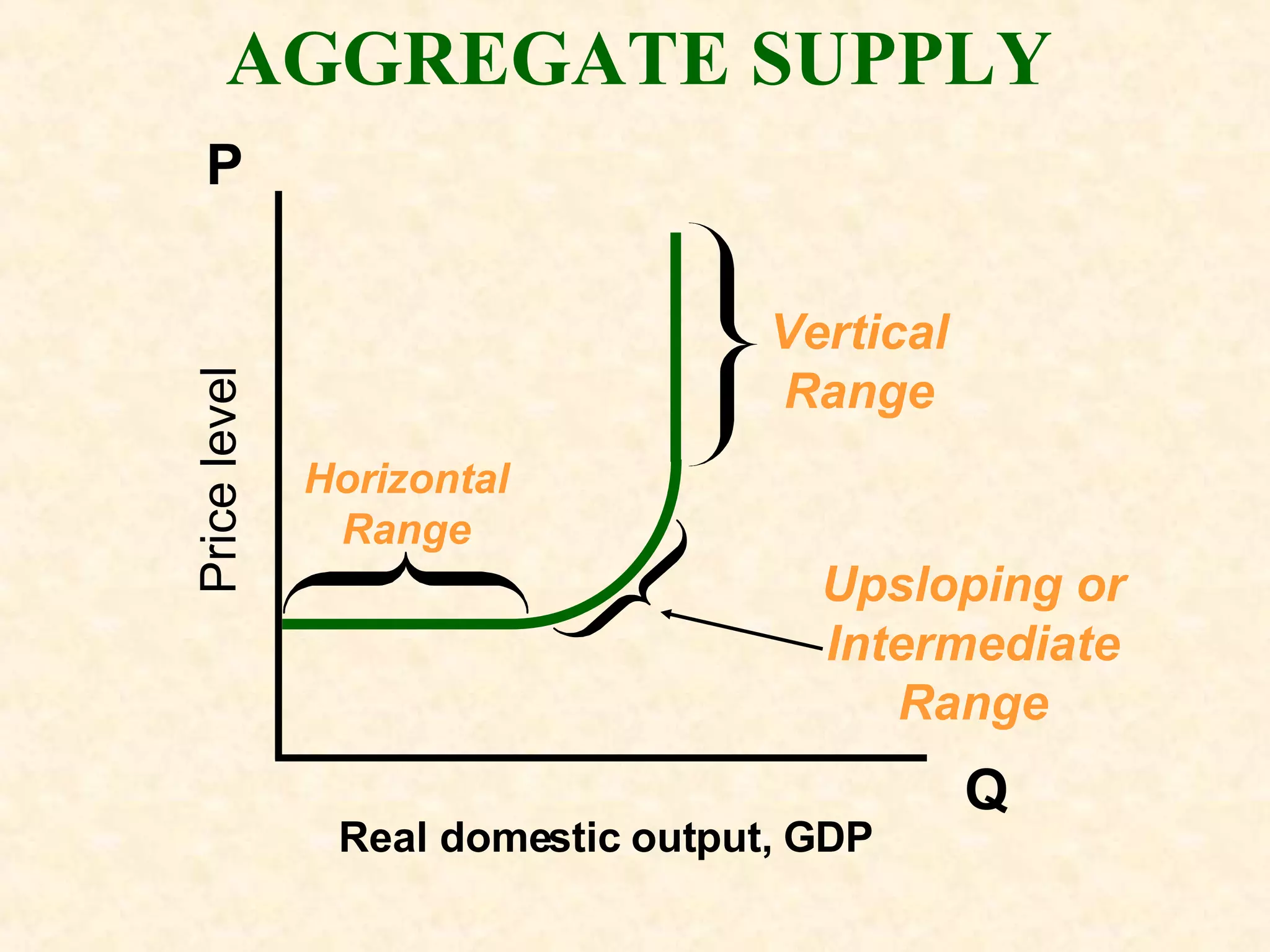
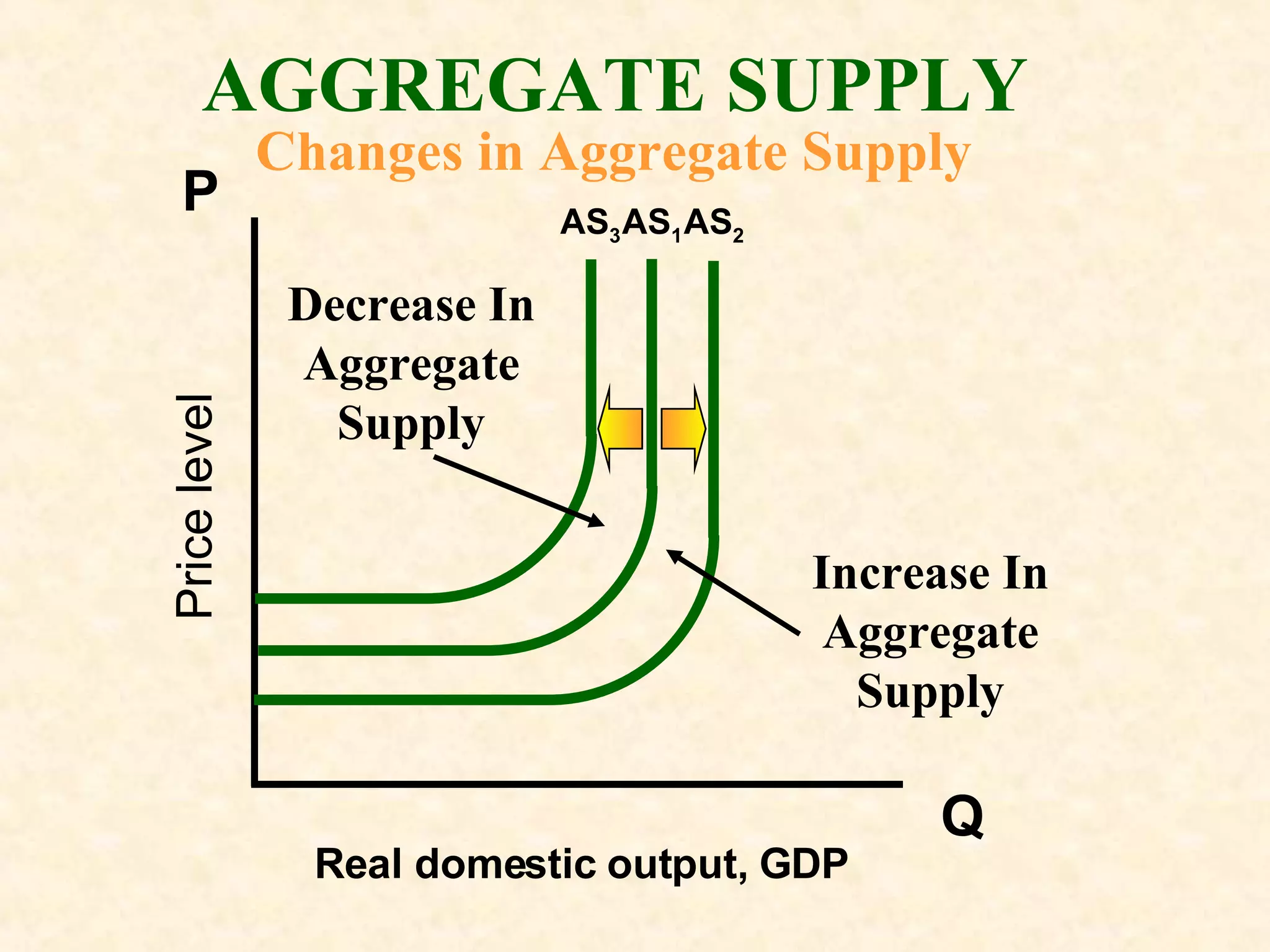
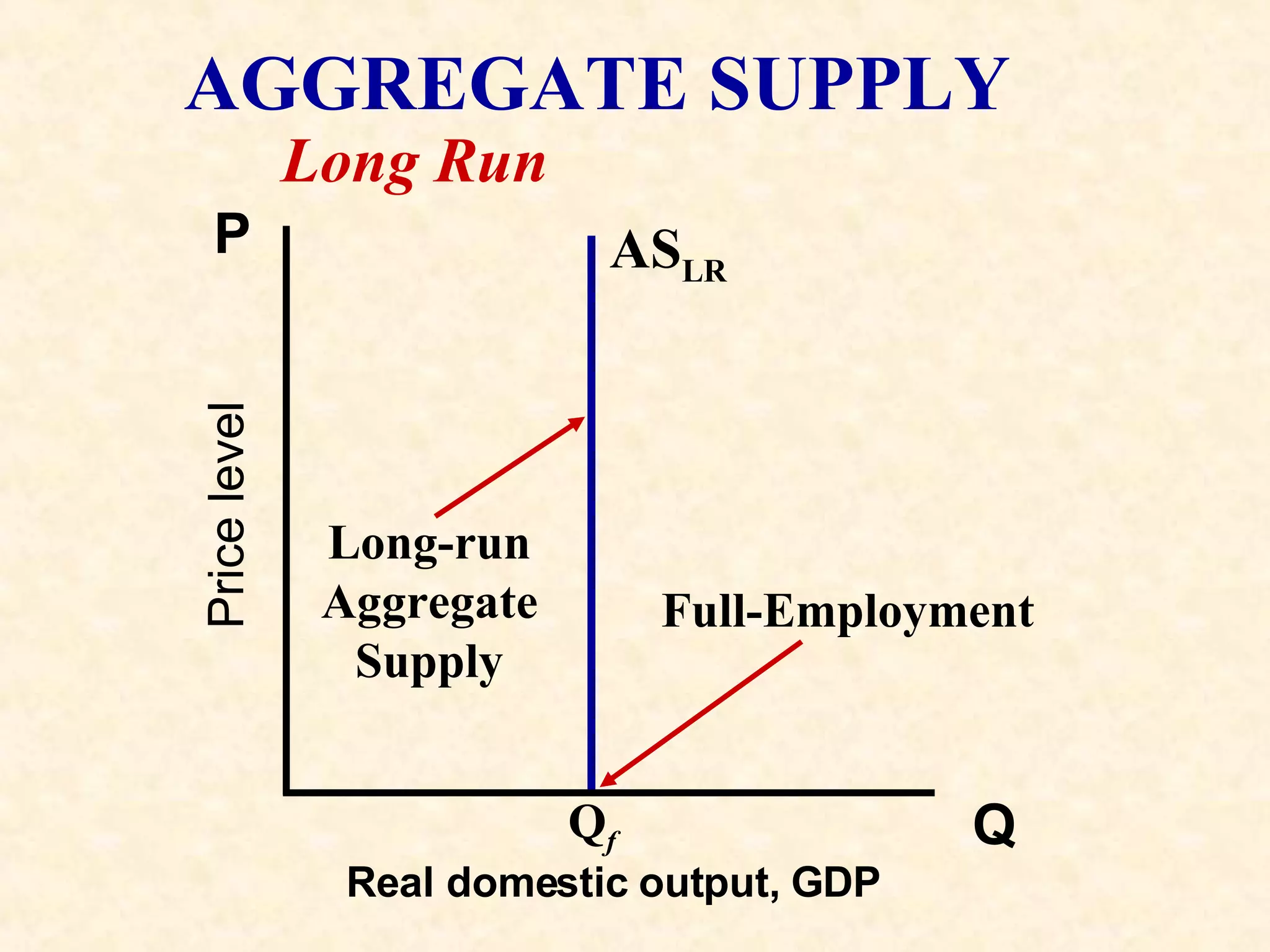
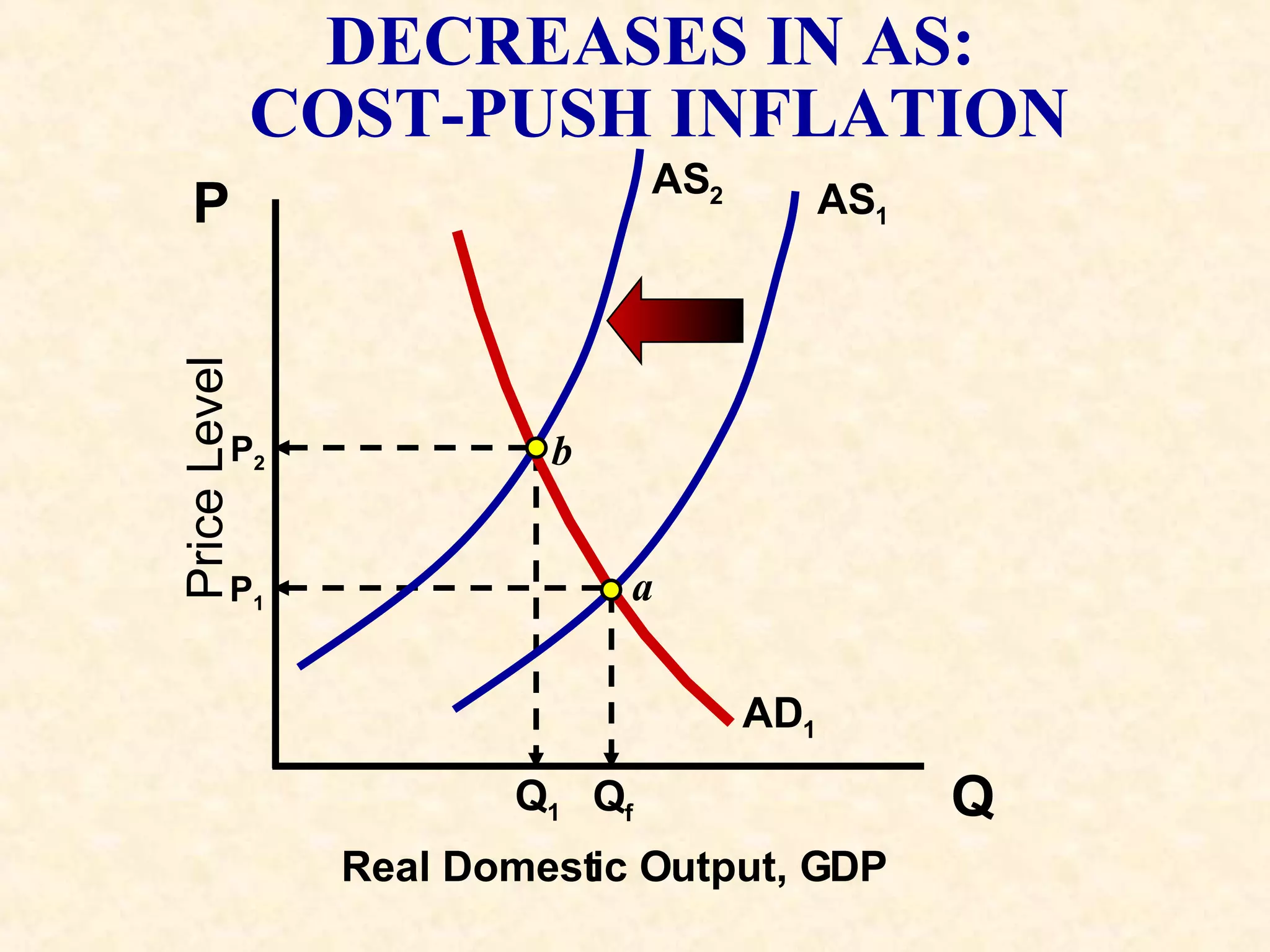
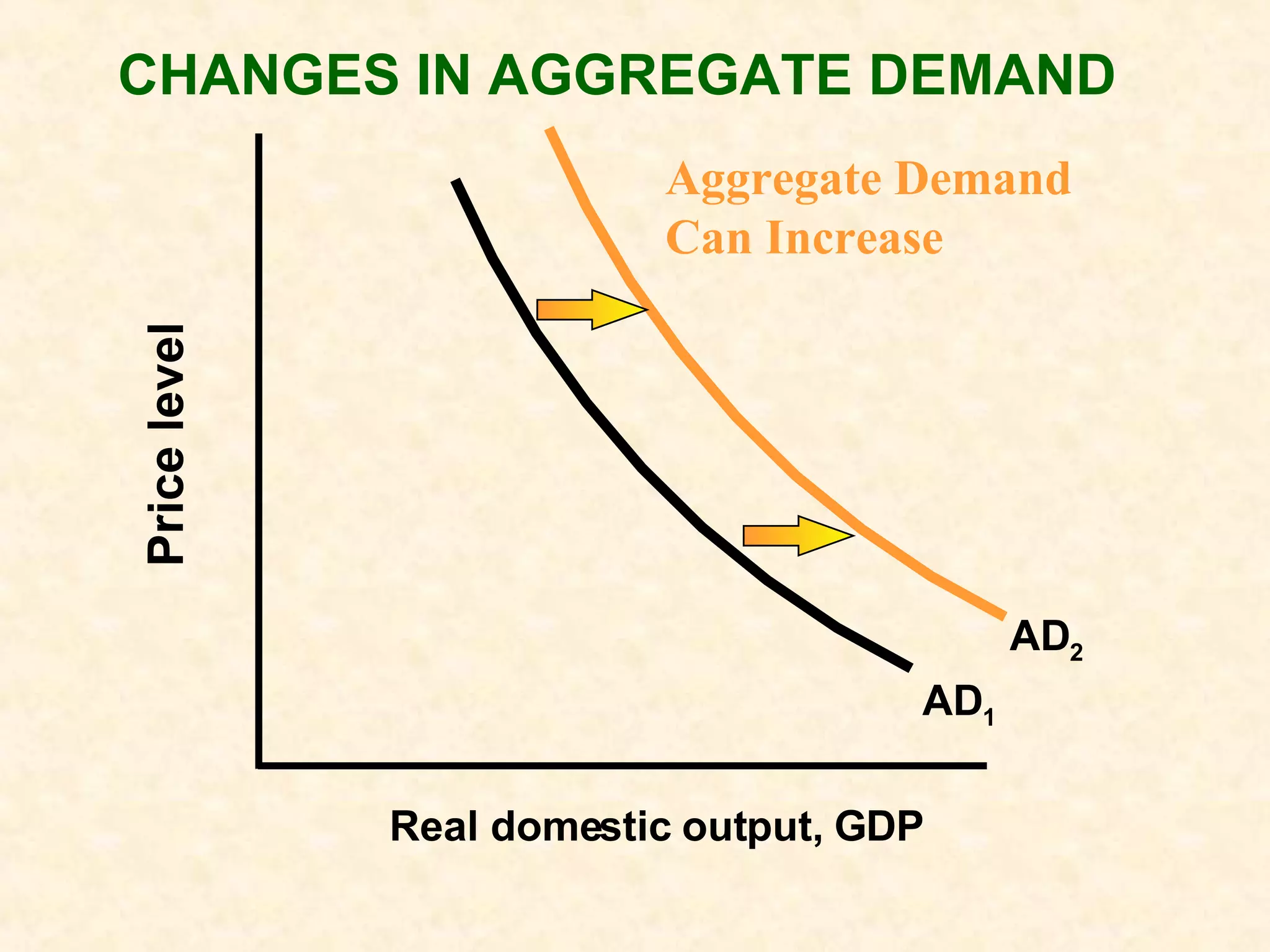
The document discusses aggregate supply and demand. It defines aggregate demand as the total output desired at different price levels, and shows the downward sloping aggregate demand curve. It then discusses factors that can cause aggregate demand to increase or decrease like consumer spending, investment, government spending, and net exports. Aggregate supply is defined as the total output firms will produce at different price levels. It shows three phases of the aggregate supply curve and how productivity, input prices, and other factors can cause shifts in the curve. The document ends by discussing how equilibrium between aggregate supply and demand can change with price levels and real output.







![3 Reasons For Downward Sloping AD Curve Real Money-balances E ffect – economy’s monetary wealth. If we buy a fixed bundle of goods & services (food/clothing/shelter), at lower prices, it now takes less money. Our accumulated savings balances [401k, CDs, bonds] will purchase more. AD Interest Rate Effect – lower interest rates increase investment and consumption. Foreign Purchase Effect – with lower U.S. prices, both Americans and foreigners buy more American goods. Market Basket PL 1 PL 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aggregate-supply-demand-1204225937658602-3/75/Aggregate-Supply-Demand-9-2048.jpg)