Embed presentation
Download to read offline
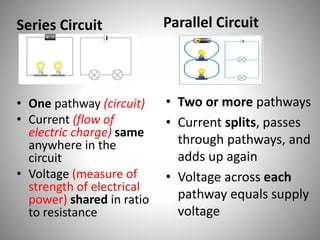
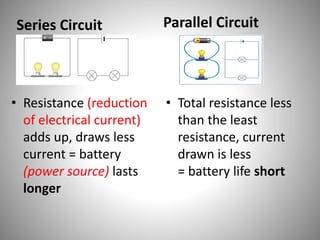
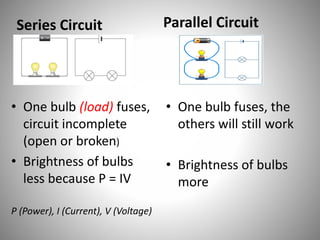

Series circuits have a single pathway where the current is the same everywhere and the voltage is shared proportionally to resistance. Parallel circuits have multiple pathways where the current splits and combines, with each pathway receiving the full supply voltage. Series circuits have higher total resistance and draw less current, extending battery life, while parallel circuits have lower total resistance and draw more current, shortening battery life. A failure in one component of a series circuit breaks the entire circuit, while parallel circuits allow other components to still function if one fails.




