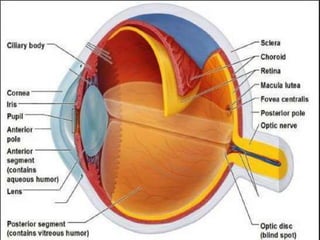
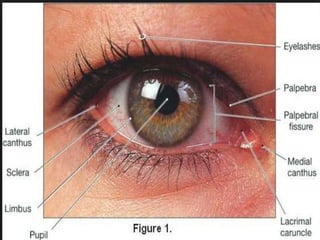
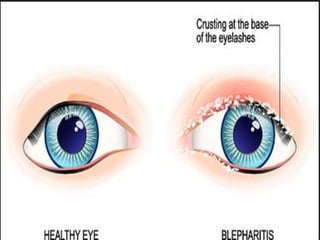
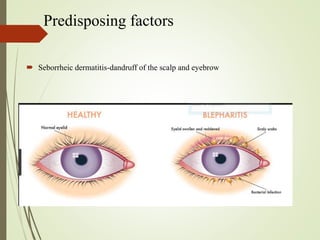
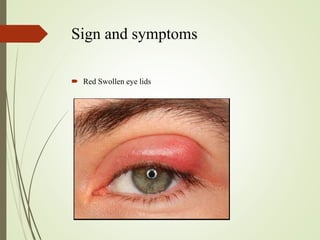
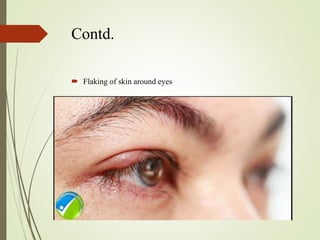
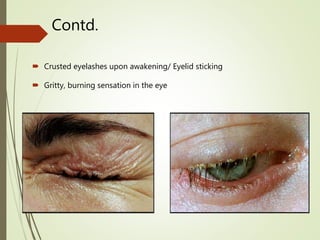
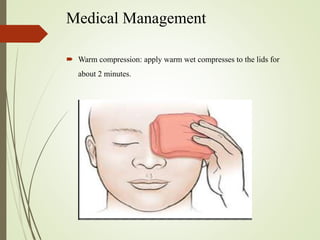
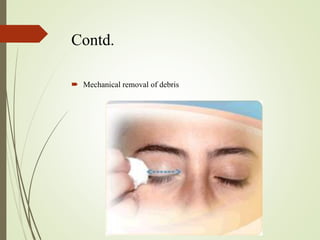
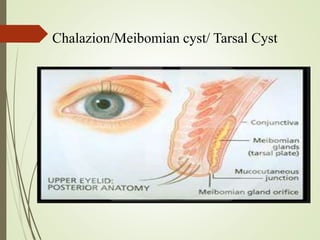
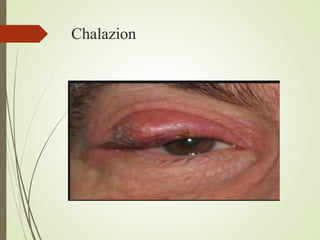
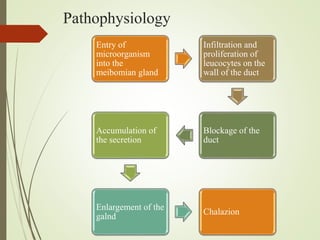
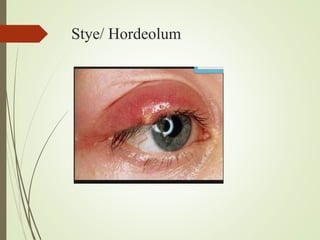
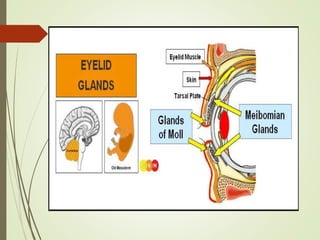
The document provides an overview of various eye disorders, primarily focusing on blepharitis, chalazion, and stye, including their definitions, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, and management strategies. Blepharitis is characterized by inflammation of the eyelid due to oil gland issues, while chalazion is a cyst caused by blocked meibomian glands, and stye is an infection of sebaceous glands. Treatment includes hygiene maintenance, warm compresses, and medications such as antibiotics, with general preventive measures highlighted for patient education.