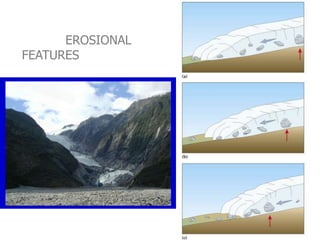
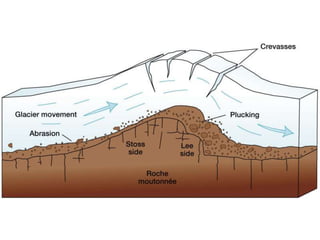
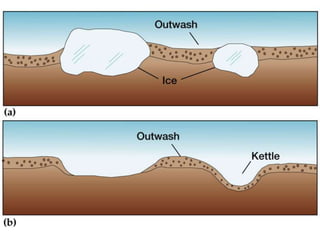
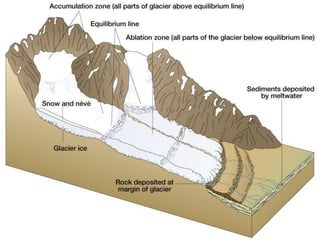
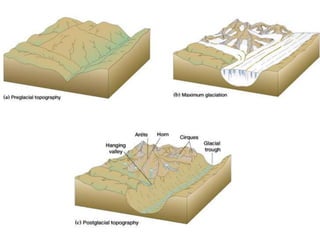
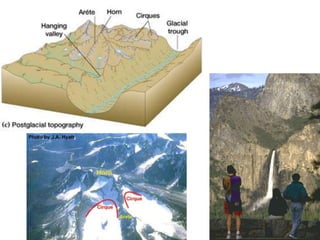
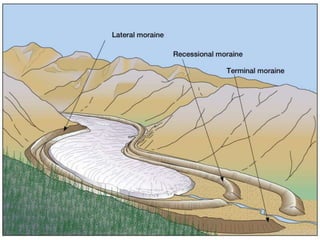
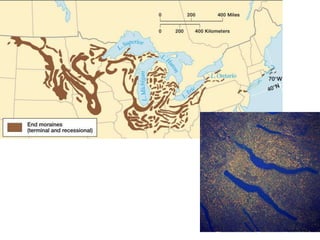
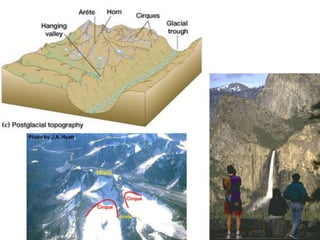
This document discusses glaciers and their landforming effects. It begins by defining what a glacier is, how they form from accumulated snow, and their two main types - continental and alpine. It then describes how glaciers erode the landscape through plucking and abrasion, polishing rock surfaces and creating U-shaped valleys. Glaciers also deposit material directly as till or in linear landforms like moraines. Examples are given of continental ice sheets that reshape entire regions and of deposition features like outwash plains and erratic boulders left by retreating glaciers. Links are provided to learn more about computers on YouTube and for computer classes.