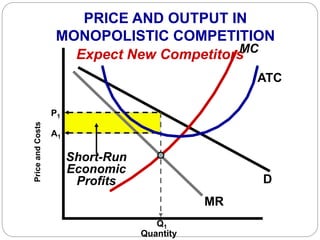
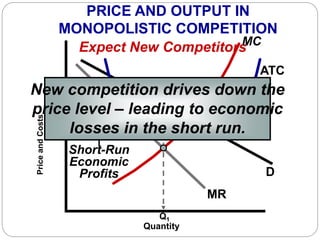
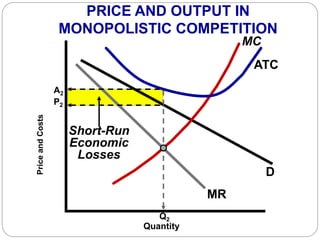
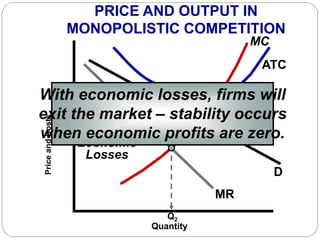
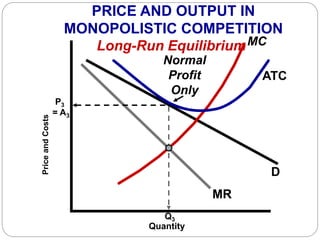
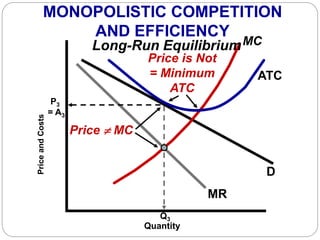
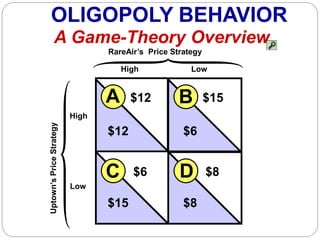
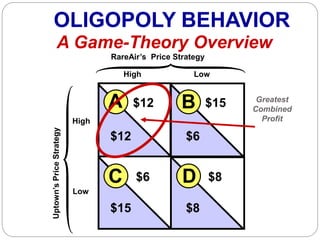
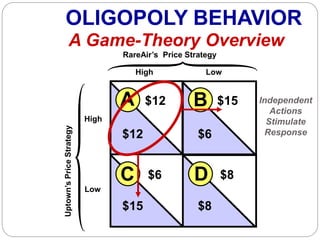
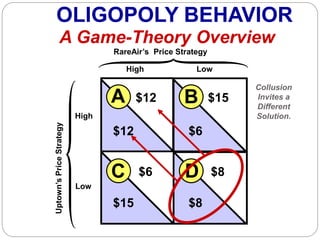
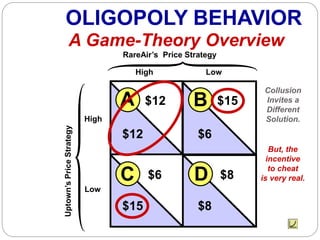
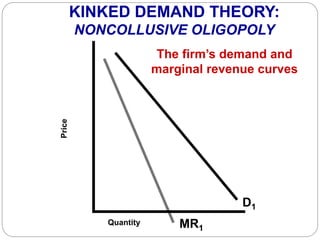
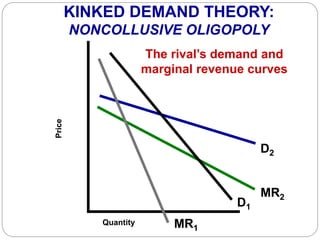
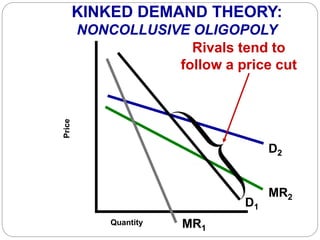
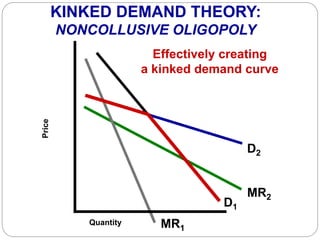
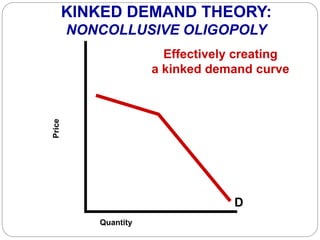
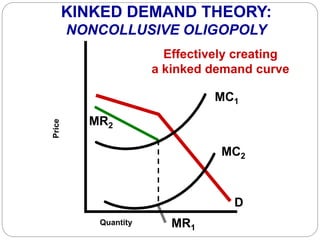
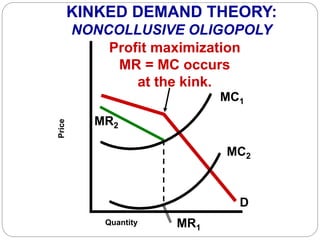
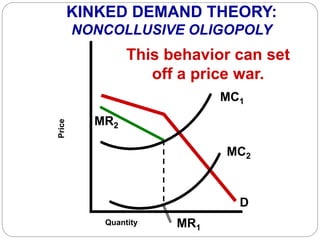
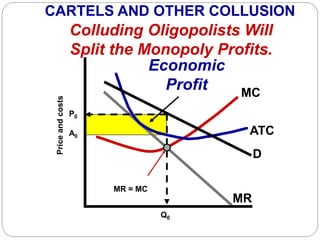
This document summarizes key concepts about monopolistic competition and oligopoly market structures. It discusses how monopolistic competition involves a relatively large number of sellers offering differentiated products, with easy entry and exit into the market. Firms have some control over price in the short run but experience zero economic profits in the long run. The document also describes how oligopolies have a small number of large producers offering either homogeneous or differentiated products, with strategic interdependence between firms. Oligopolies can involve collusion, price leadership, or noncooperative behavior modeled using game theory.