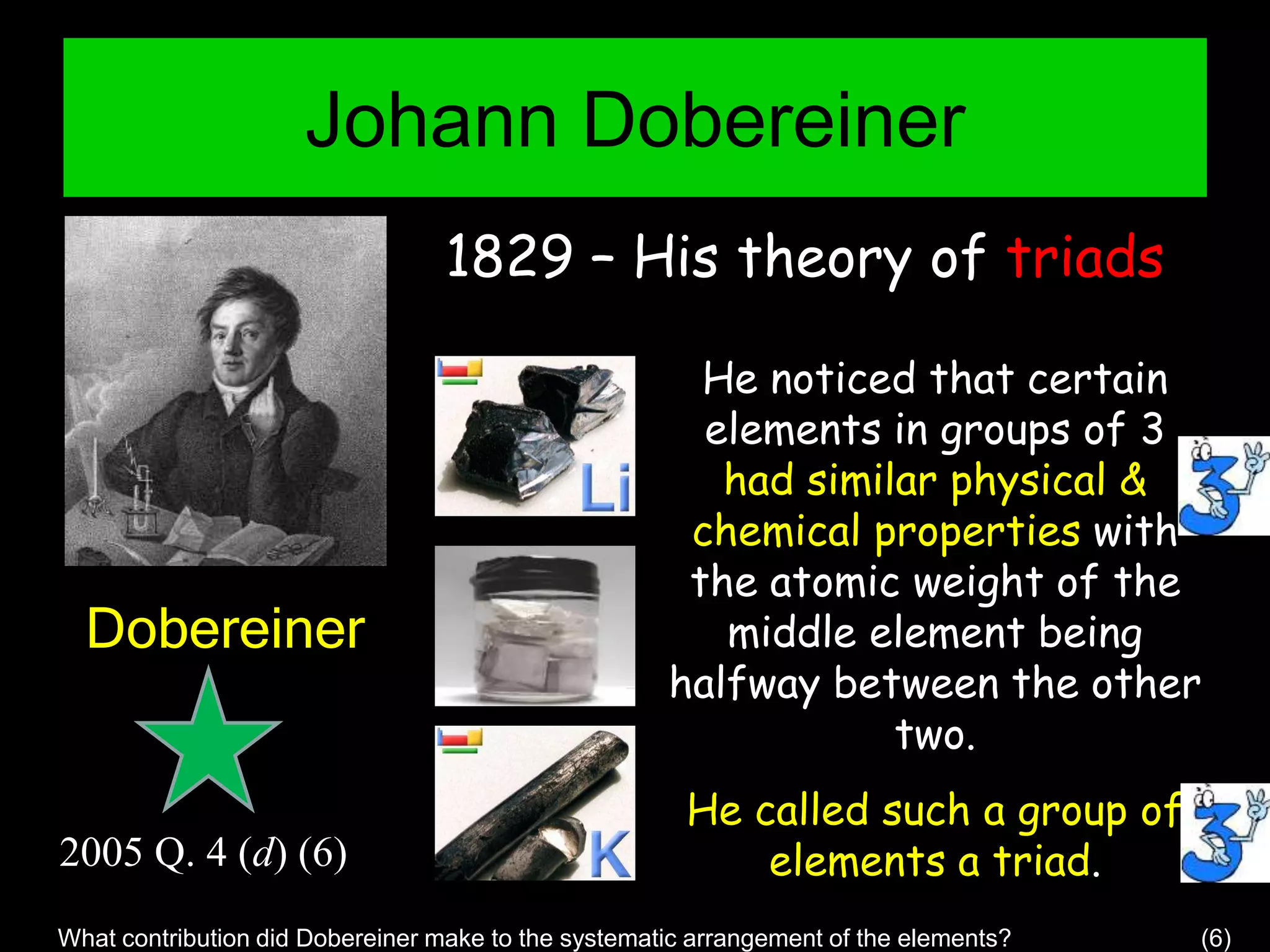
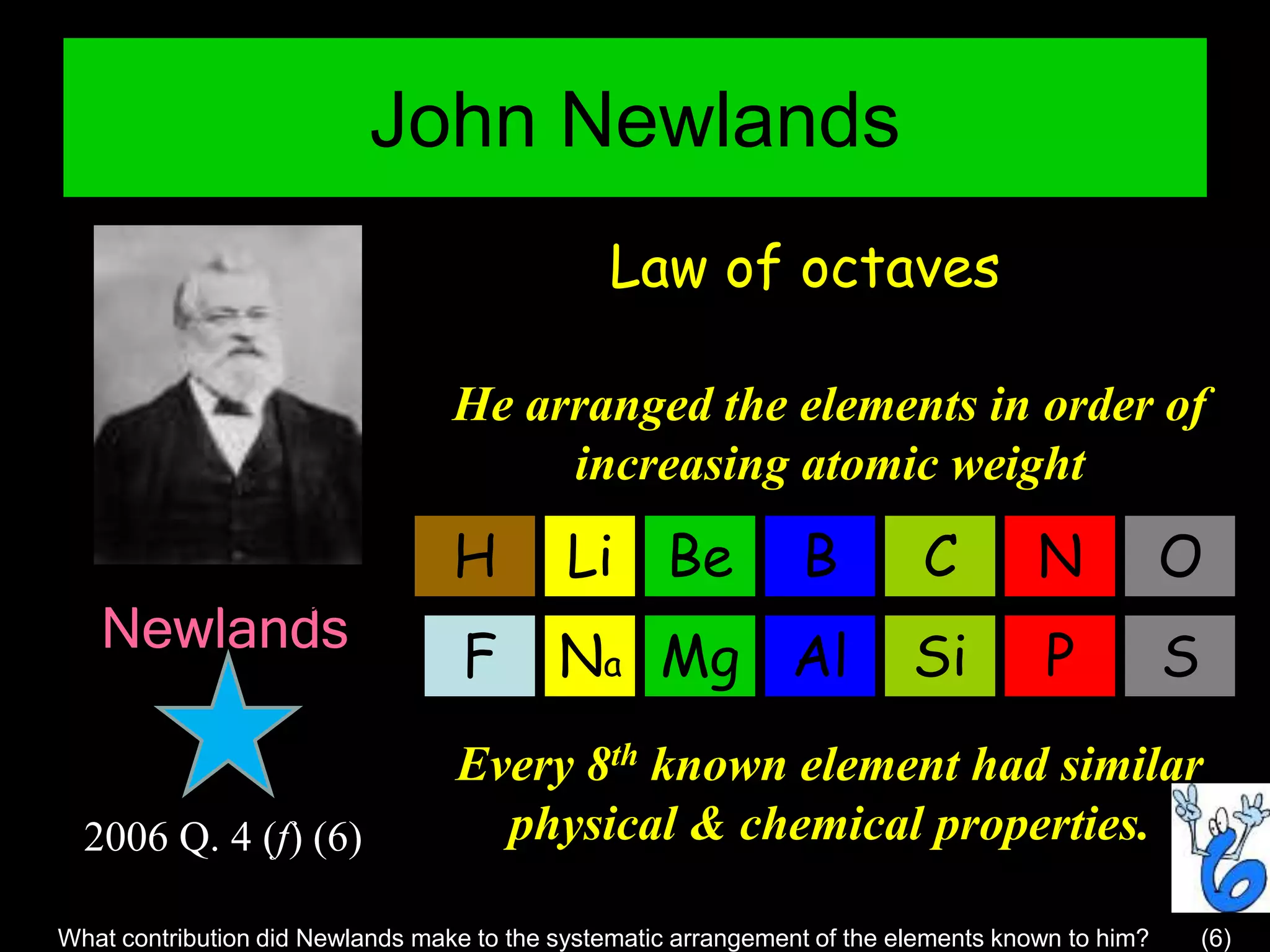
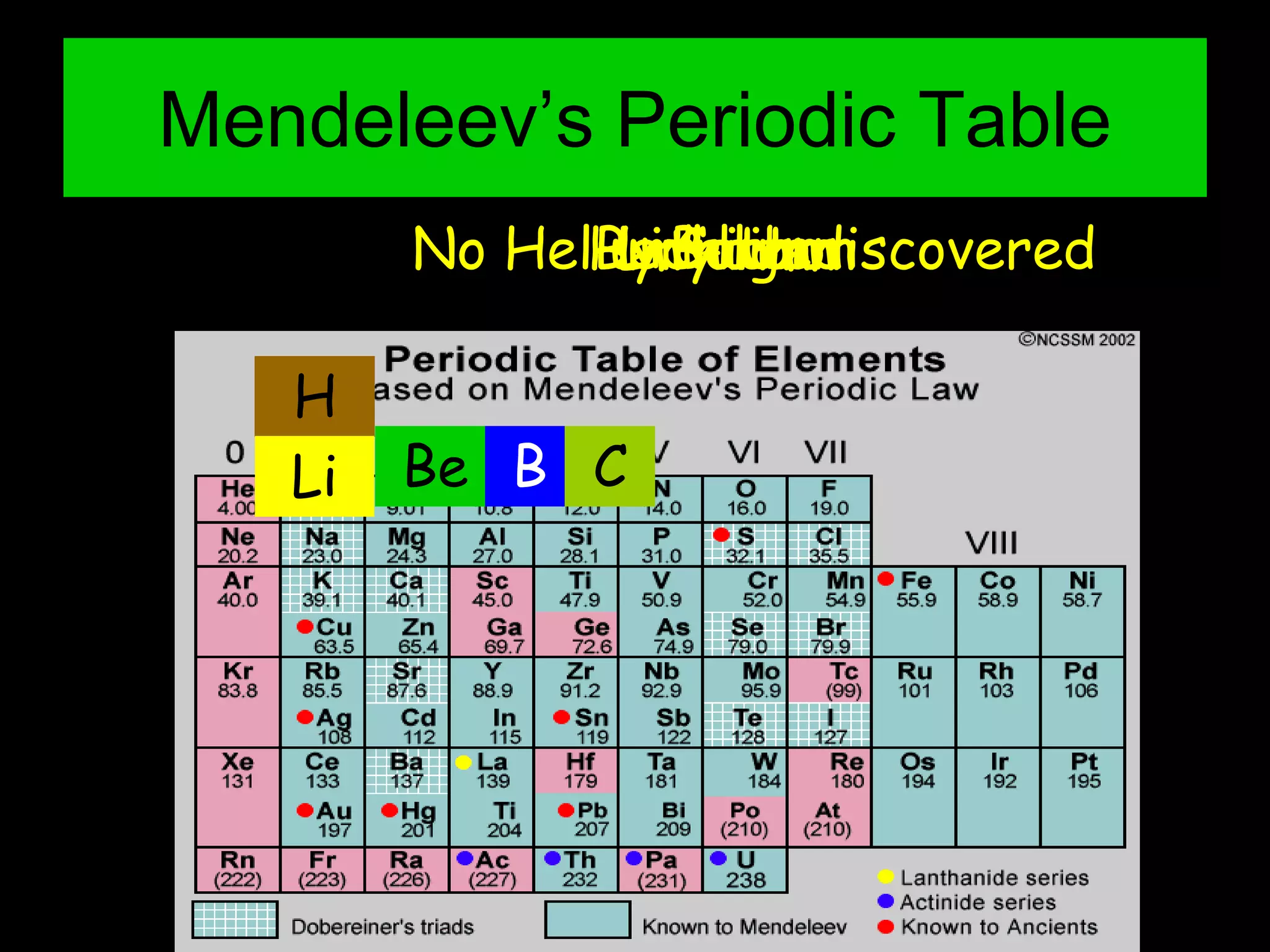
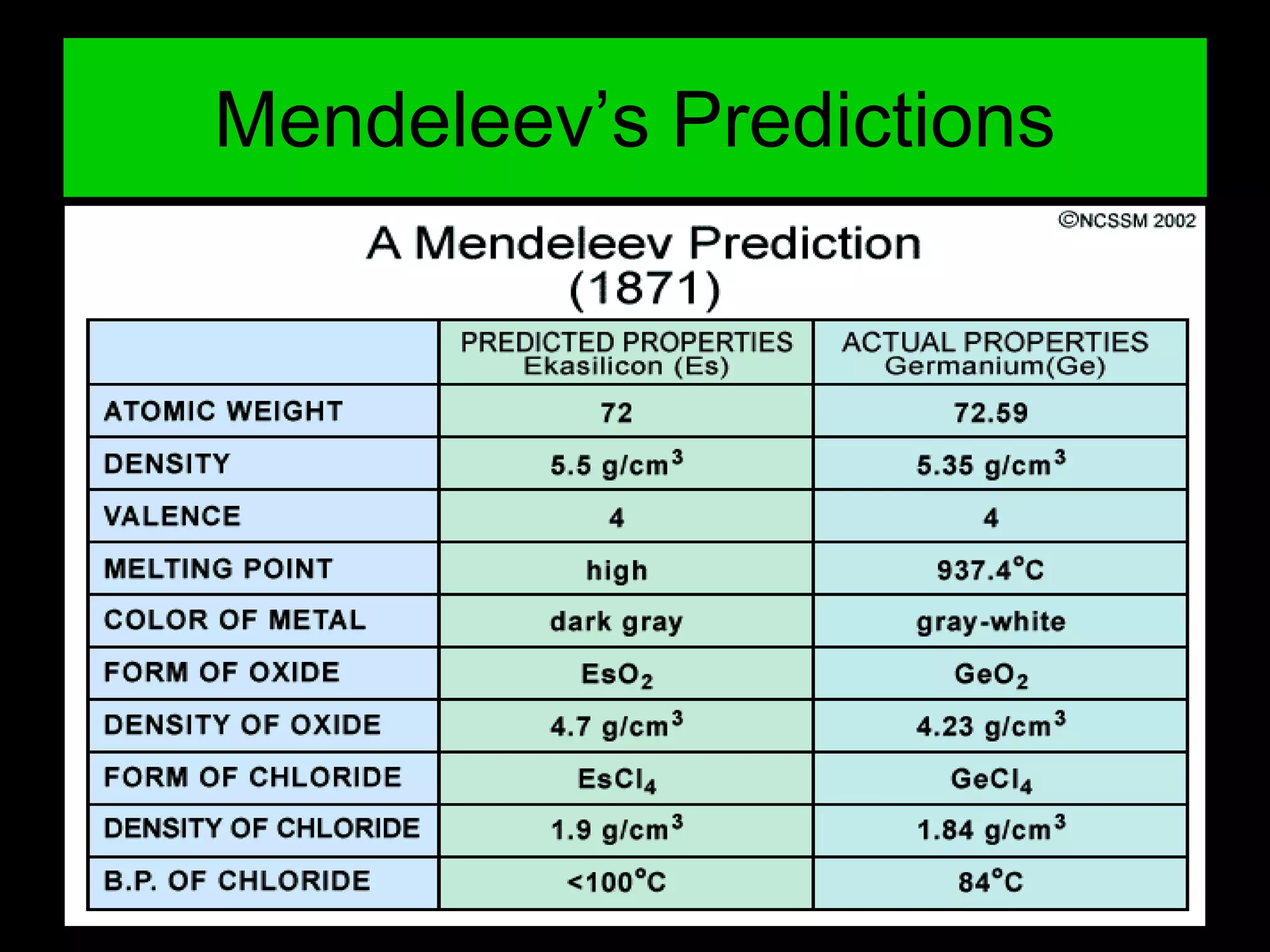
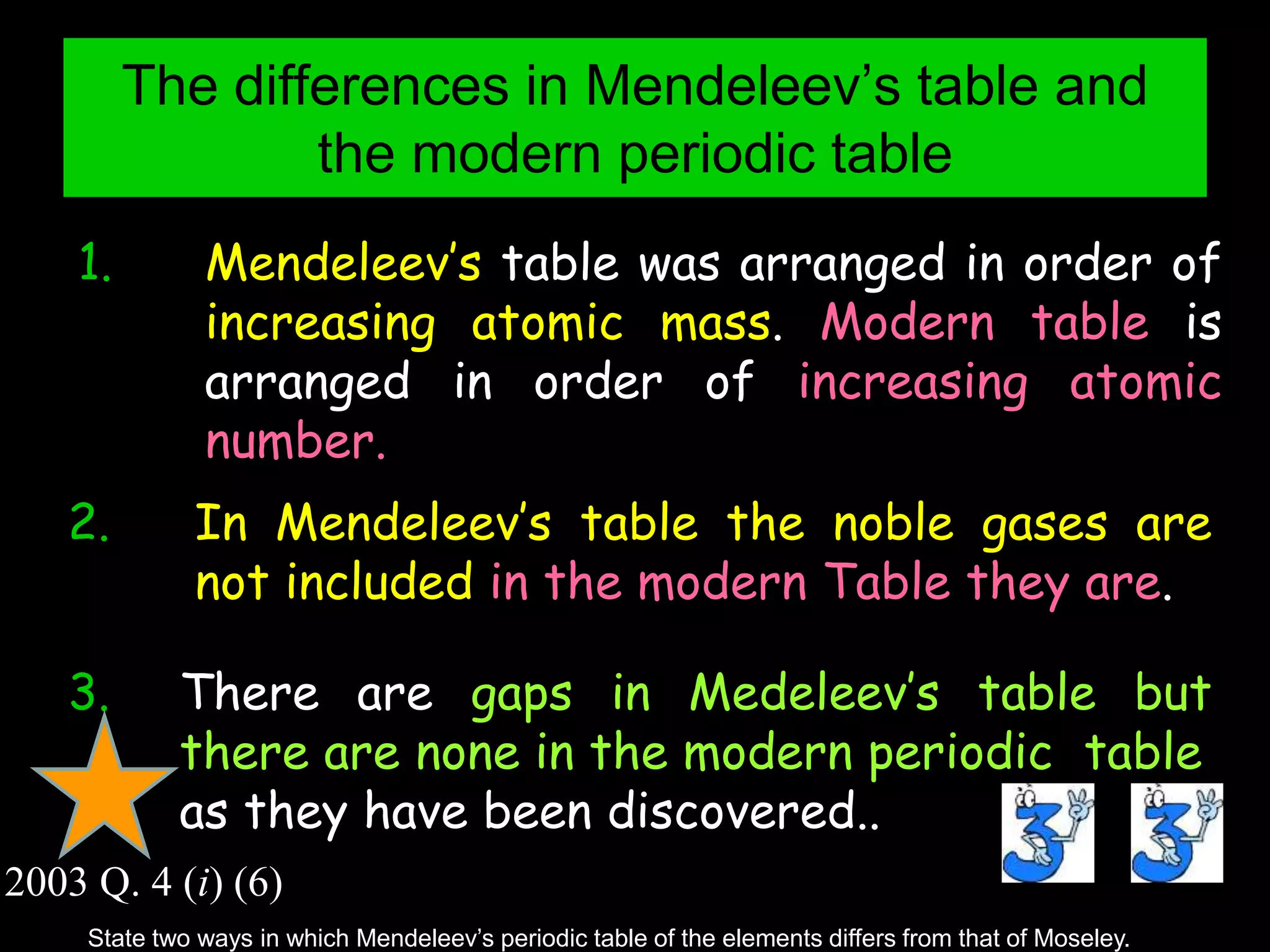
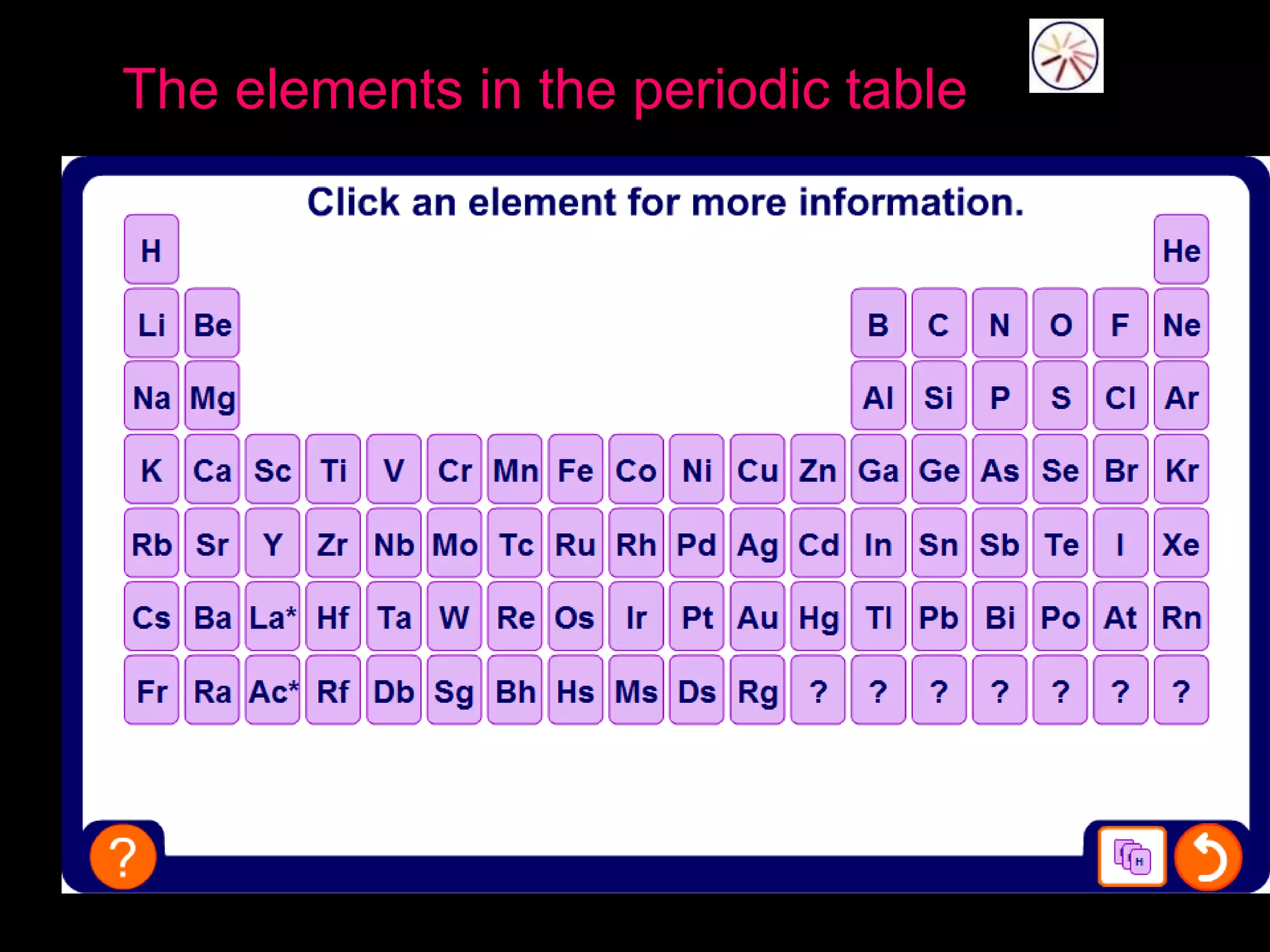
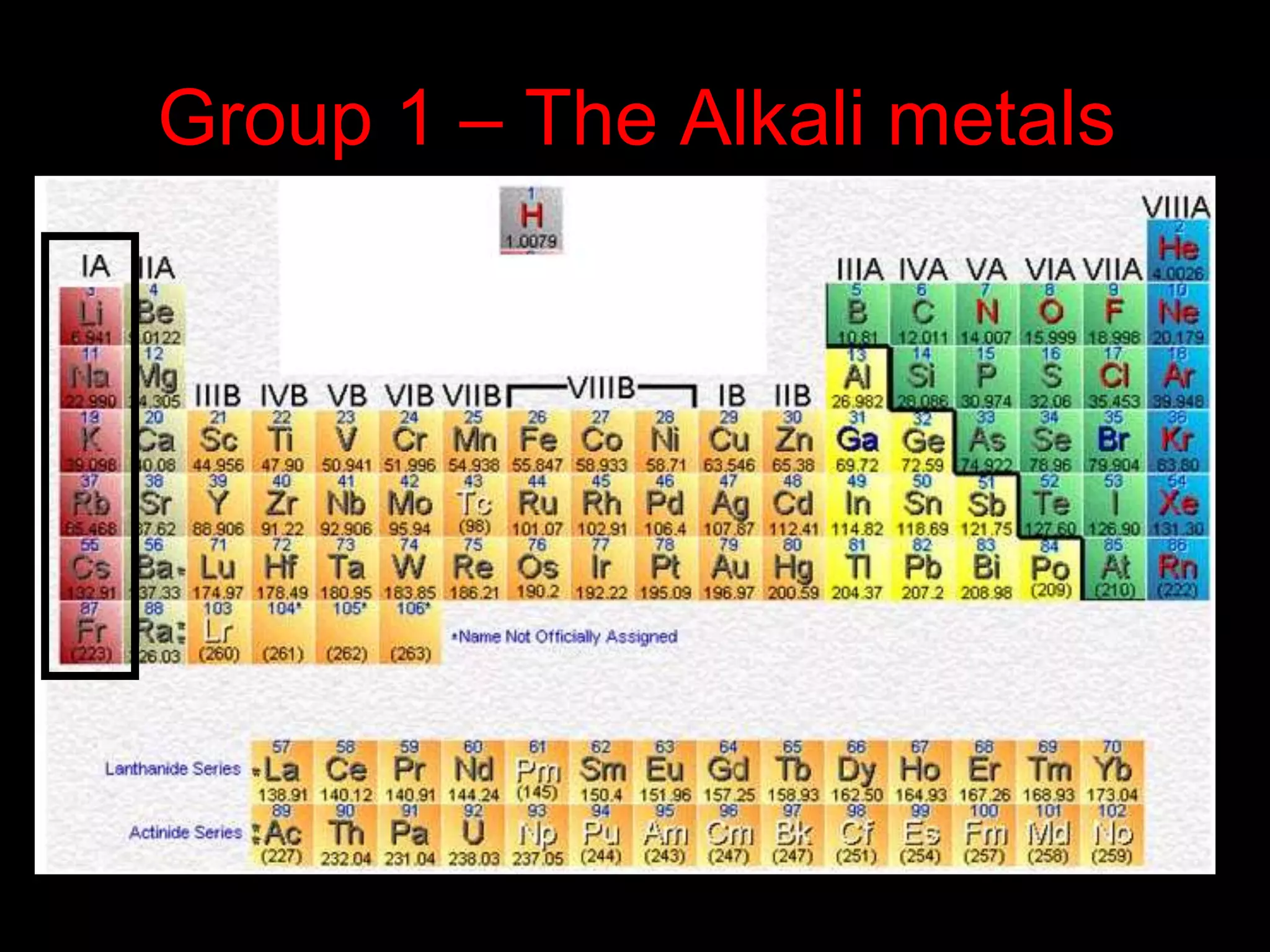
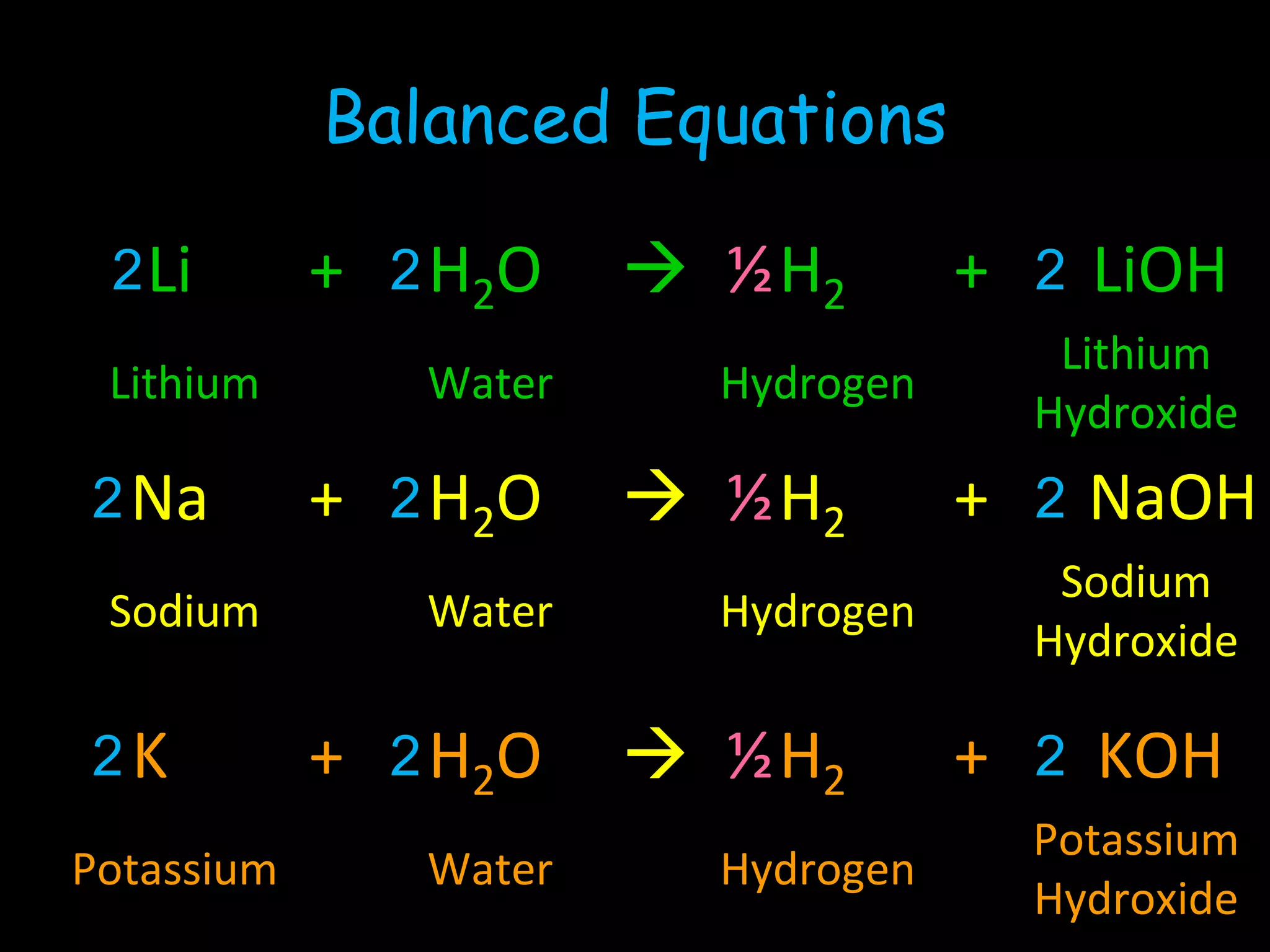
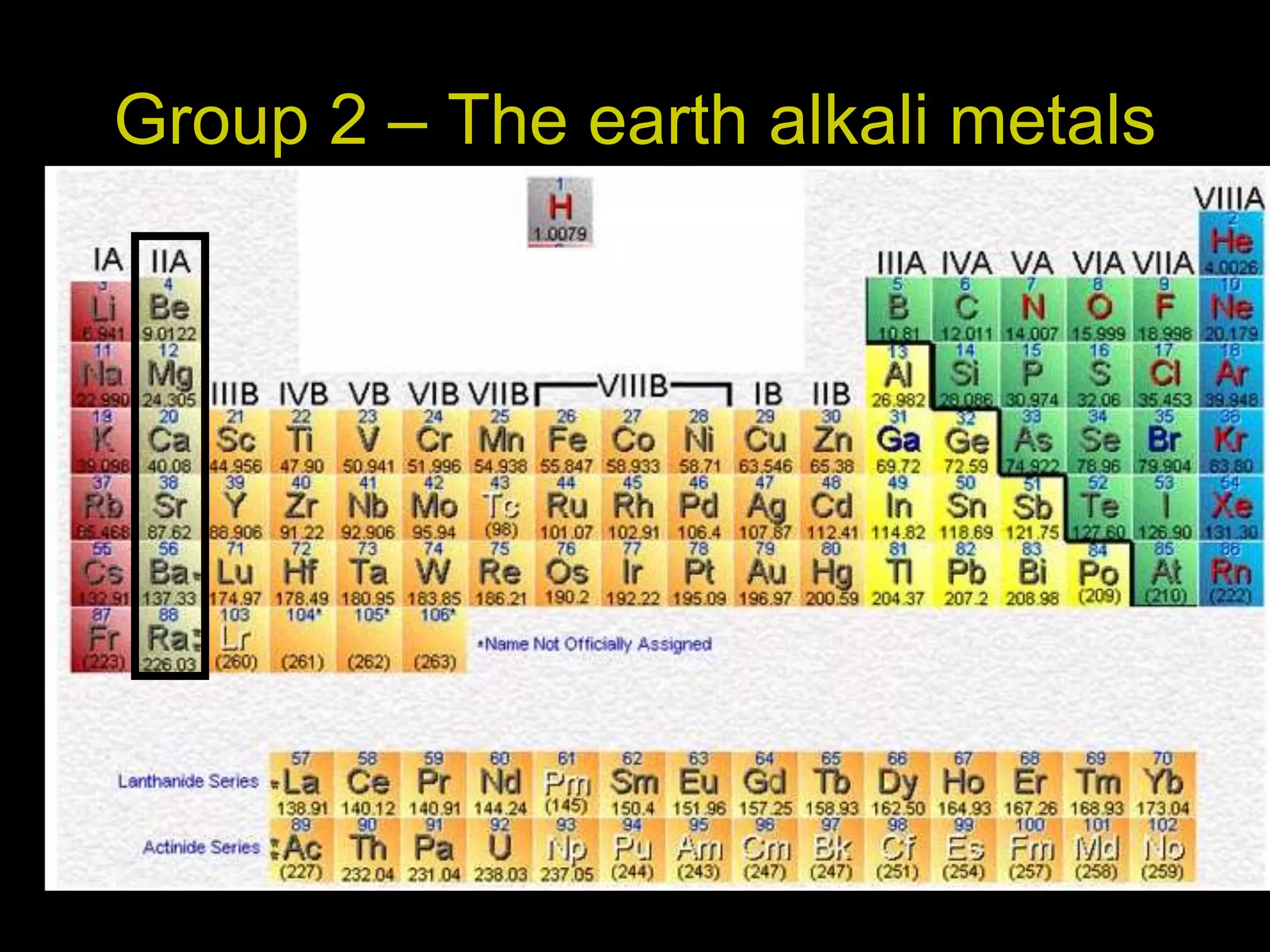
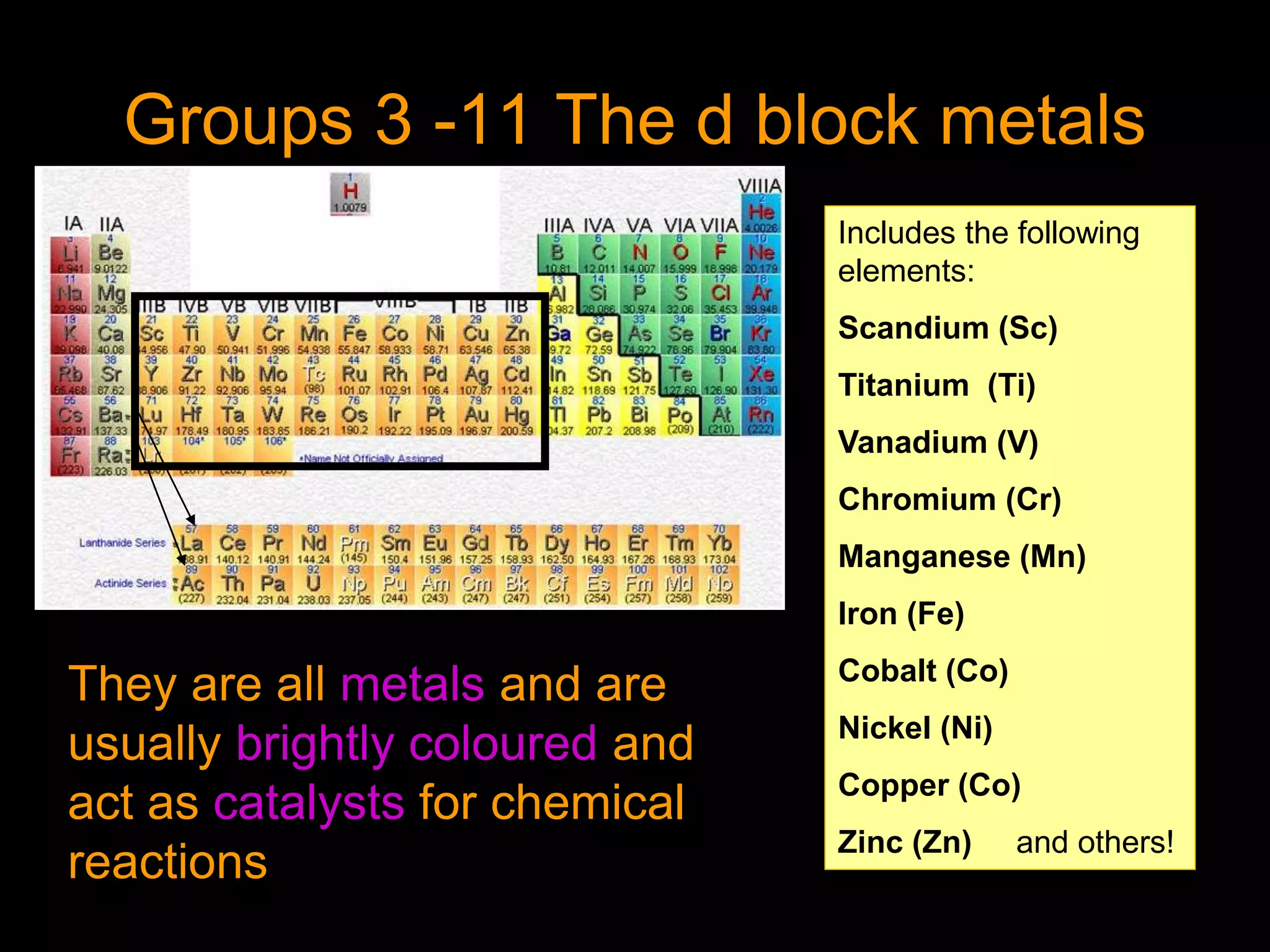
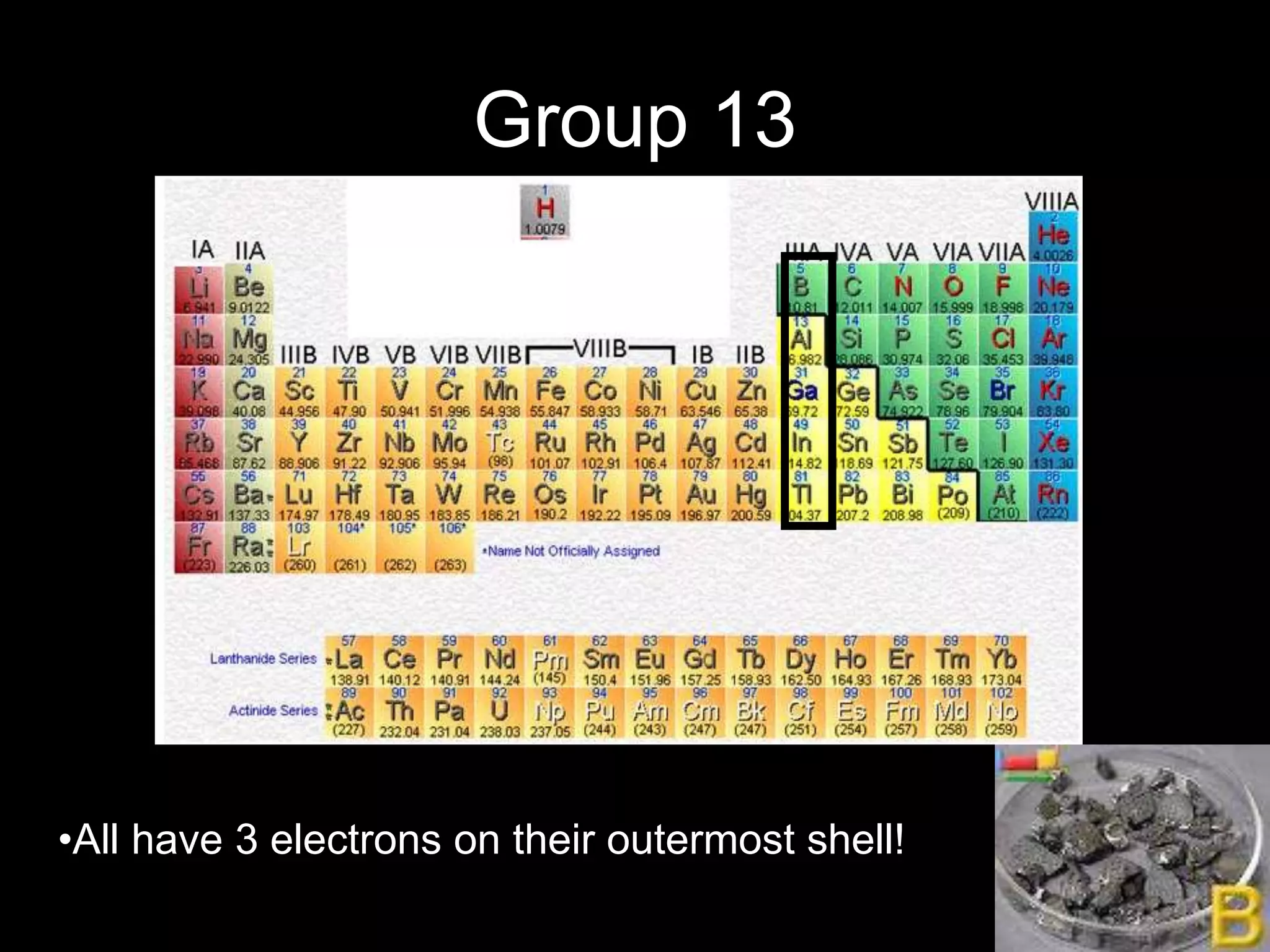
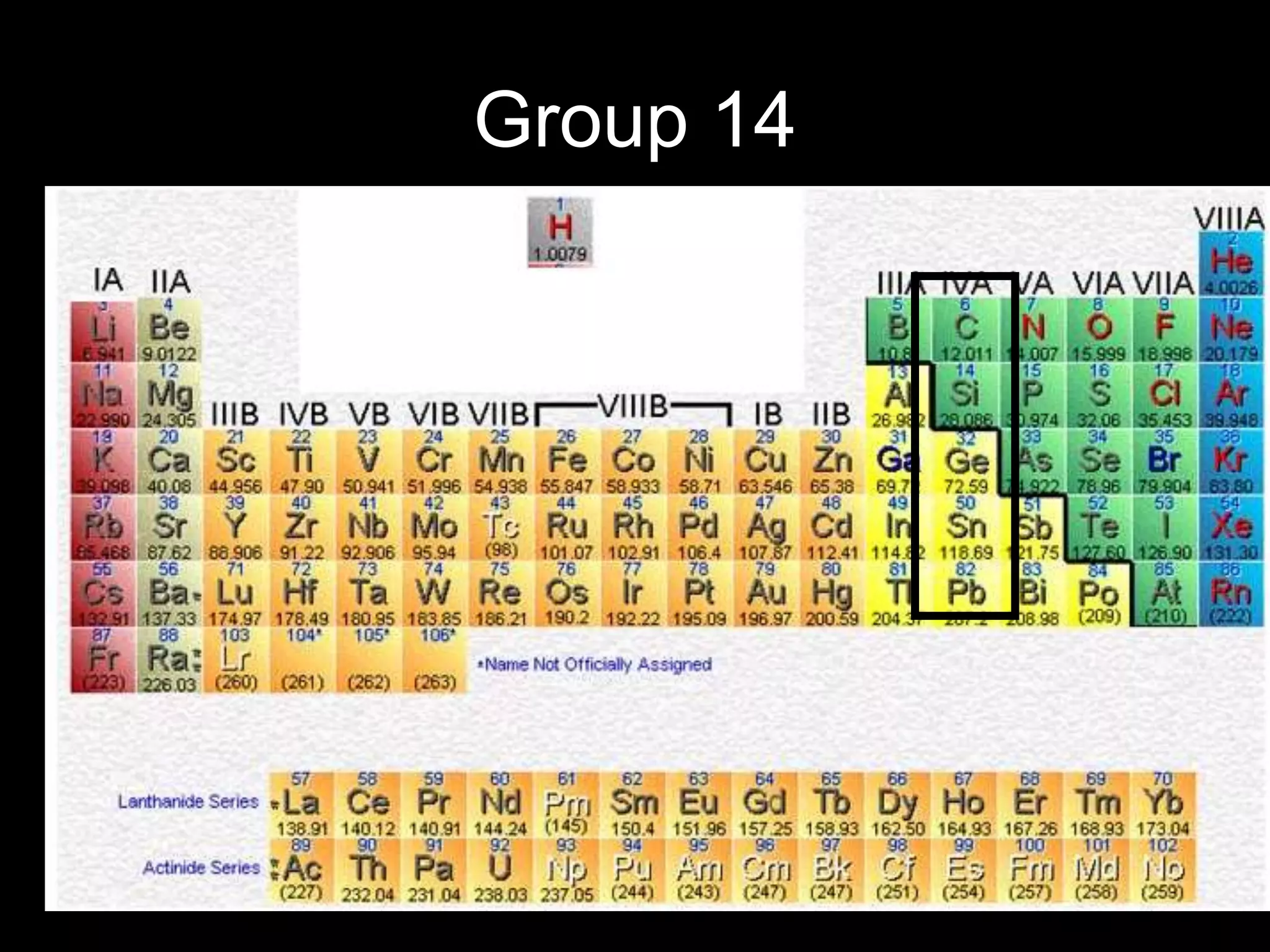
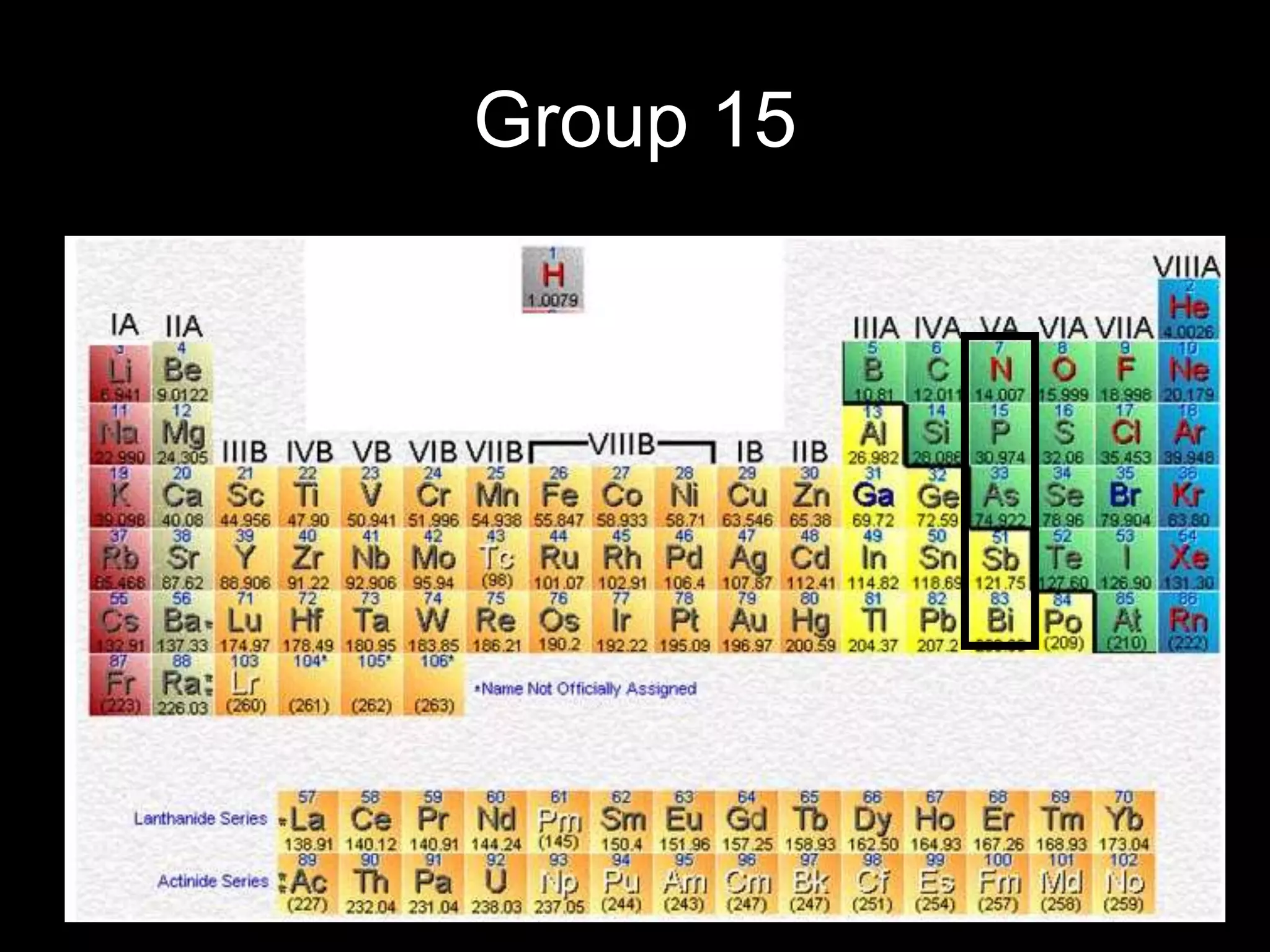
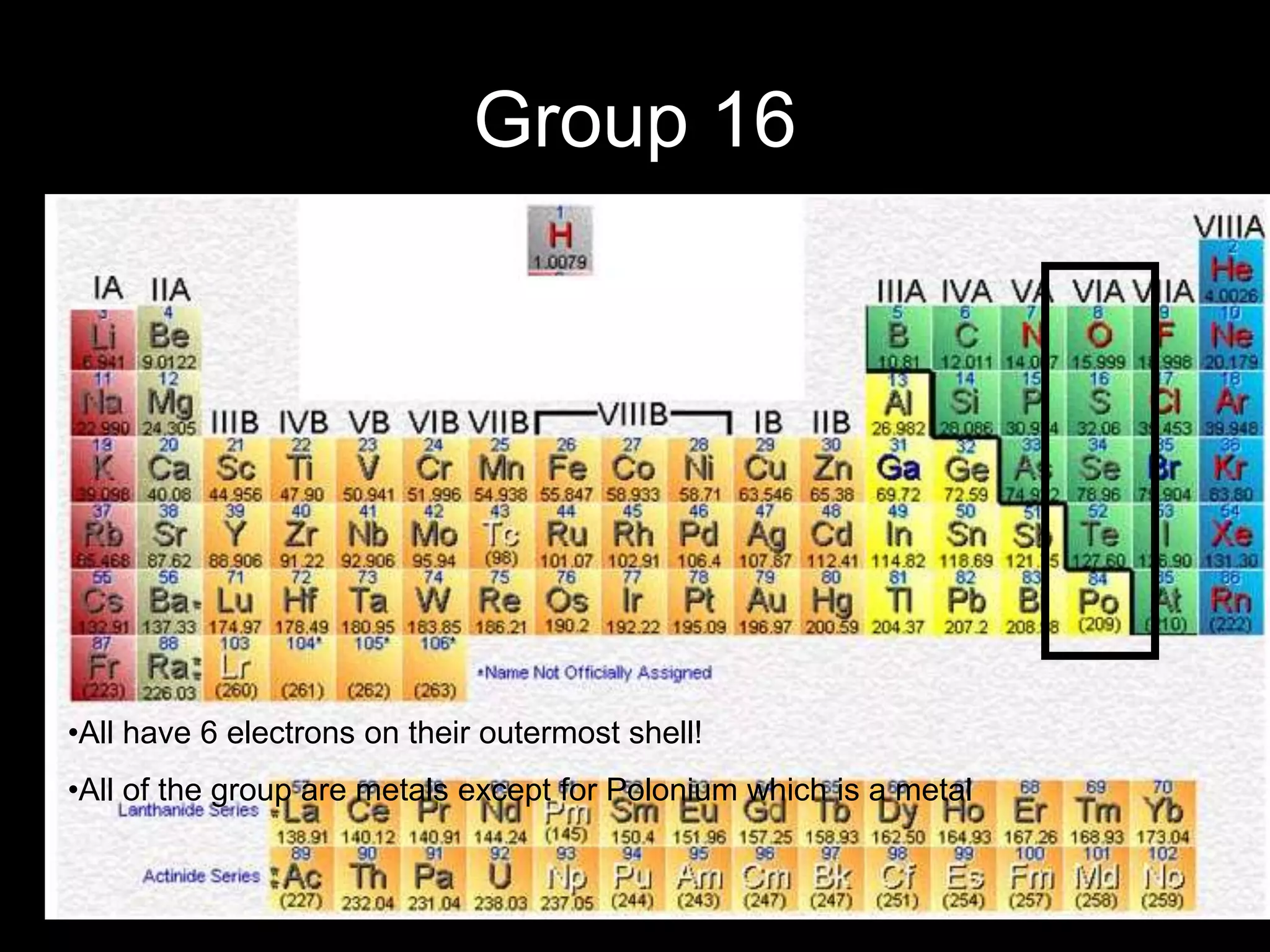
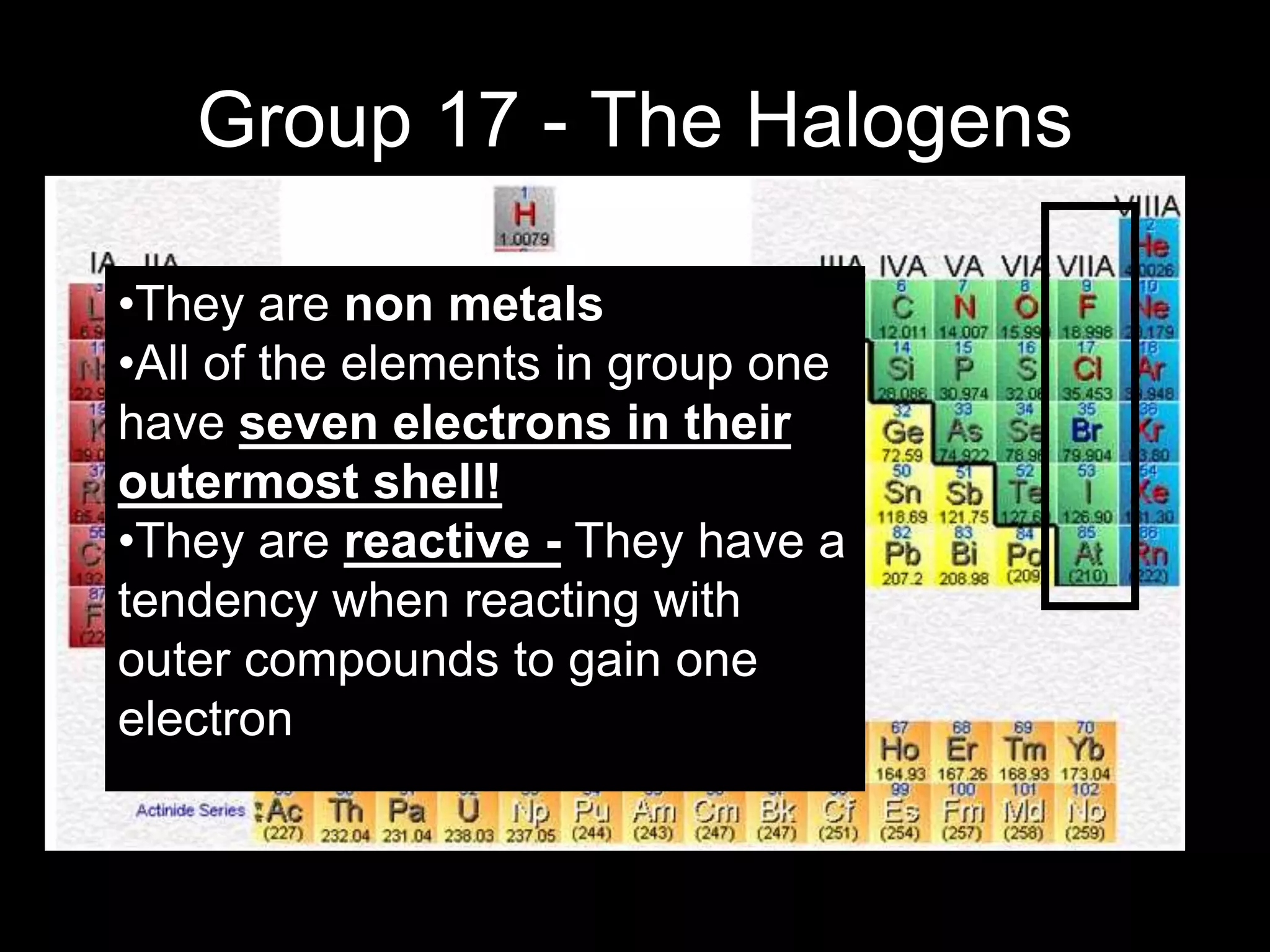
The periodic table organizes the chemical elements. Over time, scientists like Dobereiner, Newlands, and Mendeleev contributed to recognizing patterns in elements' properties that allowed organizing them into the periodic table. Mendeleev was the first to organize elements into a periodic table based on atomic mass. Later, Moseley determined elements should be organized by atomic number of protons. Today's periodic table arranges elements by atomic number, providing order and enabling prediction of undiscovered elements.