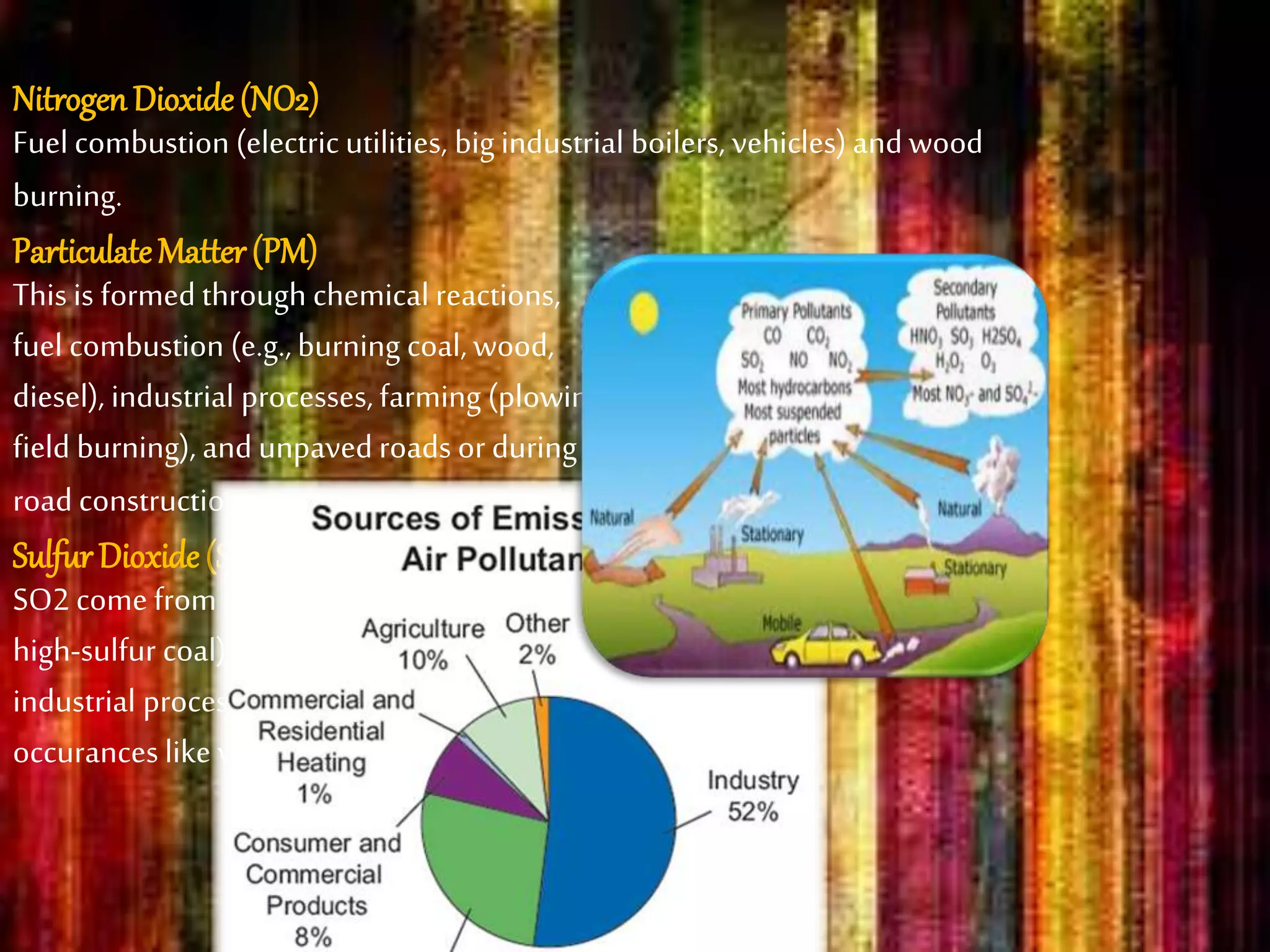
This document discusses air pollution, its causes, effects, and ways to reduce it. It defines air pollution as gases, dust, fumes or odors introduced into the atmosphere that harm humans, animals and plants. Major sources of air pollution are emissions from industries, vehicles burning fossil fuels, and household chemicals. Air pollution can acidify rain and harm aquatic life, and particulate matter causes respiratory and cardiovascular issues. Both government policies and individual actions, like using less energy and driving less, can help reduce air pollution.