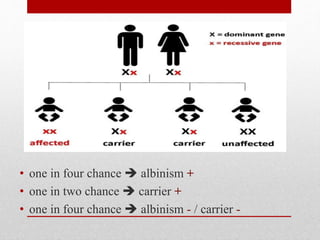
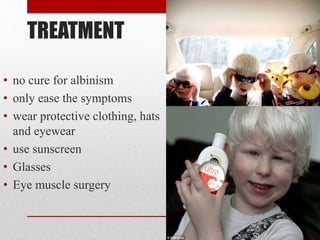
Albinism is a genetic condition characterized by little or no melanin pigment production in the body. This results in pale skin, hair and eyes that lack pigmentation. There are two main types - ocular albinism which only affects the eyes, and oculocutaneous albinism which affects the eyes, hair and skin. Problems associated with albinism include increased risk of sun damage and skin cancers due to lack of sun protection, as well as vision impairments. While there is no cure, symptoms can be managed through sun protection, eyewear and sometimes surgery. Albinism occurs in both humans and animals.