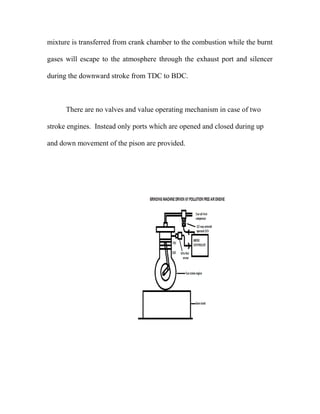
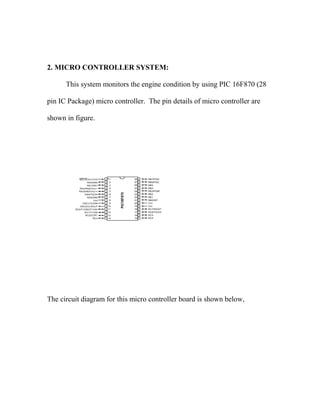
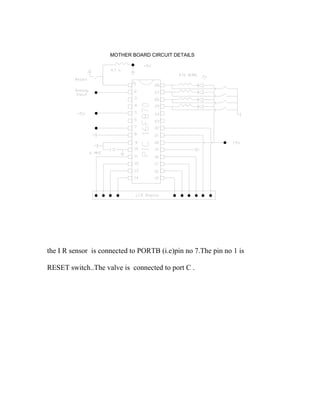
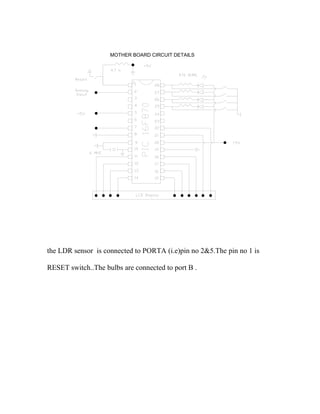
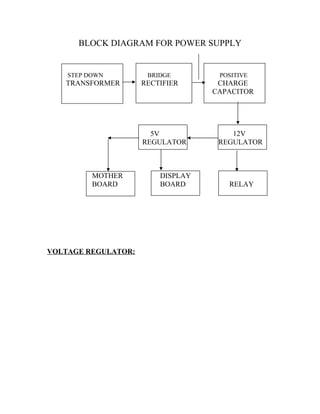
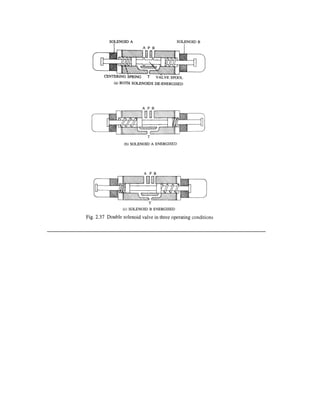
The document describes the fabrication of an air engine as a student project submitted for a diploma in mechanical engineering. It includes a cover page listing the six students who worked on the project under the guidance of their professor. It also includes typical sections like an introduction, synopsis, construction details, working principle, electrical circuit details, and a conclusion. The project involved modifying a two-stroke engine to run on compressed air instead of fuel, using a microcontroller system to control a solenoid valve that regulates the air flow based on input from an infrared sensor.