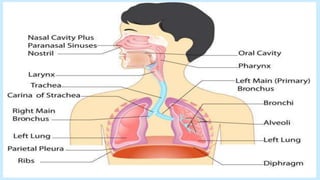
An airway obstruction occurs when the flow of air into the lungs is partially or completely blocked. This document discusses the causes, symptoms, and treatments of acute airway obstructions. Upper airway obstructions occur above the vocal cords while lower airway obstructions are below. Partial obstructions allow some air flow but breathing is difficult, while complete obstructions prevent any air from passing. Prompt treatment is needed and may include clearing the airway, administering oxygen, or performing an emergency procedure like a tracheostomy.