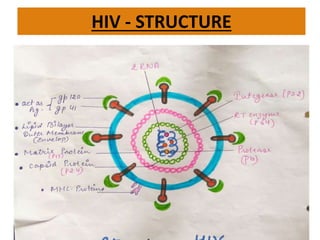
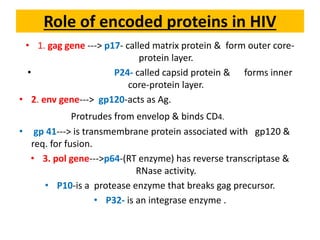
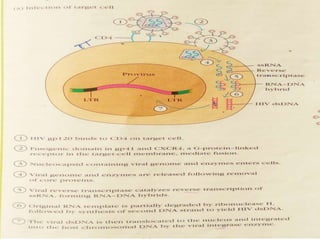
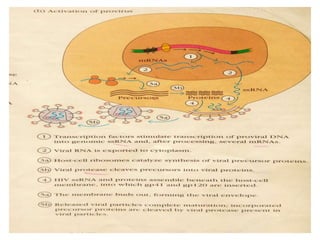
AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) is caused by the HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) which attacks cells of the immune system. HIV was discovered in 1983 by scientists in Paris and Maryland. HIV destroys CD4 cells (T cells) and makes copies of itself, gradually weakening the immune system. HIV is structured with an outer membrane and glycoprotein molecules that help it enter and fuse with host cells. Symptoms of AIDS include weight loss, fever, tiredness and opportunistic infections. HIV spreads through unprotected sex, contaminated needles, from mother to child during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Prevention methods include blood screening, safe sex practices, and not sharing equipment. ELISA and Western Blot tests