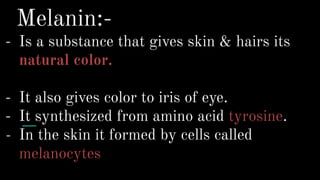
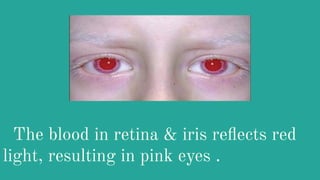
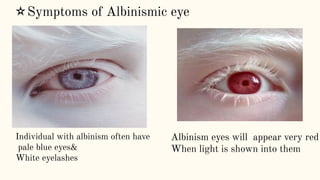
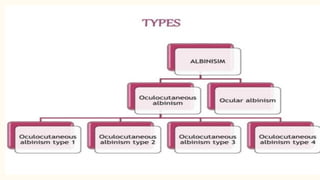
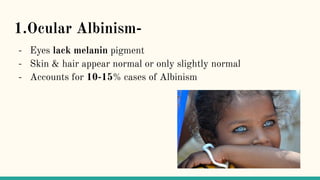
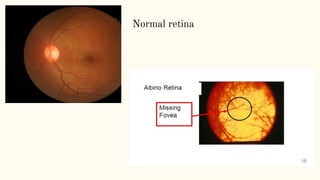
Albinism is a congenital disorder characterized by partial or complete lack of melanin pigment in the skin, hair and eyes. This results from a genetic mutation that prevents the body from producing sufficient melanin. There are three main types of albinism which vary based on the amount of melanin produced. Symptoms include very pale or white hair and skin that burns easily in the sun, visual impairments like nystagmus, strabismus and low vision. While there is no cure, treatments focus on protecting the skin from UV rays and improving vision through glasses, surgery and low vision devices.