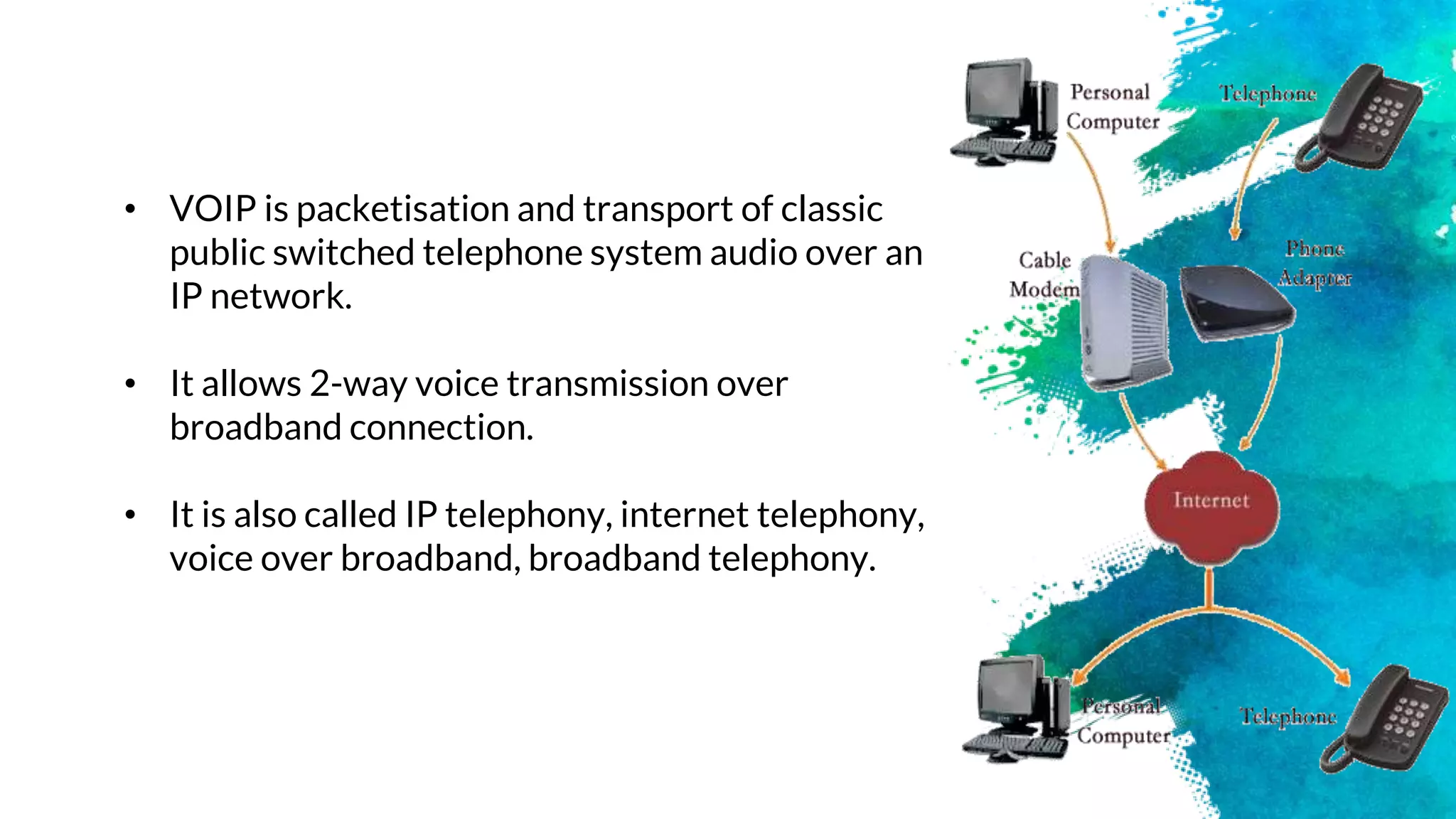
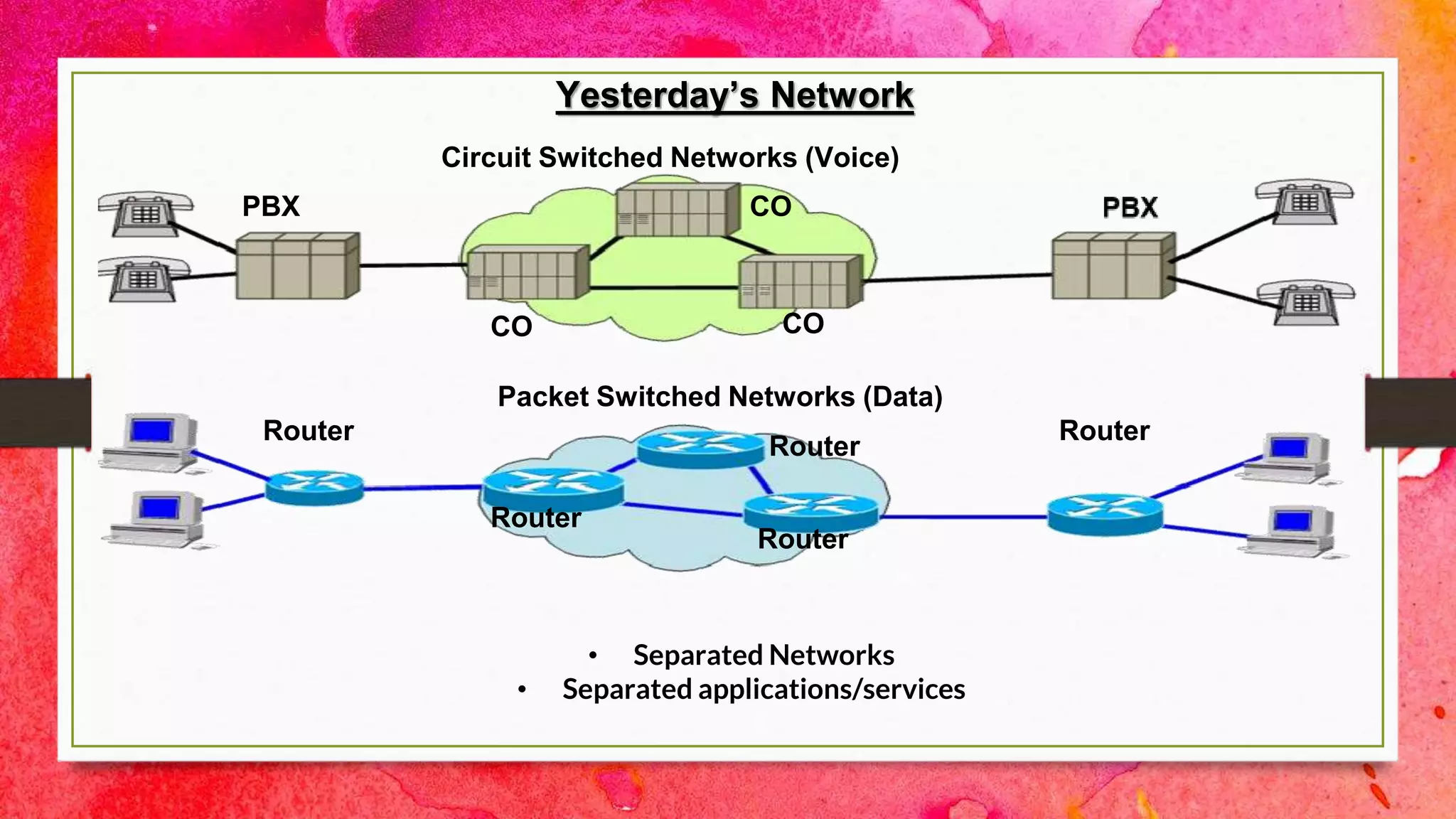
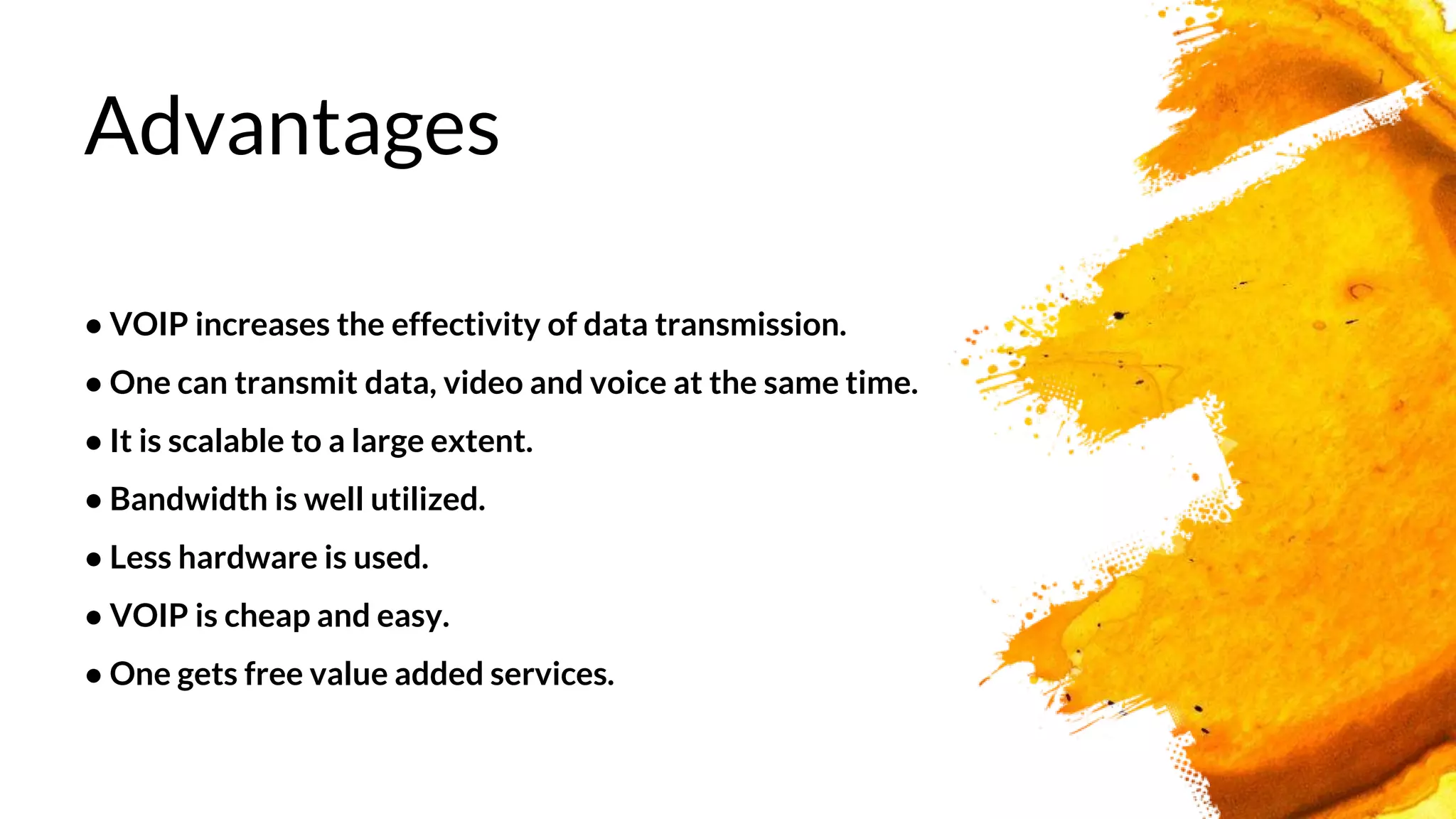
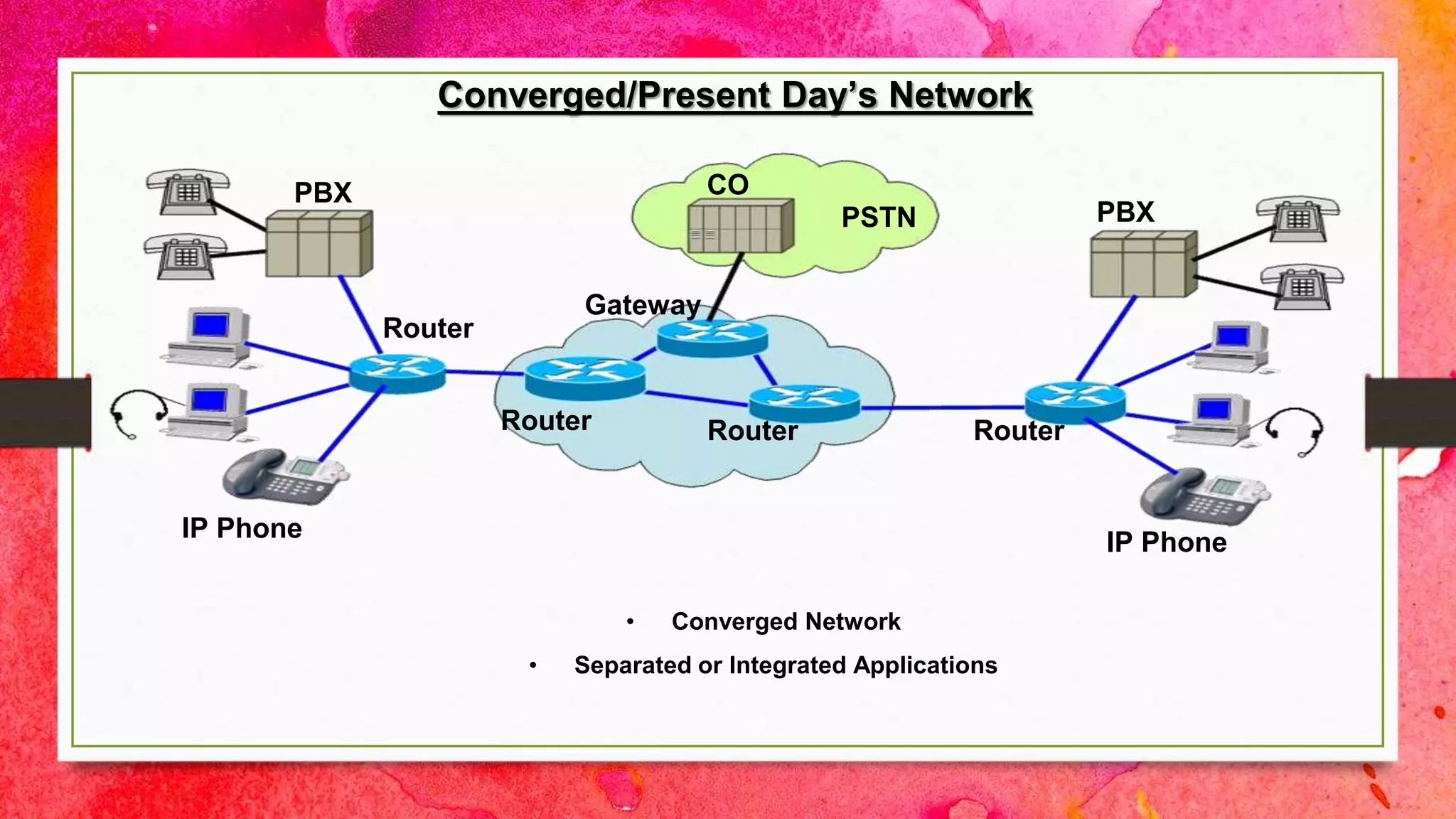
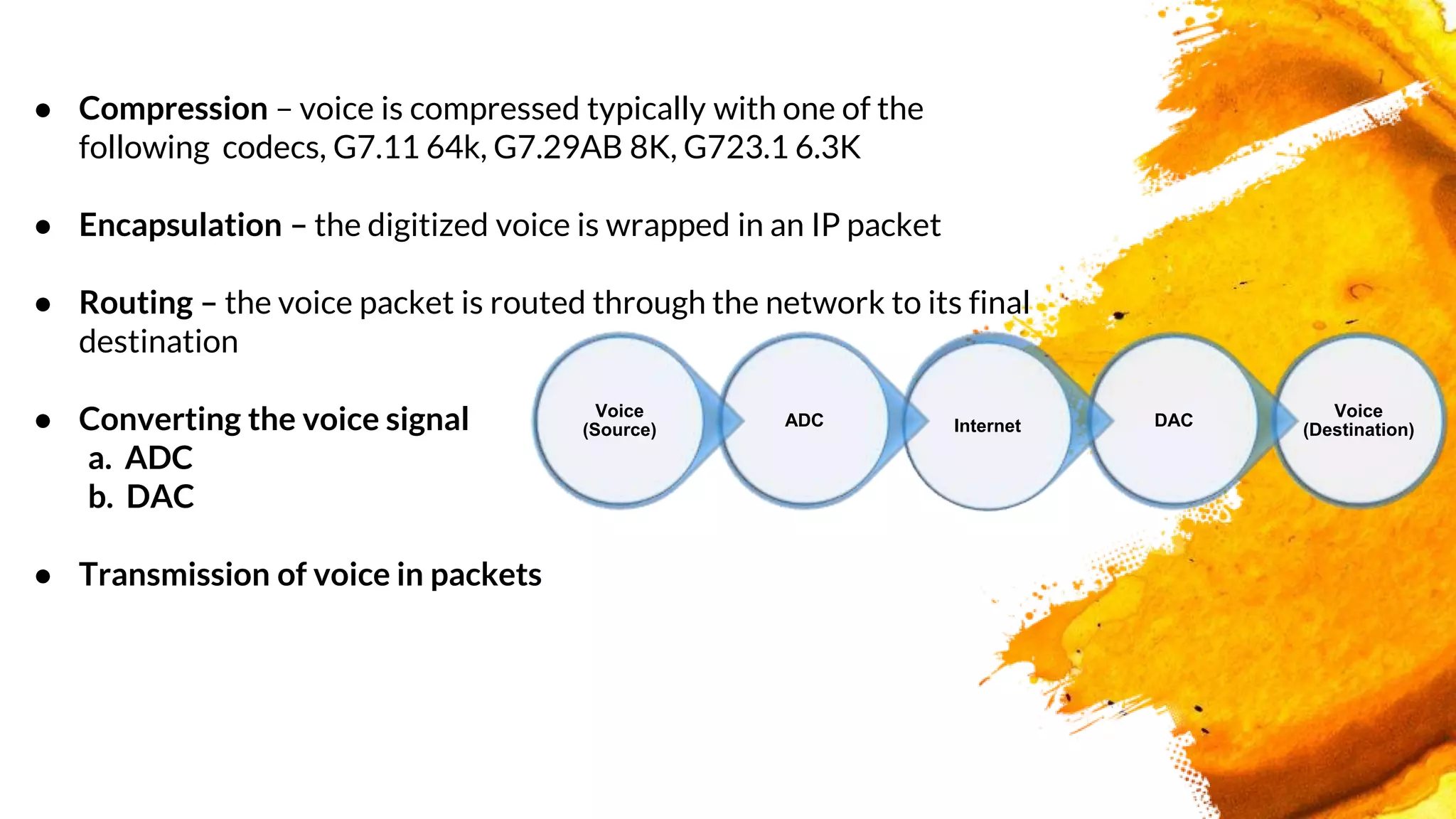
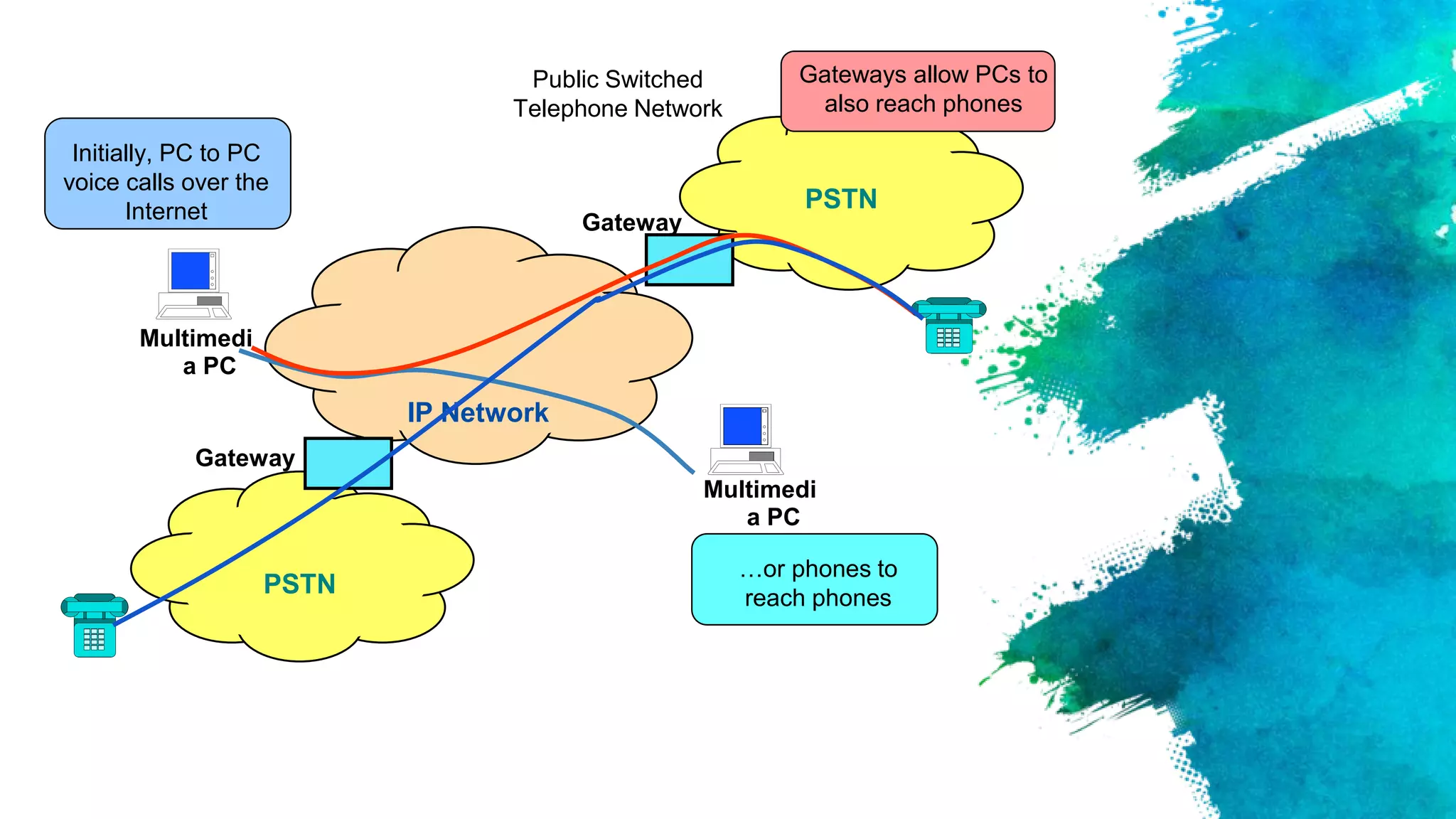
The document introduces a group presenting on Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP). The group members are listed as Akash Bista, Ankur Raj Karn, Arjun Khadka, and Saput Khadka. VOIP allows users to make phone calls over the internet rather than traditional phone lines. It compresses and converts voice signals to digital packets which are then transmitted over the internet. VOIP has advantages over traditional phone lines like lower costs, added features, and ability to transmit voice, data and video simultaneously.