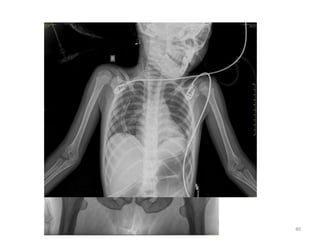
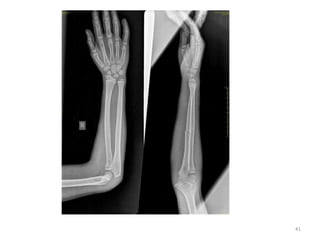
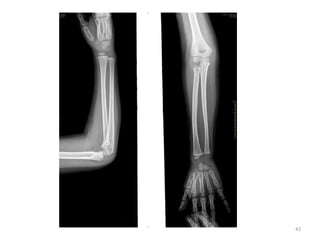
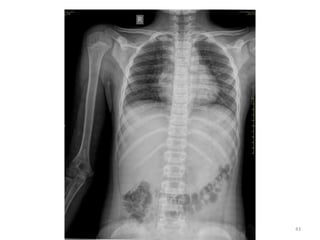
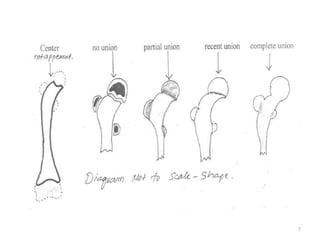
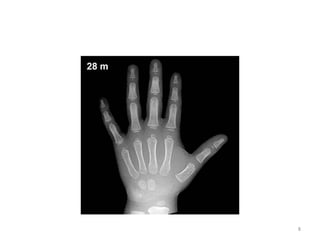
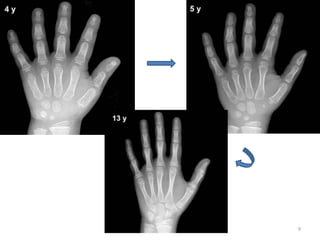
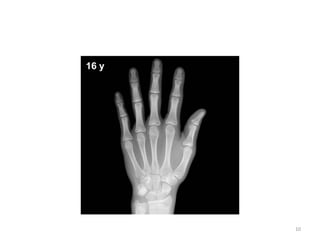
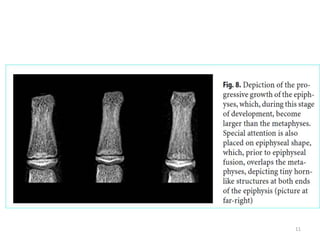
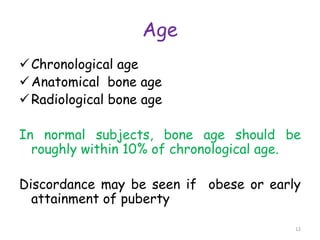
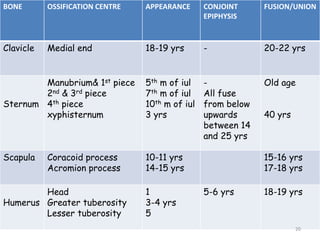
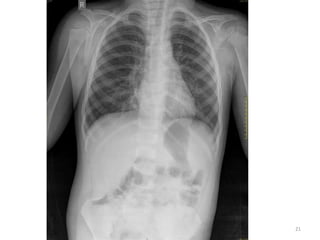
The document discusses the estimation of bone age through radiography, outlining the process of ossification and the importance of understanding skeletal age for both clinical and forensic applications. Different methods of age estimation, including physical, dental, and radiological examinations, are highlighted, as well as specific criteria for evaluating bone ossification centers. It concludes that a combination of multiple criteria should be employed, and further research is necessary in the field.













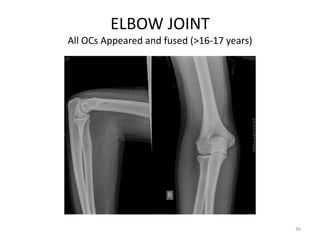
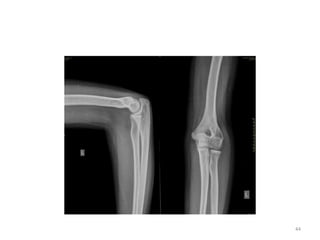
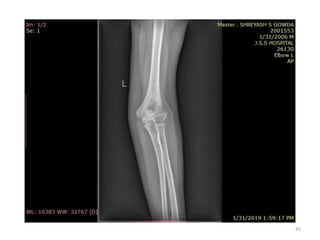
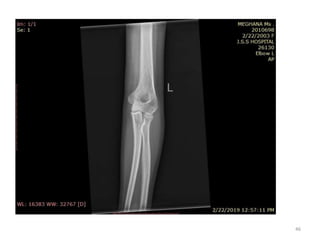
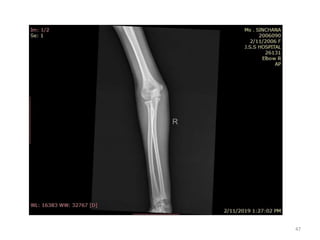
![Elbow joint
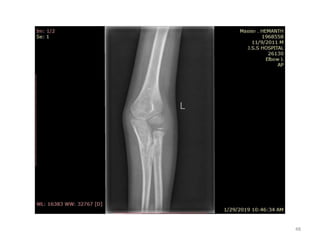
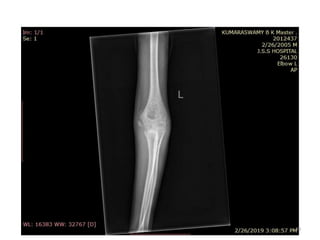
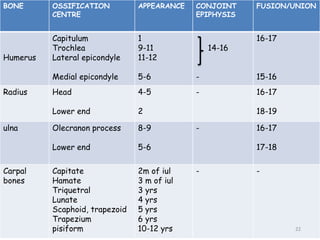
• Secondary ossification Centres : (3 bones; 6 Ocs)
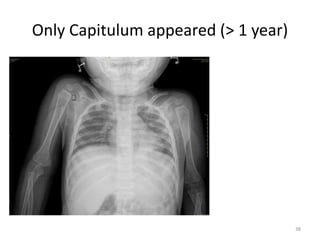
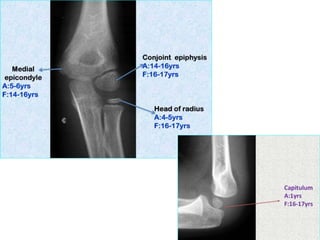
Capitulum (C) - appearance - 1 year of life
Head of Radius (R)– appearance -4 to 5 years
Medial Epicondyle (ME)
Appearance – 5 to 6 years
Fusion – 16 to 17 years
Trochlea (T) – appearance – 9 to 11 years
Olecranon Process of Ulna (OP)
Appearance - 8 to 9 years
Fusion- 16-17 years
Lateral Epicondyle(LE) – 11 to 12 years
Conjoint (Composite)Epiphysis (CE) [fusion of C+T+LE]
Formation – 14 to 16 years
Fusion – 16-17 years
Note: Fusion of O.Centres at elbow joint is 16-17 years in male, 15-16 years in female
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ageestimationbyradiology-mypptatpostings-240619084456-1fb1217b/85/Age-estimation-by-radiological-method-using-X-rays-35-320.jpg)