Embed presentation
Downloaded 142 times



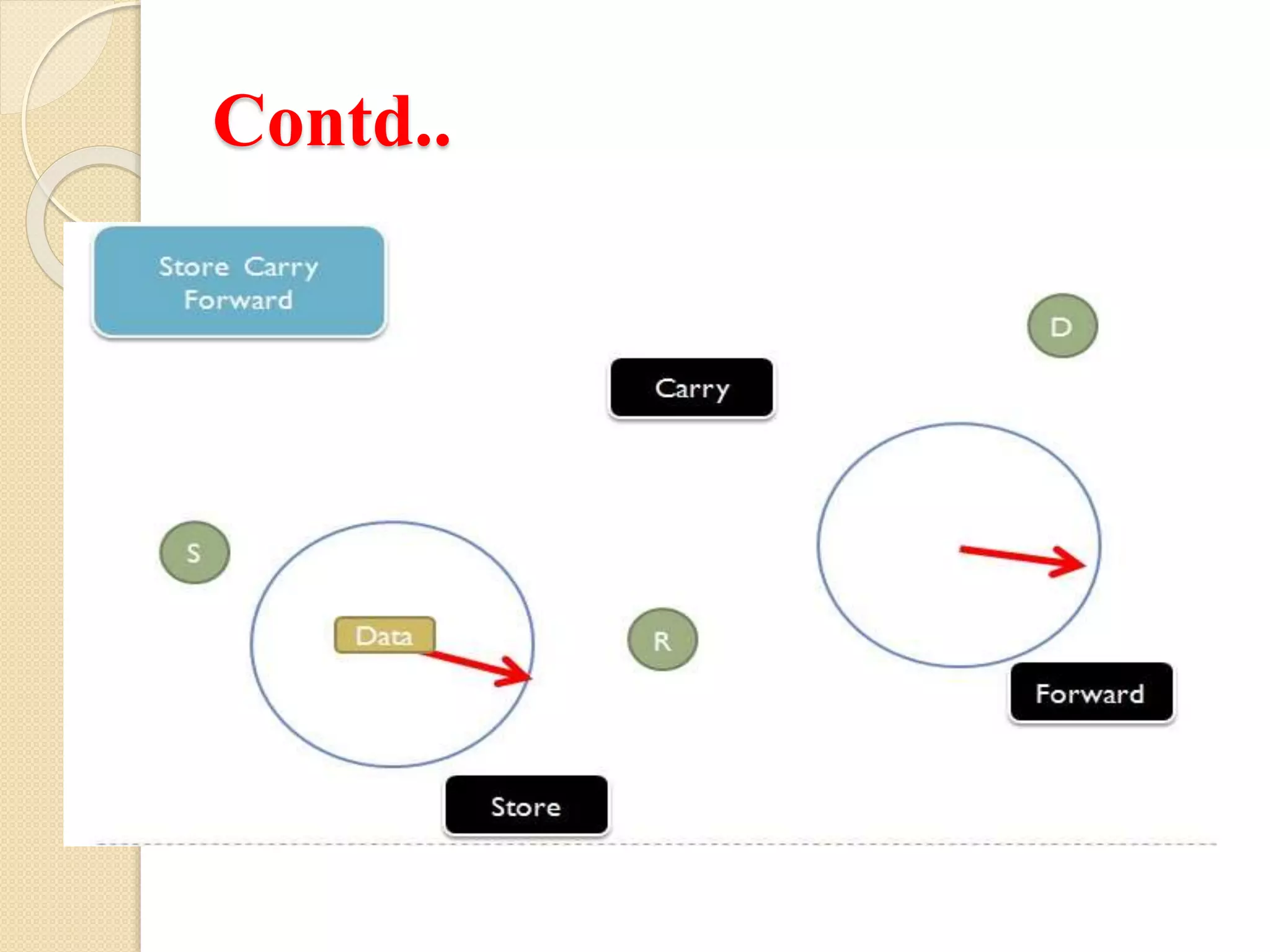




Delay tolerant networks (DTNs) allow communication in networks with intermittent connectivity by using a store-carry-forward approach. DTNs employ a set of protocols that store messages during network disconnections and forward them when connectivity is available. They can provide communication even when end-to-end paths do not exist. Key properties of DTNs include high latency, low data rates, disconnection, long queuing delays, short contact ranges, and dynamic topologies. Potential applications of DTNs include telemedicine in remote areas, social networking, communication under censorship, file sharing, and sharing cellular minutes.
This section introduces Delay Tolerant Networks (DTN), its agenda, purpose, and significance.
DTNs address connectivity issues in heterogeneous networks, enabling communication without end-to-end connectivity through store-carry-forward protocols.
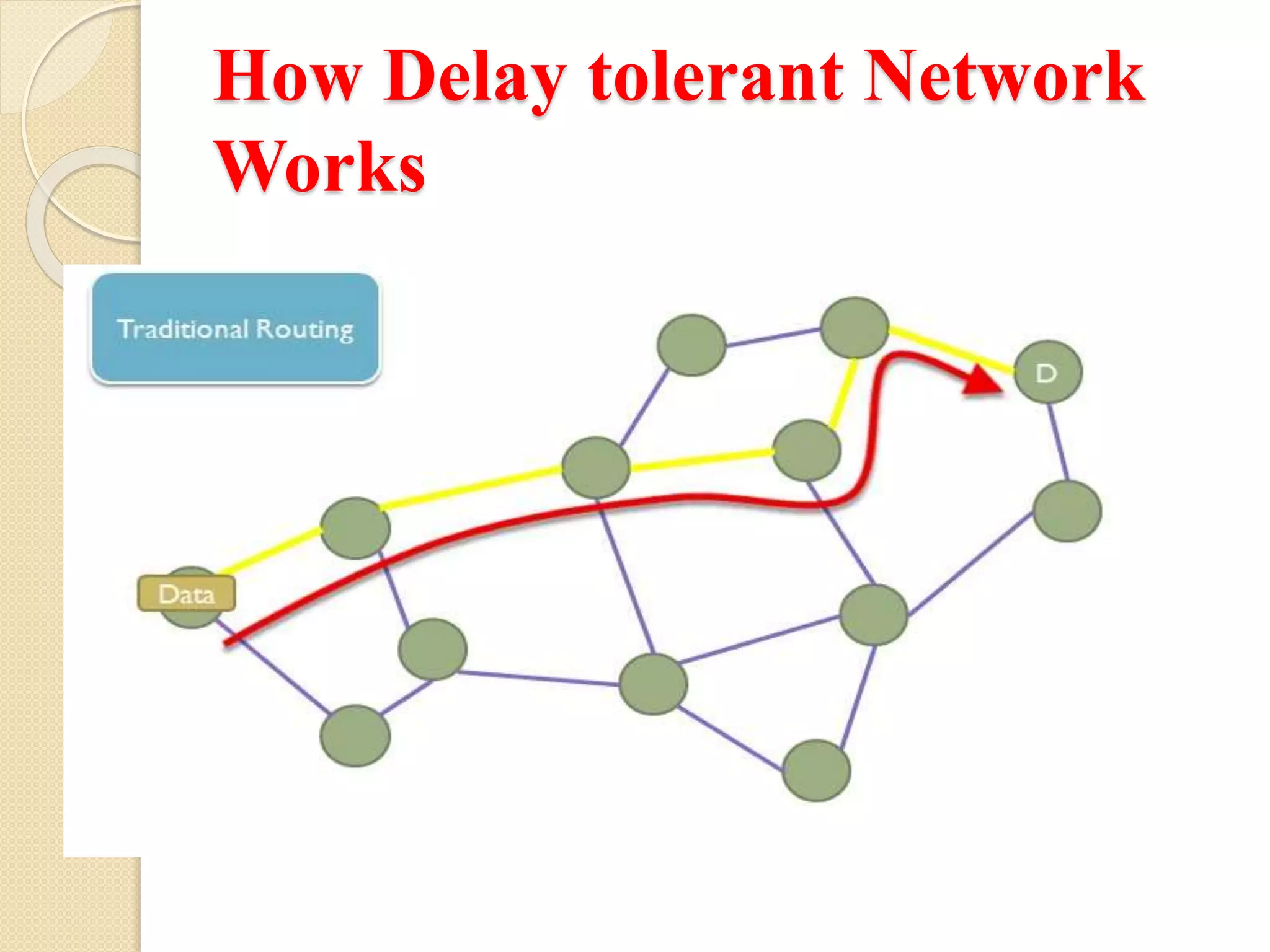
This section explores the operational mechanism of Delay Tolerant Networks, detailing how they function.
Key characteristics of DTNs include high latency, low data rate, disconnection, and dynamic topology.
DTNs feature intermittent connectivity, no end-to-end paths, and dynamic routing methods involving redundancy and topology information.
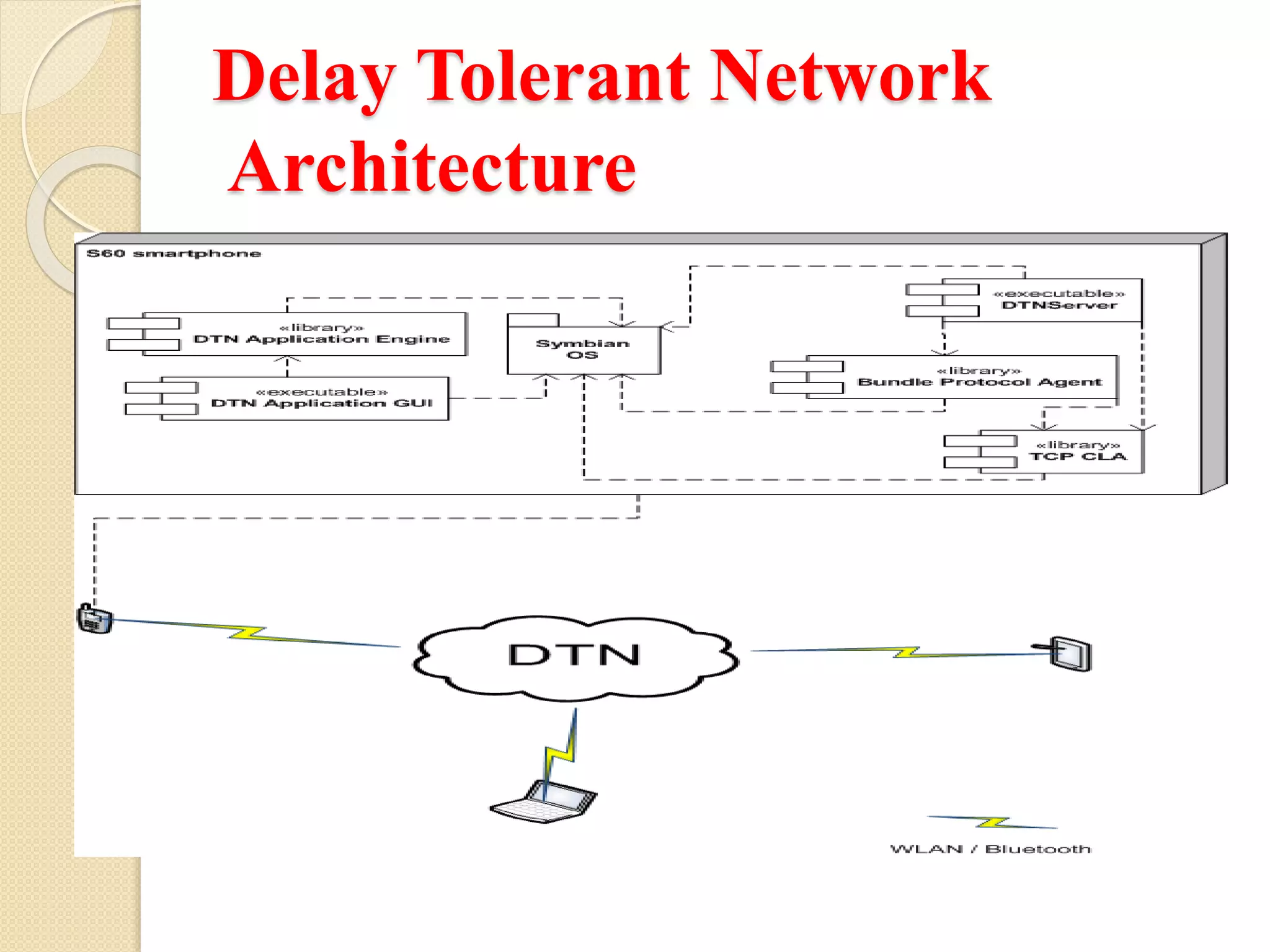
Discussion on the architecture that supports the functioning of Delay Tolerant Networks.
DTNs have diverse applications in telemedicine, social networking, oppressive environments, data transfer, and communication services.









