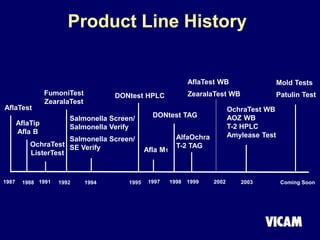
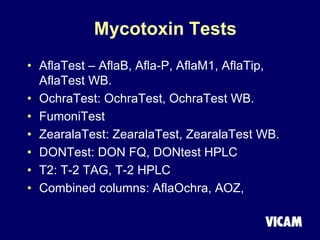
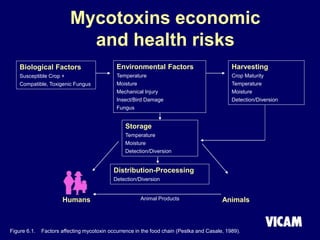
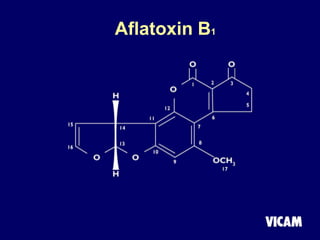
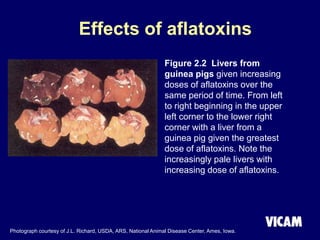
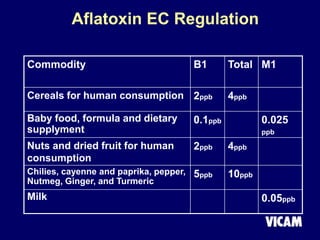
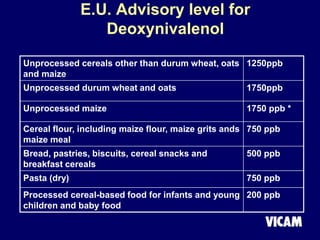
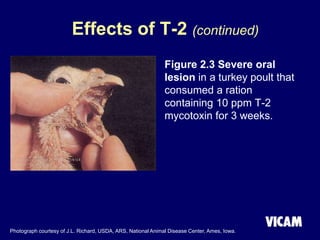
Vicam is a company established in 1985 that develops rapid mycotoxin tests for the food industry. It introduced its first products in 1987 and has since expanded its product lines and global regulatory relationships. The seminar discusses Vicam's history and corporate mission of innovative, high-quality testing. It also provides information on major mycotoxins like aflatoxins, ochratoxin, fumonisins, zearalenone, deoxynivalenol, and T-2; their producing fungi, health effects, regulations limits, and Vicam's tests to detect them.