The document provides information on airway assessment and predictors of difficult intubation. It discusses:
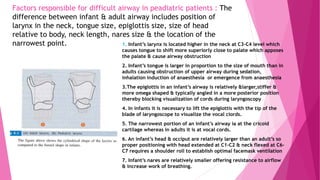
1) The importance of airway management expertise and maintaining a patent airway. Failure to do so can be life-threatening.
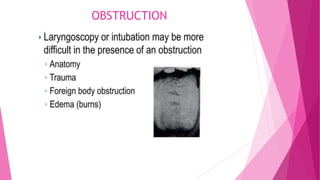
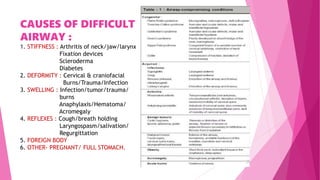
2) Causes of difficult airway include anatomical issues like limited neck movement, swelling, and deformities as well as medical conditions.
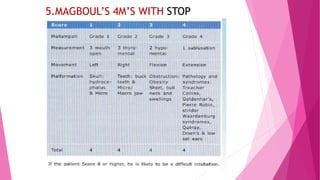
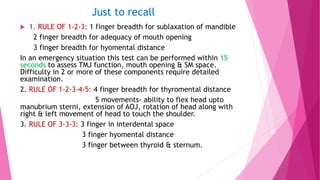
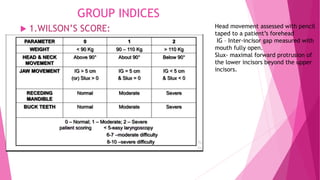
3) Physical tests that can help predict difficult intubation include the Mallampati score, range of neck movement, thyromental distance, and sternomental distance. Group indices like LEMON, Wilson score, and 4 D's can also help assess airway difficulty.








![ANATOMY OF AIRWAY IN ADULTS
It refers to the normal passage for air entry & exit in a human being for efficient gas exchange at
the lungs.
It may be divided into
1.Upper airway
2.Lower airway
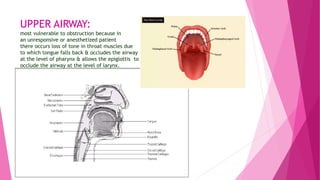
UPPER AIRWAY- Comprises of mouth/oral cavity, nasal cavity,pharynx,nasopharynx
oropharynx & the larynx
1. Mouth/Oral cavity- Extends from the mouth opening to anterior tonsillar pillars.
2. Nasal cavity- Extends from the naris to the end of the turbinates.
3. Nasopharynx : It extends from the posterior end of turbinates to posterior pharyngeal wall
above soft palate.
4. Oropharynx : It extends from soft palate above to epiglottis below & anteriorly from anterior
tonsillar pillar to posterior pharyngeal wall.
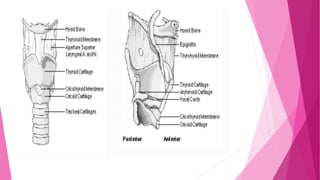
5. Larynx :It extends from laryngeal inlet [C3-C4 in adults] to lower border of cricoid cartilage [ C6
in adults]. Larynx includes 3 paired & 3 unpaired cartilages
3 large Unpaired cartilages are cricoid, thyroid & epiglottis
3 Paired smaller cartilages are arytenoids, corniculate & cuneiform.
Thyroid is the largest of the laryngeal cartilages having 2 alae which meets anteriorly at an angle of
90 degrees in males & 120 degrees in females. Vocal cords are attached to its middle.
The cricoid is the only complete ring cartilage.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-10-320.jpg)

![LOWER AIRWAY
It includes trachea ,bronchi in bronchioles, which after multiple divisions finally terminate into
alveoli.
TRACHEA – Trachea extends from lower border of cricoid cartilage [ C6] to its division into 2 main
bronchi [T4]. It is 11-13 cm long.
Carina is a very sensitive structure
& its stimulation can evoke un-
wanted responses.
Tubes/catheters should be kept
away from it.
The trachea divides at carina into
right main bronchus at approx. 20-25
degrees angle & the left main bronchus at
approx. 45-55degrees angle.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-14-320.jpg)

![MEAN AIRWAY DISTANCES/ANGLES IN
ADULTS OF INTEREST TO THE
ENDOSCOPIST :
1. Mean distance from lips to carina= 28.5 [M] & 25.2[F]
2. Mean distance from base of nose to the carina =31[M] & 28.4[F]
3. Mean angle of right main bronchus =20-25 degrees
4. Mean angle of left main bronchus =40-50 degrees.
REQUIREMENTS OF NECK WHILE INTUBATION OR LARYNGOSCOPY
: 1. HEAD EXTENSION= >80-85 degrees- ask the patient to look at the ceiling
without raising eyebrows to test A-O joint function.
2. NECK FLEXION =>25-30 degrees –ask the patient to
touch his manubrium sternii with his chin & assess the movement
3. HEAD/NECK ROTATION= >70-75 degrees.
NECK FLEXION ON CHEST BY 25-30 DEGREES & A-O JOINT EXTENSION BY 85
DEGREES IS CALLED SNIFFING OR MAGILL’S POSITION – gives an easy
laryngoscopic view.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-16-320.jpg)








![GROUP INDICES FOR DIFFICULTY TO FACE
MASK VENTILATE : OBESE
1. O : OBESE [ Body mass index more than 26kg/m2]
2. B : BEARDED
3. E : ELDERLY [ Than 55yrs]
4. S : SNOARERS
5. E : EDENTULOUS [ No teeth] [= BONES]
Another one to remember : MOANS
This is identical to BONES except M : Mask seal difficulty due to receding mandible, syndromes with facial
abnormalities, burns, strictures.[ also may be due to small hands of the trainer, wrong size mask, oddly shaped
face,bushy beard,blood/vomit]
O : OBESITY- use 2 hands for mask seal & jaw thrust, avoid pushing in on soft tissues under jaw
A : ADVANCED AGE
N : NO TEETH- place gauge at site of leak as cheeks fall inward or put gauge inside mouth to ‘puff out’ cheek
S : SNORER.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-25-320.jpg)


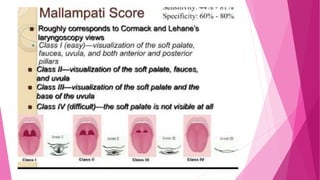
![a. ANATOMICAL CRITERIA
:
i. RELATIVE TO TONGUE/PHARYNGEAL SIZE [ MALLAMPATI
CLASSIFICATION & SCORE ] :As the class increases there is difficulty
in intubation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-28-320.jpg)
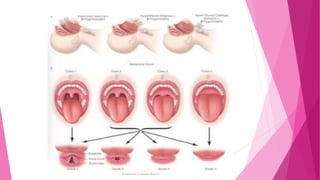
![PRE-REQUISITES FOR MALLAMPATI TEST :
1.See for free movement of – a. head on cervical spine
b. joints of cervical spine permitting
flexion & extension of neck
c. temperomandibular joint to open mouth
widely.
2. Have patient sit up, with head protruding forward [ sniffing position] & stick out
tongue without phonation which lowers the grade by one step [ grade 2 becomes
grade 1]
3. The observer’s eye should be at the level of the patient’s open mouth.
MAY BE UNABLE TO ASSESS PROPERLY IN AN EMERGENCY SITUATION.
MODIFIED VERSION IS TO USE A LARYNGOSCOPE BLADE LIKE A TONGUE BLADE TO
VISUALIZE OROPHARYNX.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-29-320.jpg)


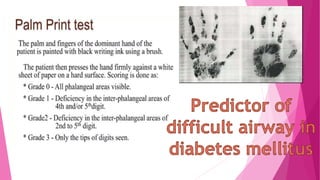
![PRAYER SIGN
A positive “prayer sign” can be elicited on examination with the patient
unable to approximate the palmar surfaces of the phalangeal joints while
pressing their hands together.
SEEN IN DIABETES.
It represents cervical spine immobility & a potential for a difficult
intubation [ STIFF JOINT SYNDROME IN JUVENILE DIABETES ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-33-320.jpg)
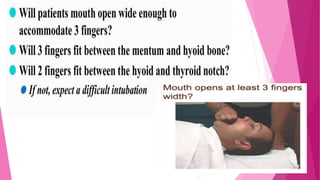
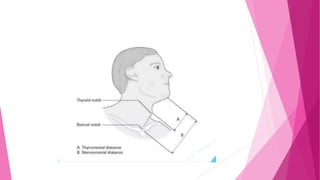
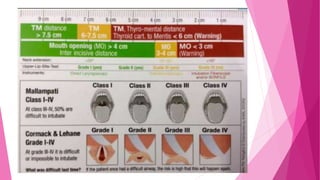
![iii.ASSESSMENT OF MANDIBULAR SPACE :
THYROMENTAL DISTANCE [ PATIL’S TEST ]
HYOMENTAL DISTANCE
STERNOMENTAL DISTANCE [ SAVVA TEST]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-35-320.jpg)
![THYROMENTAL DISTANCE [ PATIL’S TEST]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-36-320.jpg)
![ LIMITATIONS – A. Little reliability in prediction unless comb-
-ined with other tests. [ grade 3 or 4 mallampati who also has
a thyromental distance of less than 7cm is likely to present with
difficulty in intubation ]
B. Variation according to height, ethnicity
MODIFICATIONS TO IMPROVE THE ACCURACY :
1. Ratio of height to thyromental distance [ RHTMD]
2. Useful bedside screening test
3. RHTMD > 23.5 very sensitive predictor of difficult laryngoscopy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-37-320.jpg)
![HYOMENTAL DISTANCE [ 2 finger breadth]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-38-320.jpg)
![STERNOMENTAL DISTANCE [SAVVA TEST]
Distance from the upper border of the manubrium to the tip of mentum, neck
fully extended, mouth closed.
Mininal acceptable value – 12.5
SINGLE BEST PREDICTOR of difficult laryngoscopy & intubation [ has high
sensitivity & specificity].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-39-320.jpg)





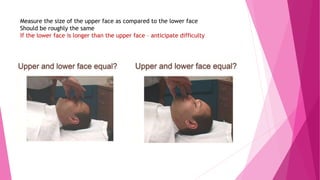
![ADEQUACY OF OROPHARYNX FOR
LARYNGOSCOPY & INTUBATION
1. MALLAMPATI GRADING [SAMSOON & YOUNG MODIFICATION] : CLASS III & IV
signifies angle between base of tongue & laryngeal inlet is more acute & not
conductive for easy laryngoscopy. [ good predictor in pregnancy, obesity &
acromegaly]
2. NARROWNESS OF THE PALATE
A narrow, high arched palate offers
Very little space for laryngoscopy
& endotracheal intubation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-46-320.jpg)
![ASSESSMENT FOR QUALITY OF GLOTTIC VIEW
DURING LARYNGOSCOPY
1. INDIRECT MIRROR LARYNGOSCOPIC VIEW- classification
• Complete vocal cords visible
• Posterior commissure visible
• Epiglottis visible
• No glottis structures visible.
2. DIRECT LARYNGOSCOPY “ AWAKE LOOK” – CORMACK & LEHANE GRADING
3. GRADING EASE OF INTUBATION-
• GRADE 1- No extrinsic manipulation of larynx is required
• GRADE 2- External manipulation of larynx is necessary to intubate.
• GRADE 3- Intubation possible only when aided by a stylet.
• GRADE 4- Failed intubation
4. POGO [PERCENTAGE OF GLOTTIC OPENING] SCORING-
Entire glottic structure visualized – 100%
No glottis structures are visible not even arytenoids -0%
Lower third of vocal cords & arytenoids visible- 33%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-47-320.jpg)
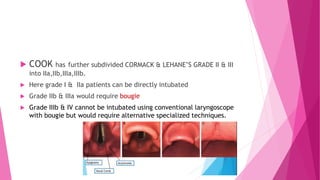
![b.DIRECT LARYNGOSCOPY
CORMACK & LEHANE grading
Grade I : FULL APERTURE IS VISIBLE [A]
Grade II : LOWER PART OF CORDS VISIBLE [B]
Grade III : ONLY EPIGLOTTIS VISIBLE [C]
Grade IV : EPIGLOTTIS NOT VISIBLE [D]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-48-320.jpg)


![2.BENUMOF’S 11 PARAMETER ANALYSIS:
PARAMETER MINIMUM ACCEPTABLE VALUE
1.BUCK TEETH( overriding of maxillary
teeth on the mandibular teeth) NO OVERRIDING.
2. LENGTH OF UPPER INCISORS <1.5cm
3. INTER-INCISOR GAP >3cm
4. PALATE CONFIGURATION NO ARCHING/NARROWNESS
5. MALLAMPATI CLASS CLASS II OR LESS
6.VOLUNTARY PROTRUSION OF MANDIBULAR
TEETH ANTERIOR TO MAXILLARY TEETH MANDIBULAR TEETH PROTRUDED BEYOND
MAXILLARY TEETH
7. TM DISTANCE >5cm
8. SUBMANDIBULAR SPACE COMPLIANCE SOFT TO PALPATION
9.NECK THICKNESS QUALITATIVE [>33cm DI]
10.LENGTH OF NECK >8cm
11. HEAD/NECK MOVEMENT SNIFFING POSITION( HEAD
EXTENSION 85 DEGREES & NECK FLEXION 35
DEGREES)
4-2-2-3 RULE
4STEPS ON TEETH [1,2,3,6]
2 STEPS INSIDE MOUTH[4,5]
2 STEPS FOR MANDIBULAR SPACE]
3 STEPS IN NECK EXAMINATION
[9,10,11]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airwayassessmentfinal-230420192635-c29bc049/85/AIRWAY-ASSESSMENT-FINAL-pptx-56-320.jpg)