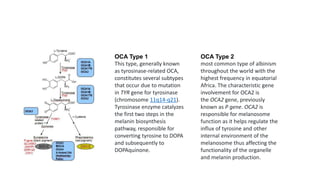
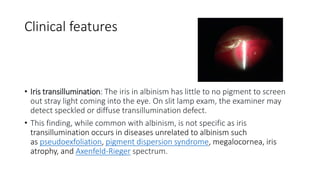
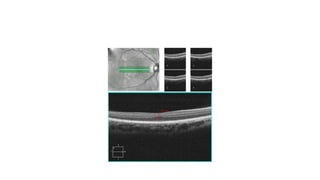
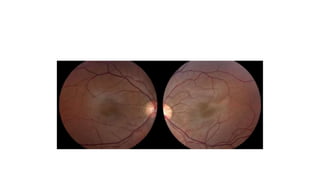
Albinism is characterized by absent or decreased skin pigment and can affect the eyes, hair, and skin. It is caused by mutations that impact melanin production and can be divided into two main types: oculocutaneous albinism, which affects multiple areas, and ocular albinism, which is limited to the eyes. Clinical features include iris transillumination, foveal hypoplasia, abnormal crossing of the visual pathways, photophobia, and refractive errors. Management focuses on sun protection and early vision screening.