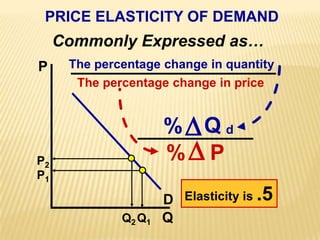
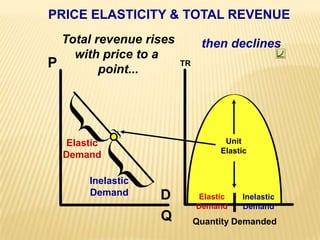
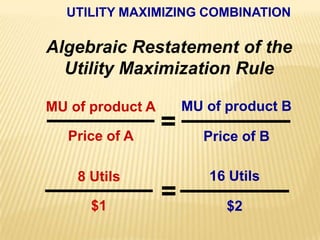
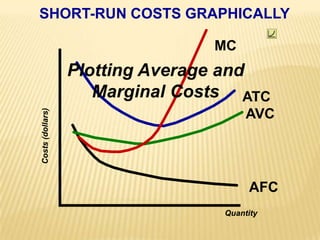
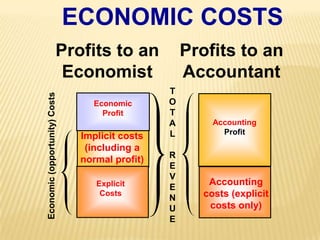
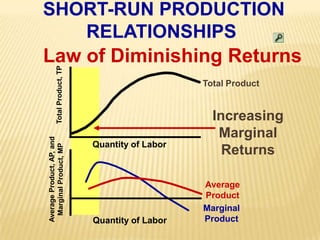
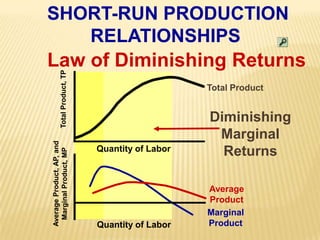
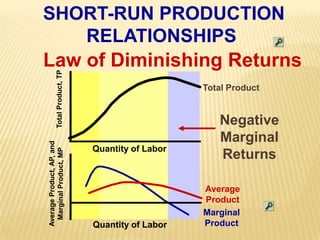
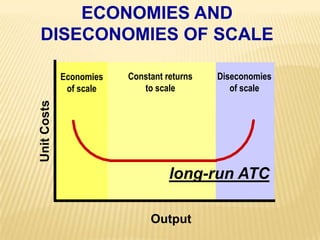
1. The document covers various microeconomics concepts including price elasticity of demand, production costs, profit maximization, market structures, and resource markets.
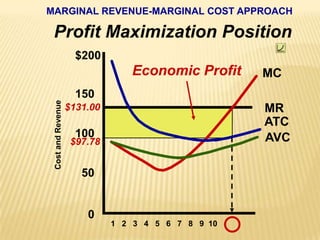
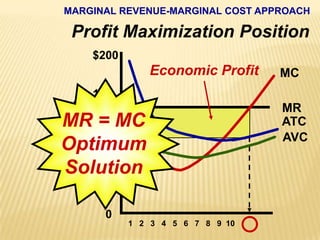
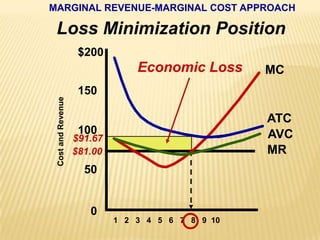
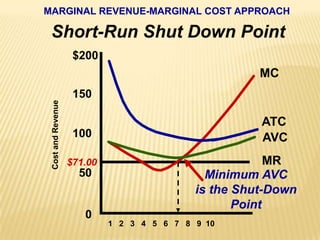
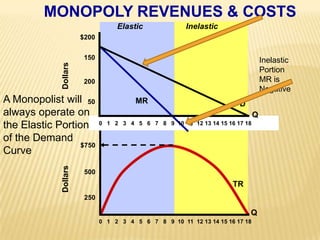
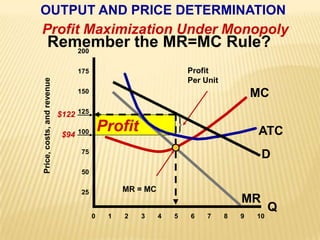
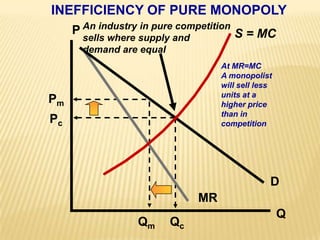
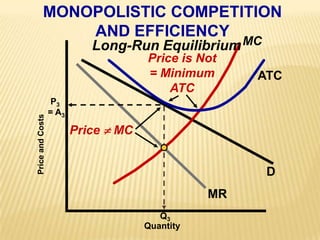
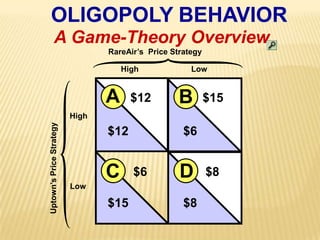
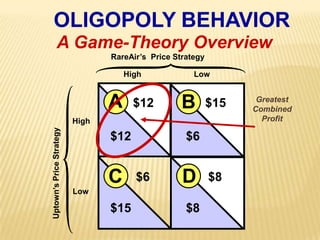
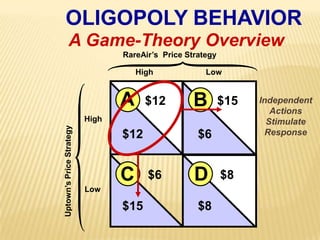
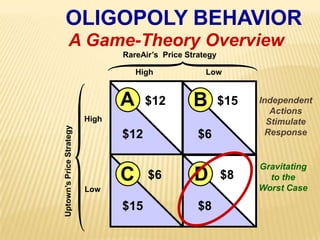
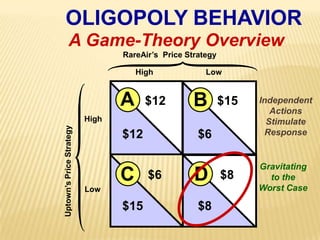
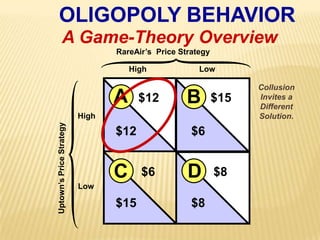
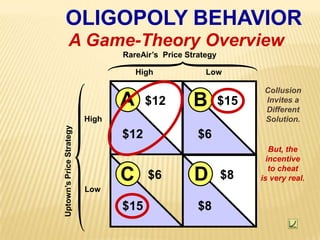
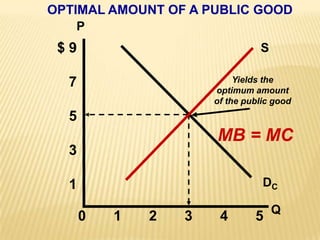
2. Key graphs show the relationships between marginal revenue and marginal cost in determining profit-maximizing output for different market structures like perfect competition, monopoly, and oligopoly.
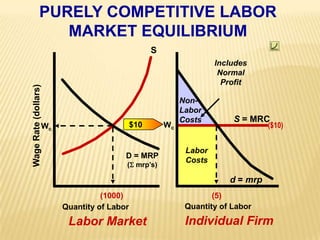
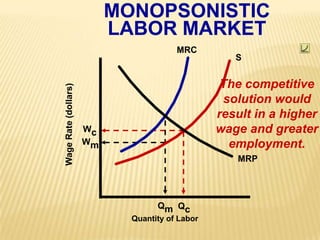
3. Labor market graphs illustrate the equilibrium wage rate and employment level under conditions of perfect competition and monopsony.