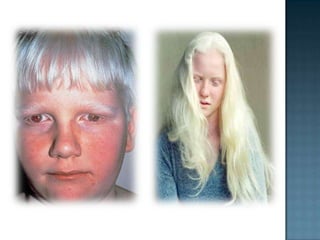
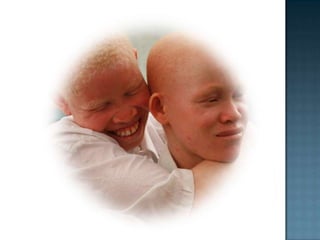
This document discusses albinism, a congenital disorder characterized by little or no pigmentation in the skin, hair and eyes. It is caused by a recessive gene that results in a lack of the enzyme tyrosinase needed to produce melanin. There are different types of albinism that can affect the eyes only or eyes, skin and hair. Albinism is associated with vision defects like photophobia, nystagmus and astigmatism as well as sun sensitivity. Diagnosis involves genetic testing or eye exams. Treatment focuses on protecting the skin from sun exposure and addressing vision problems. The condition does not affect lifespan except in rare cases of associated disorders.