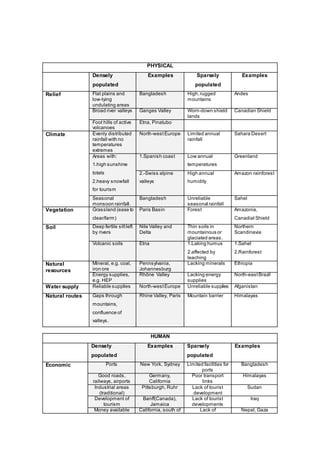
- Population change is determined by the balance between birth and death rates, and is affected by migration. Throughout history, population has generally increased except during times of war, disease, or improved family planning/education.
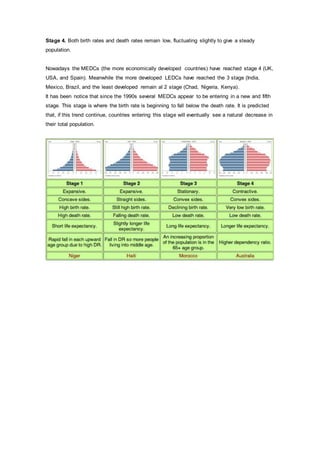
- The demographic transition model describes 4 stages of population growth: Stage 1- high birth/death rates with small growth; Stage 2- falling death rates with rapid growth; Stage 3- falling birth rates with slow growth; Stage 4- low/stable birth/death rates with steady population. More developed countries are in Stage 4 while less developed are in Stages 2-3. Some countries may now be entering a Stage 5 of falling populations.