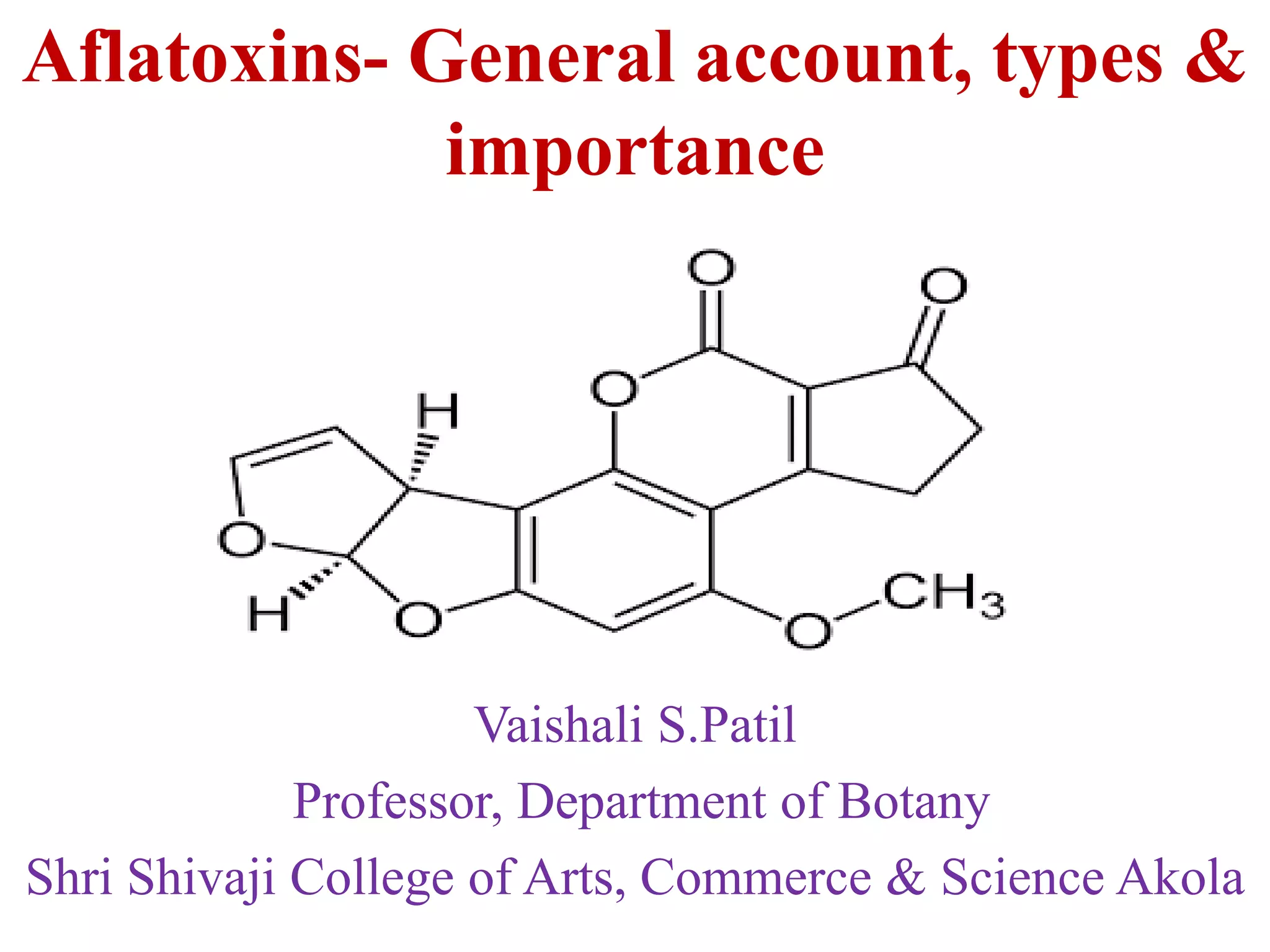
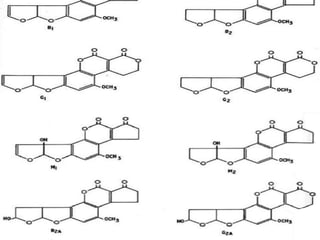
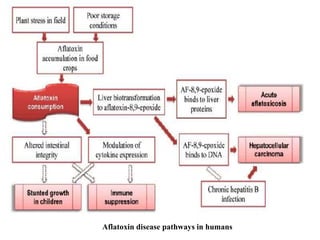
Aflatoxins are toxic and carcinogenic metabolites produced by certain molds that grow on agricultural crops like corn, peanuts and tree nuts. There are several types of aflatoxins including B1, B2, G1, G2, M1, and M2. Aflatoxin B1 is the most toxic and a potent liver carcinogen. Humans can be exposed through consuming contaminated foods or animal products from livestock fed contaminated feed. Chronic exposure has been linked to liver cancer and impaired immune function and childhood exposure stunts growth. Preventing mold growth and proper storage of agricultural crops can help reduce aflatoxin contamination.