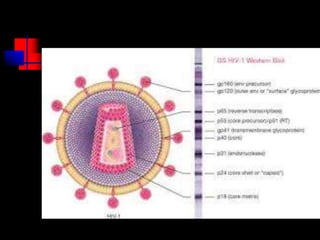
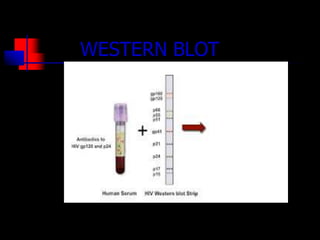
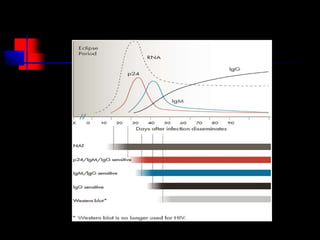
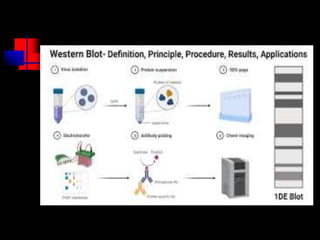
The document summarizes key information about HIV and AIDS, including:
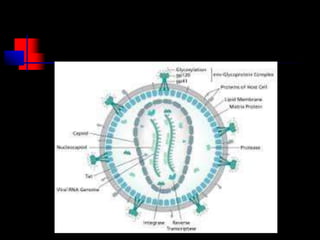
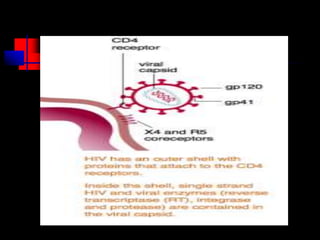
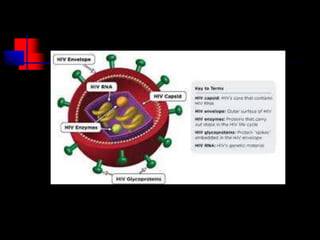
- HIV infects and replicates within CD4 immune cells, weakening the immune system and potentially causing AIDS.
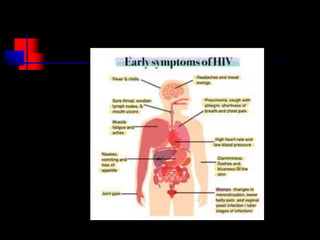
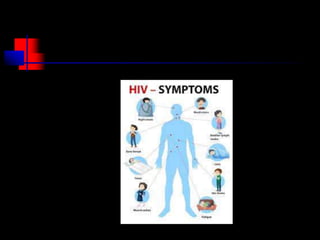
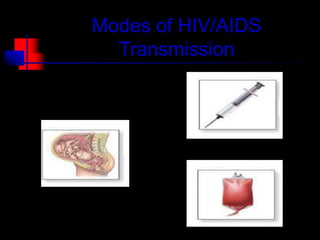
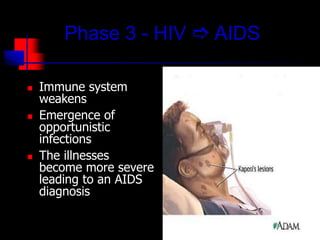
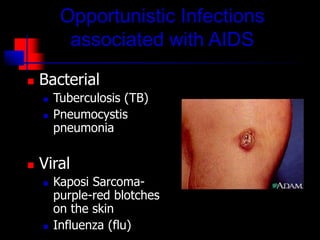
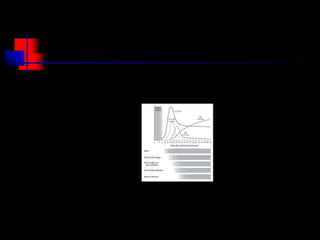
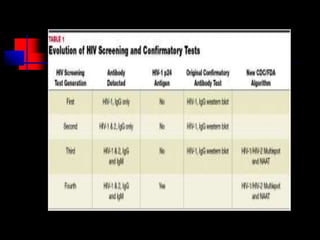
- HIV progresses through three main phases: asymptomatic, symptomatic, and AIDS. It is transmitted through bodily fluids and can be tested for through antibody and viral load tests.
- While there is no cure for HIV/AIDS, treatment involves antiretroviral drugs that target different stages of the HIV lifecycle to suppress viral replication and slow disease progression.