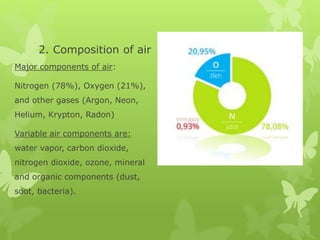
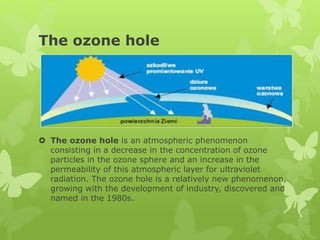
The document discusses air pollution in Poland. It begins by stating that environmental protection starts locally, in one's home and daily activities. It then provides details on the composition of air and sources of natural and anthropogenic air pollution. A major source of pollution in Poland is low emissions from the 3 million boilers and stoves used for home heating, as coal burned in them often contains impurities and standards are lacking. This causes widespread smog. The effects of air pollution discussed include smog, the greenhouse effect, acid rain, and the ozone hole. Poor air quality is a serious problem in Poland, with 36 of Europe's 50 most polluted cities located there. Reducing pollution from home heating will be an important step