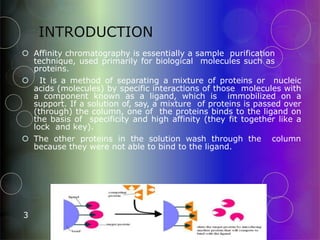
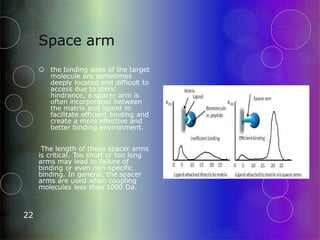
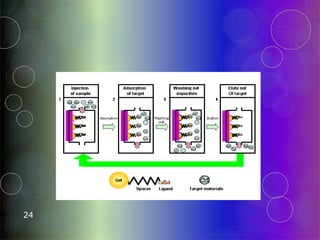
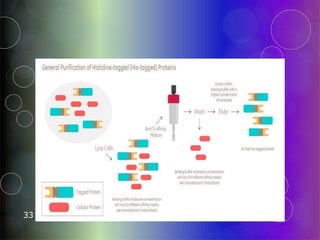
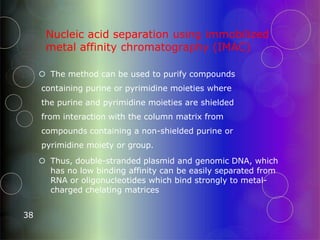
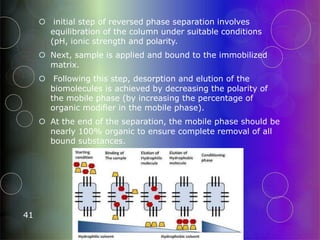
Affinity chromatography is a purification technique that relies on specific, reversible interactions between molecules. It involves immobilizing a ligand that binds selectively to the desired molecule on a support matrix. When a sample mixture passes through the column, the desired molecule binds to the ligand while other molecules pass through. The bound molecule can then be eluted by altering conditions like pH or ionic strength to break the binding interaction selectively. Common applications include purifying antibodies, recombinant tagged proteins, and lectins.