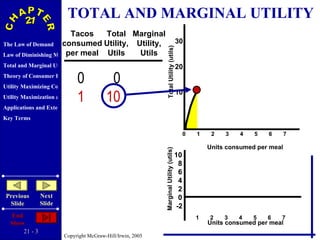
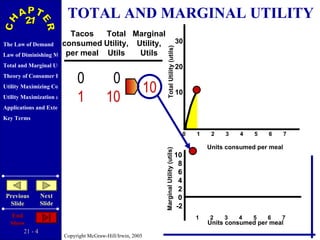
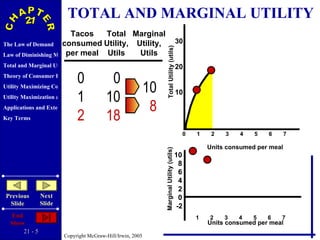
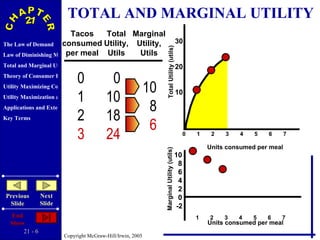
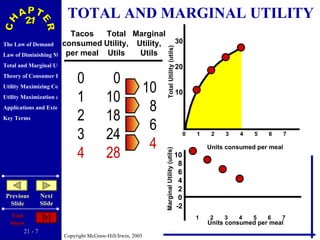
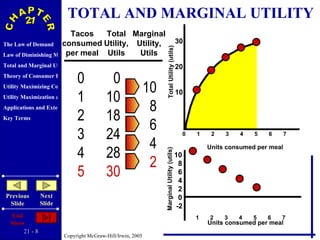
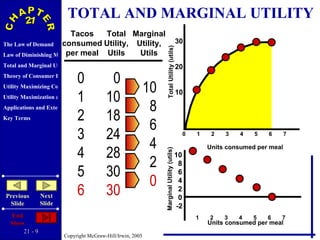
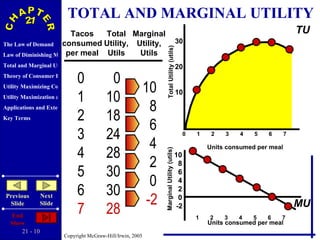
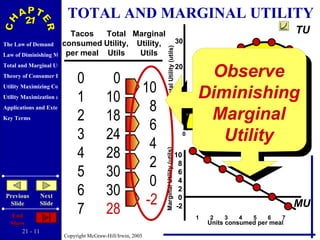
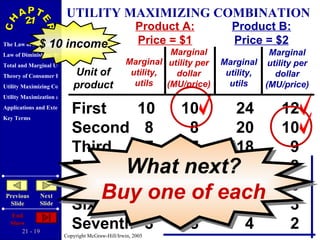
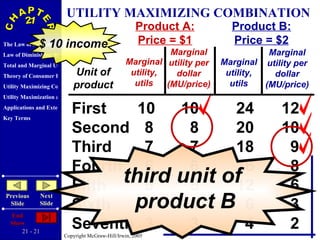
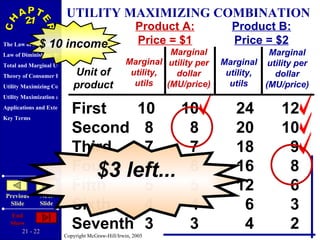
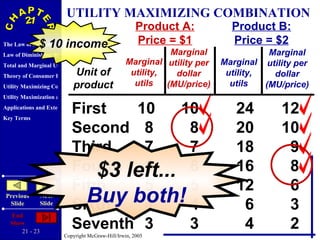
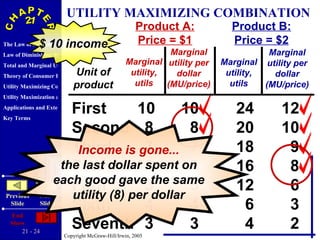
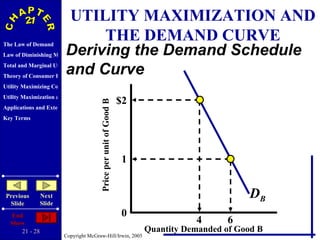
The document discusses concepts related to consumer behavior and utility maximization. It provides examples of how consumers will allocate their budget to maximize total utility based on the principles of marginal utility and diminishing returns. When the price of a good changes, consumers will alter their consumption through income and substitution effects to stay on the highest indifference curve permitted by their new budget constraint. Graphs and algebraic representations are used to derive the demand schedule and demand curve from utility-maximizing choices.