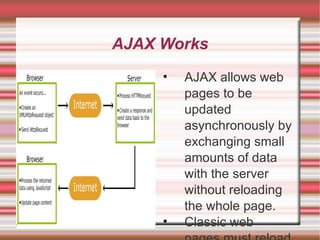
AJAX allows web pages to update parts of a page without reloading the entire page. It uses a combination of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, XML, and XHR to asynchronously retrieve data from a web server in the background without interfering with the display and behavior of the existing page. The XMLHttpRequest object sends and receives data from the server, and JavaScript is used to display or modify the HTML page without reloading. Examples of AJAX applications include Google Maps, Gmail, YouTube, and Facebook tabs.