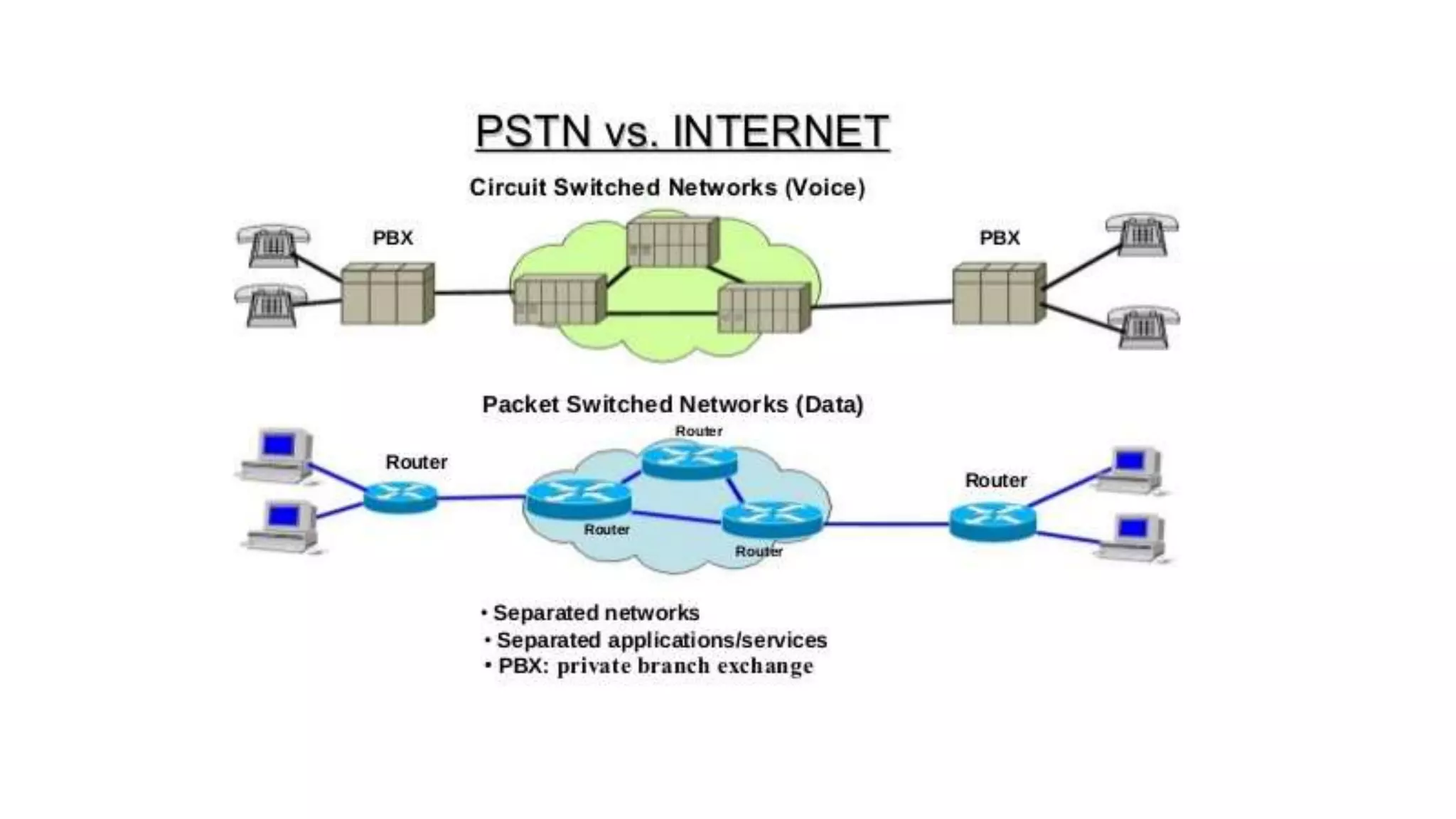
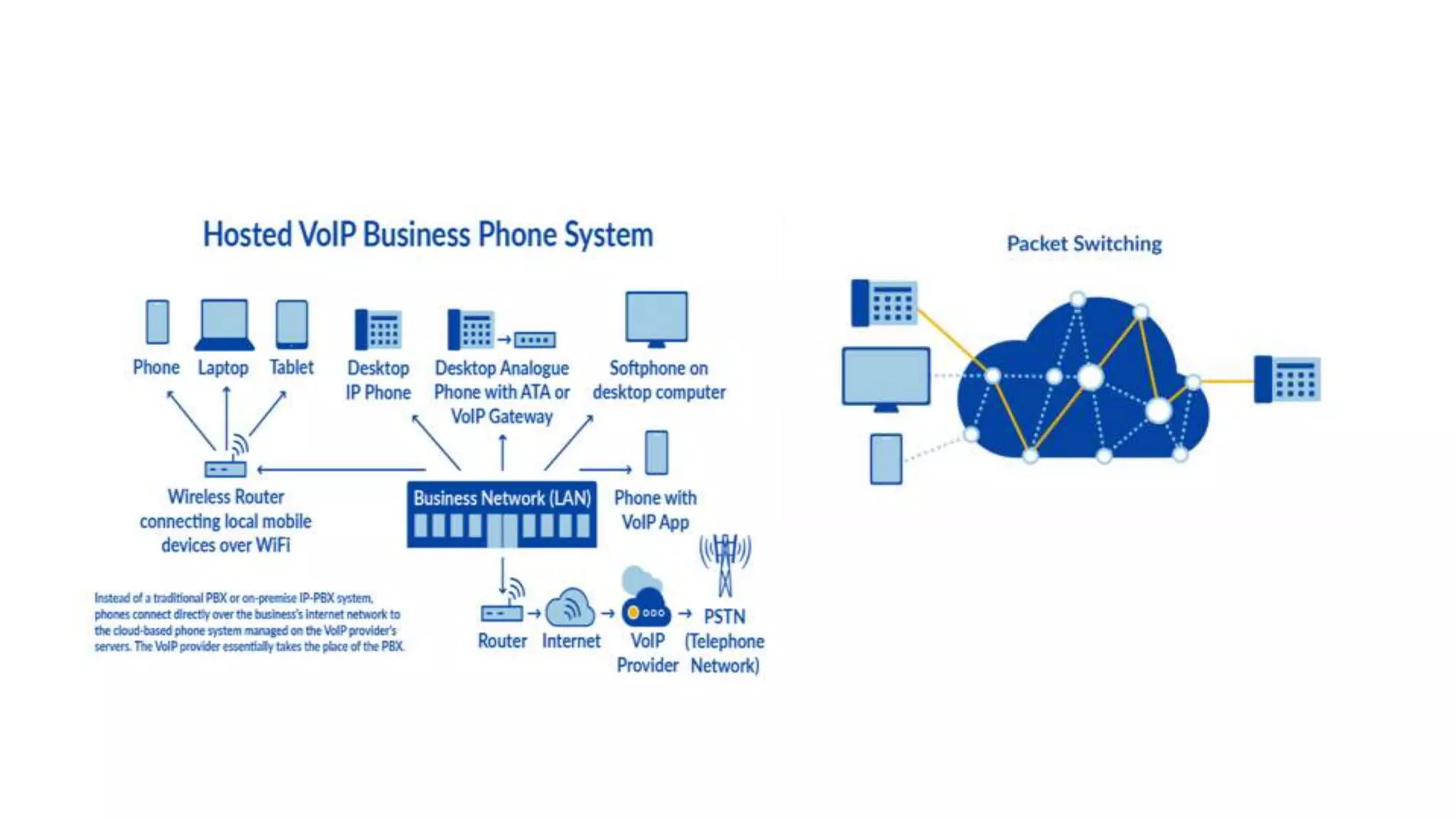
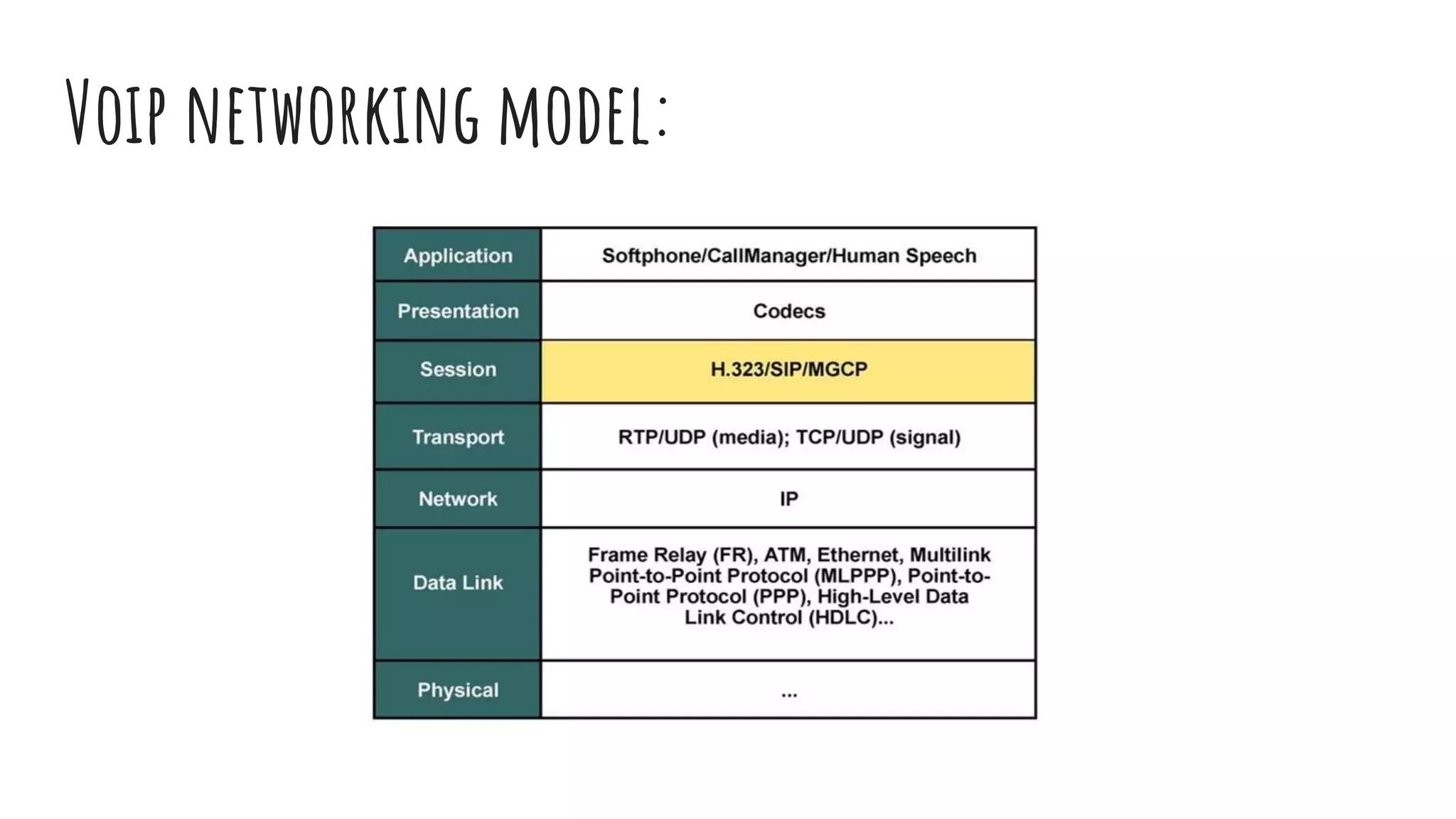
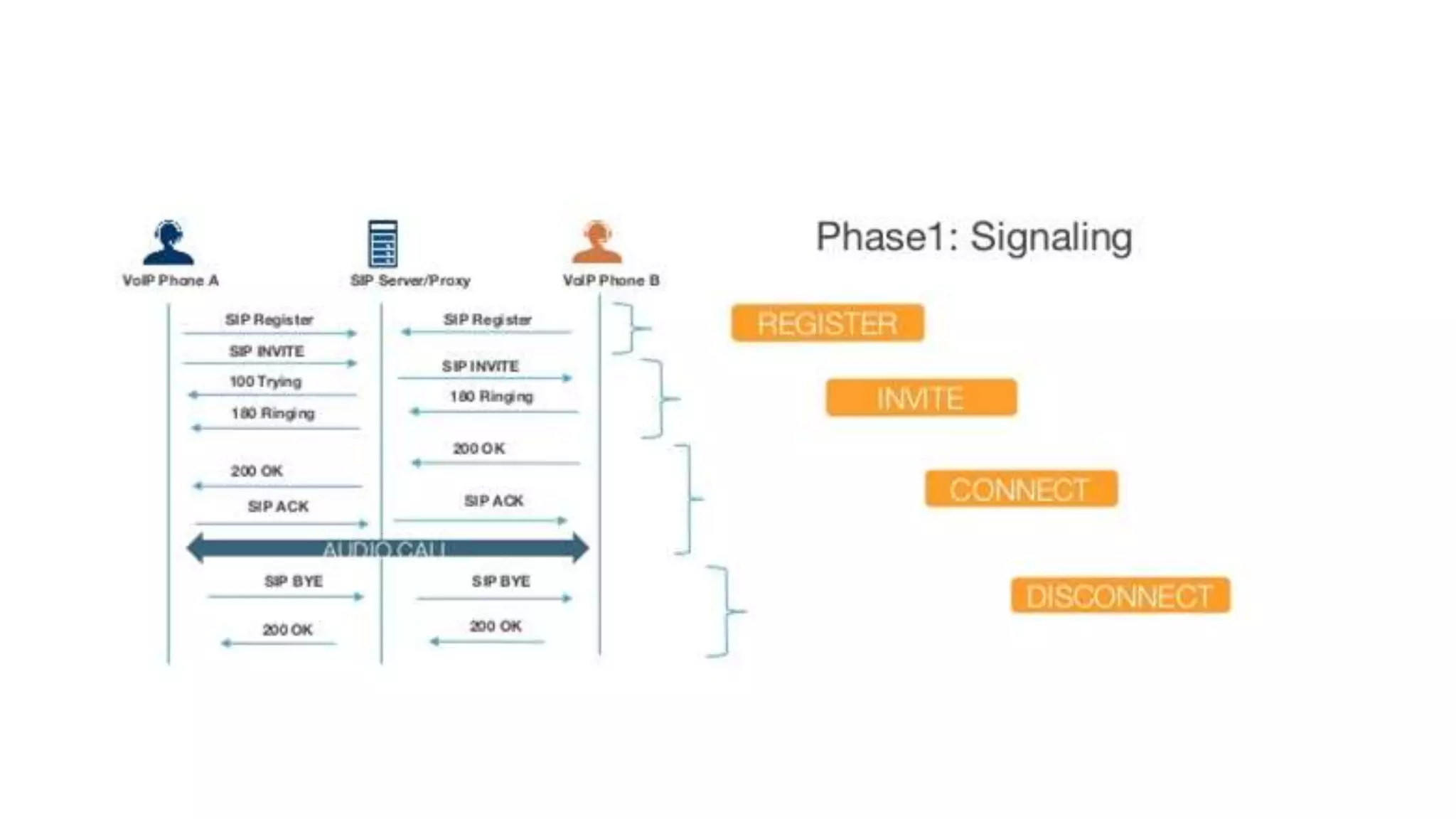
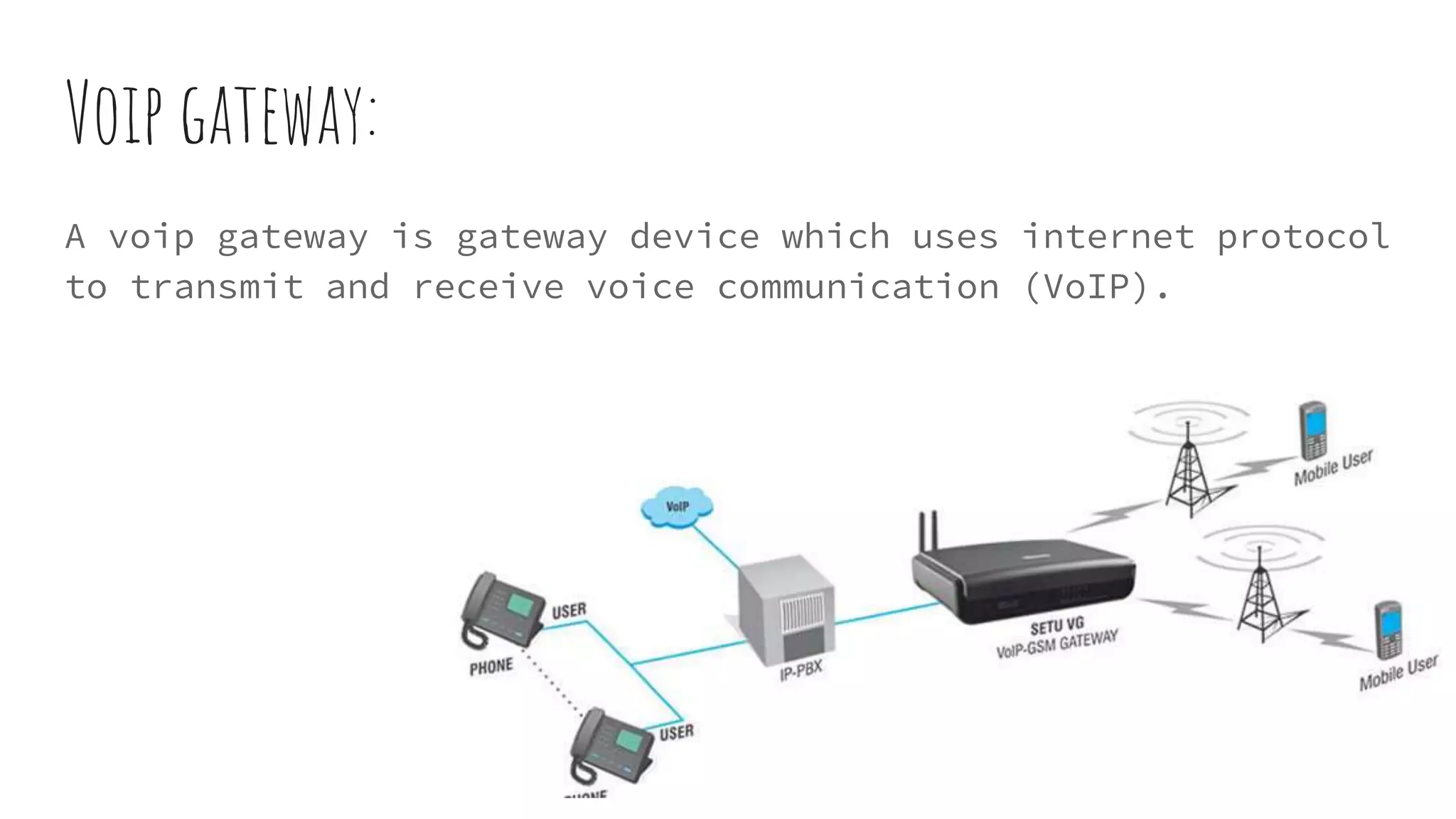
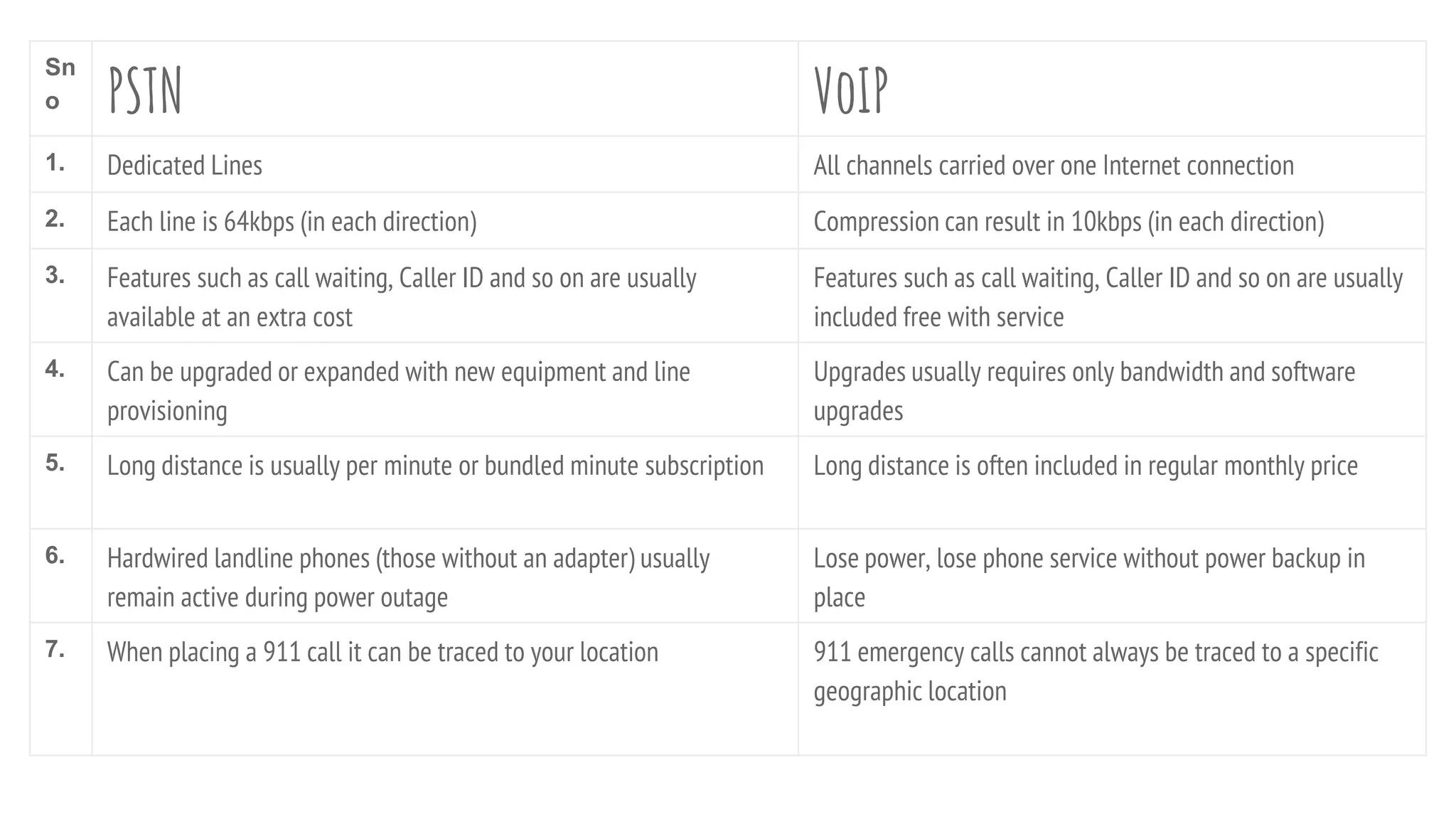
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) allows users to make phone calls using an Internet connection instead of traditional telephone lines. It works by converting voice signals into digital data packets that are transmitted over the Internet and then reconverted at the destination. Key aspects include using codecs to compress voice, encapsulating the digital voice within IP packets, and routing these packets through the network. While VoIP provides benefits like inclusion of features and lower long distance costs, it also faces some security risks due to using the public Internet for phone calls.