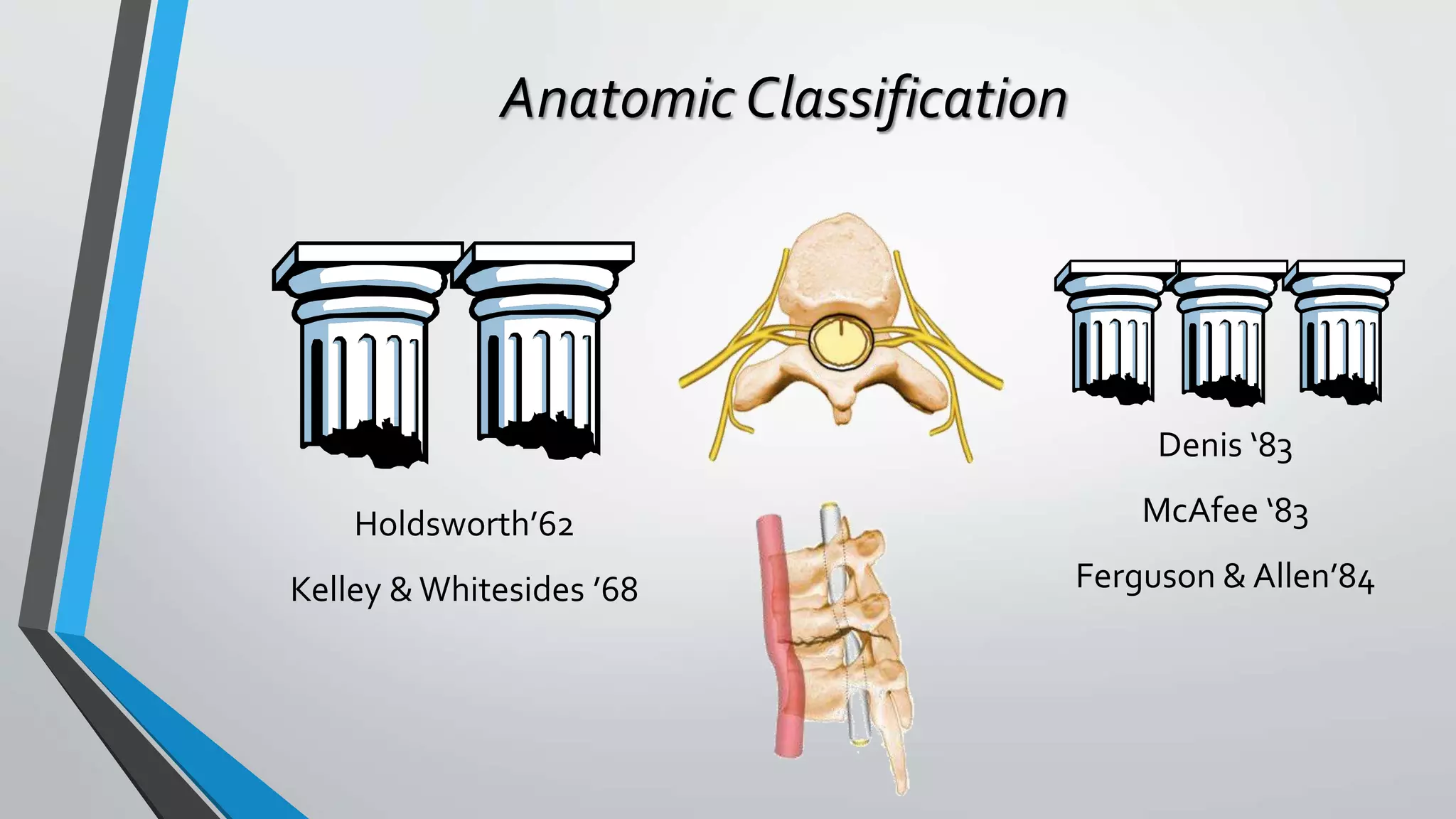
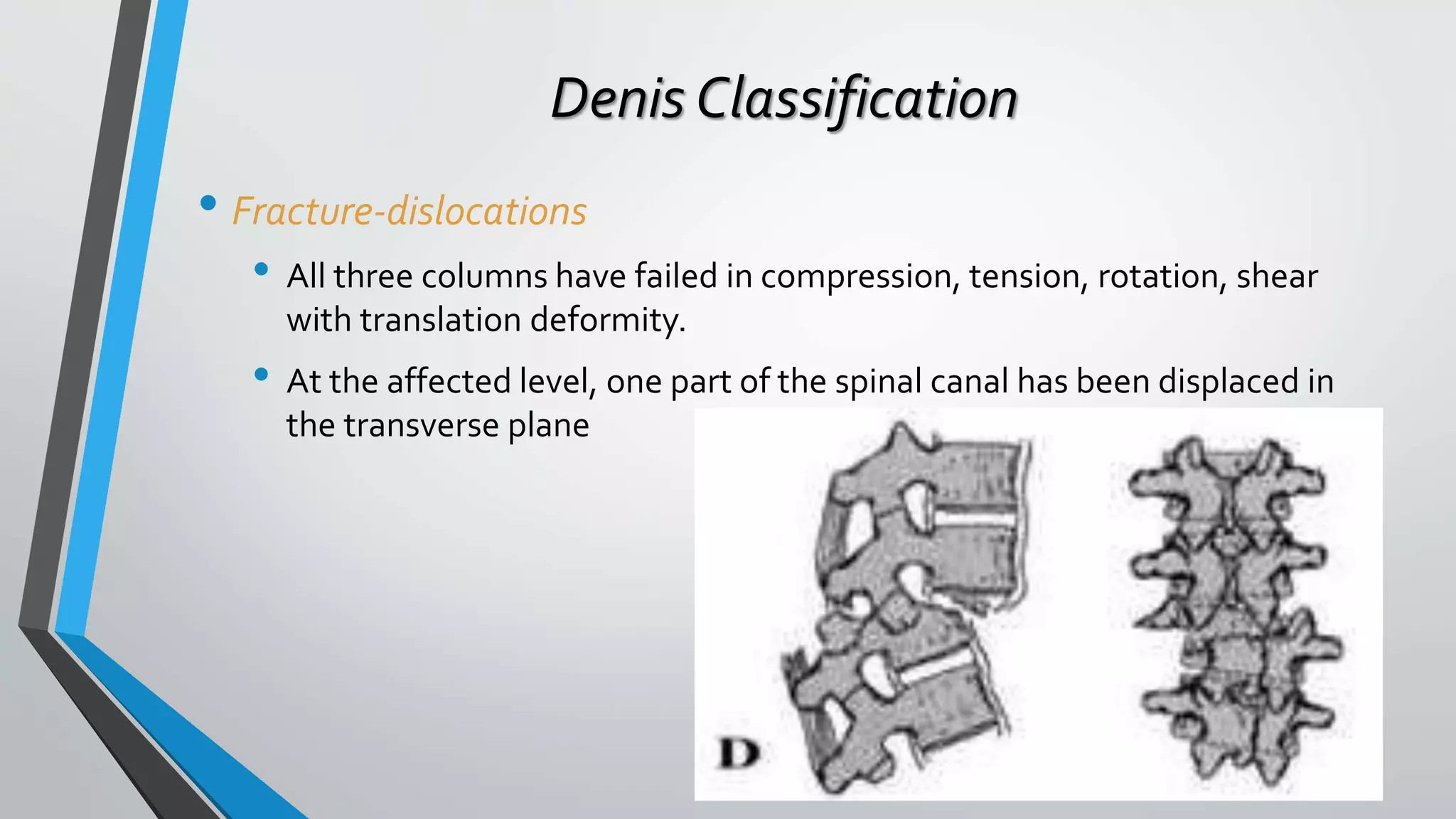
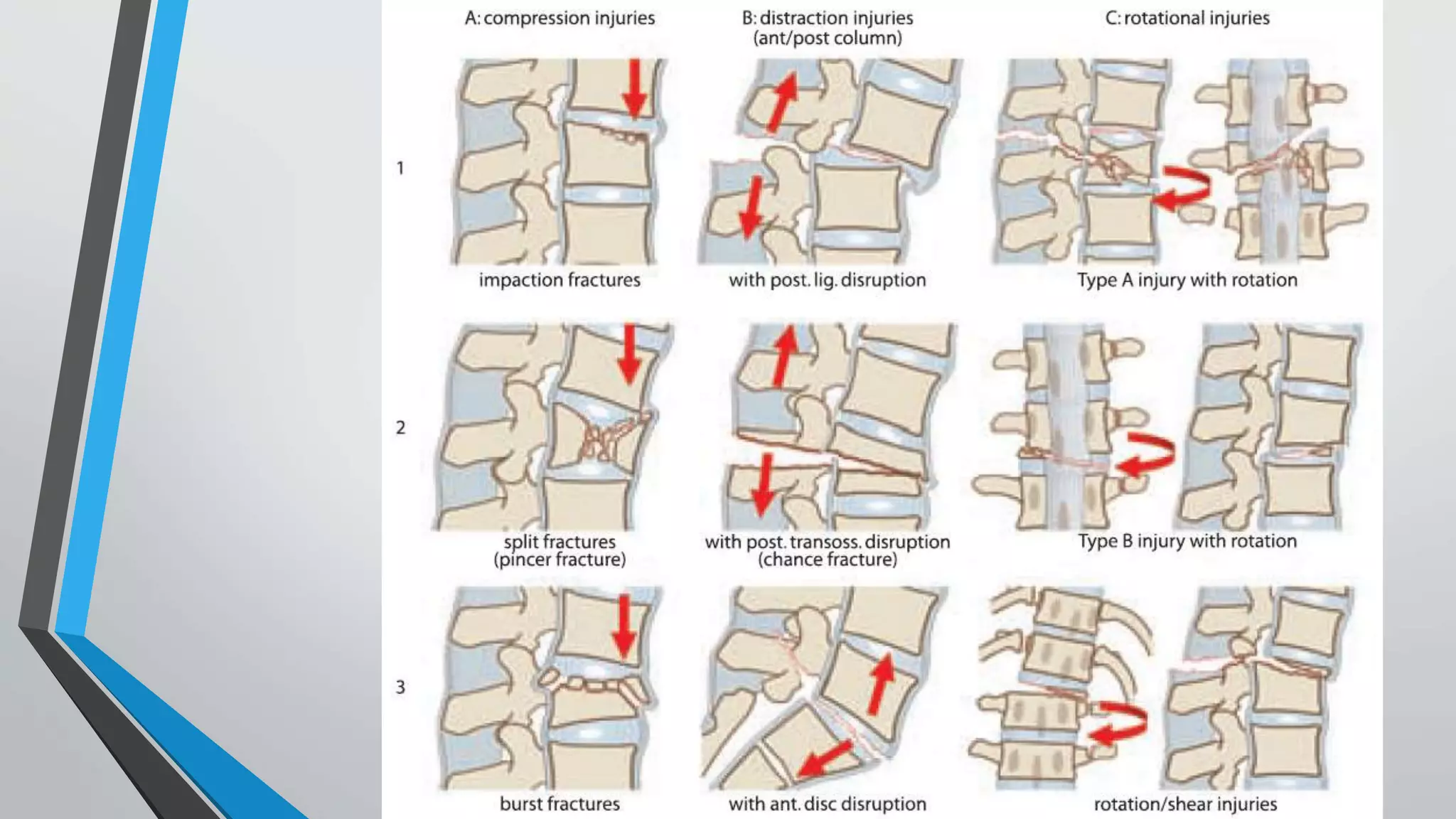
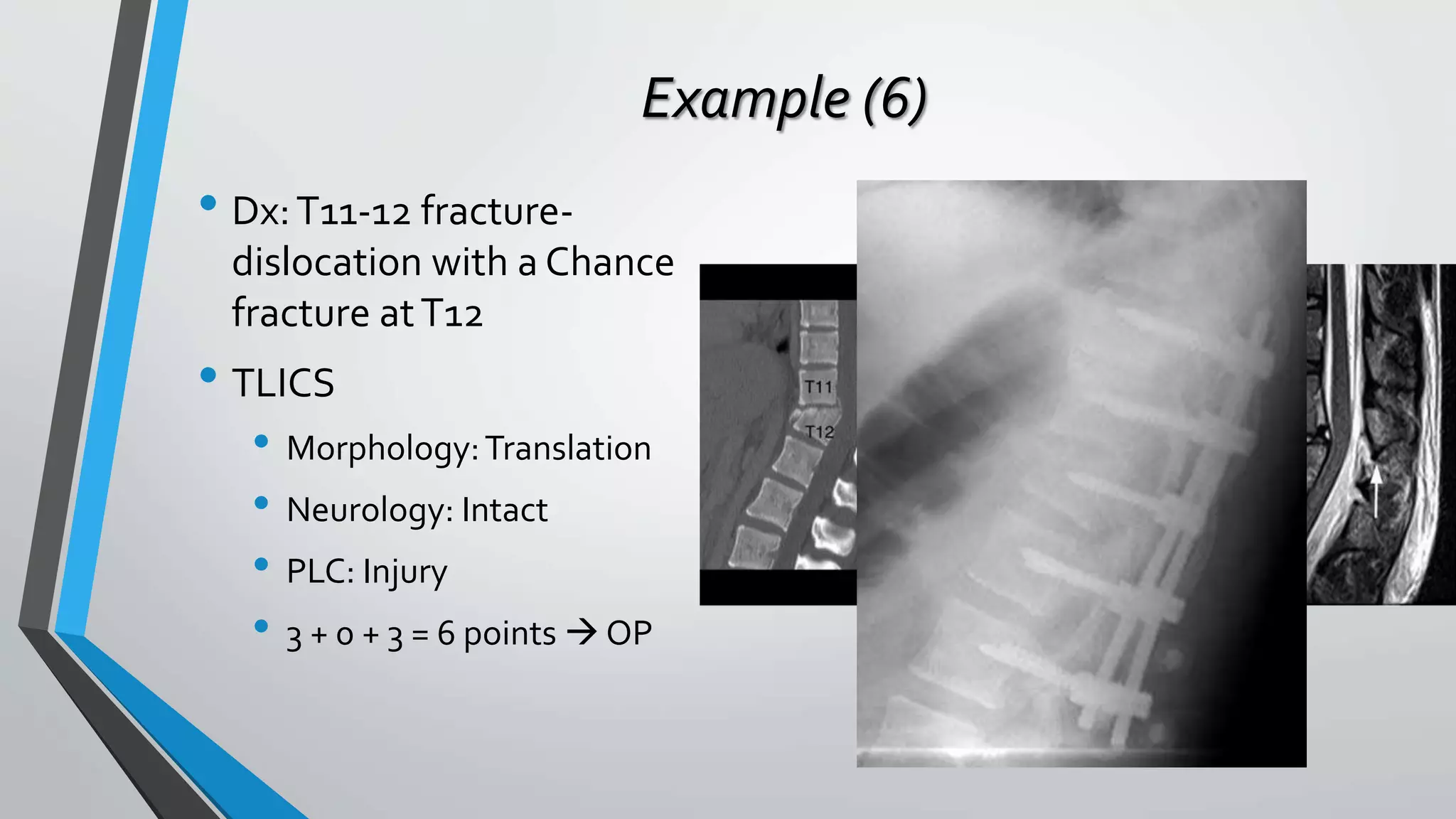
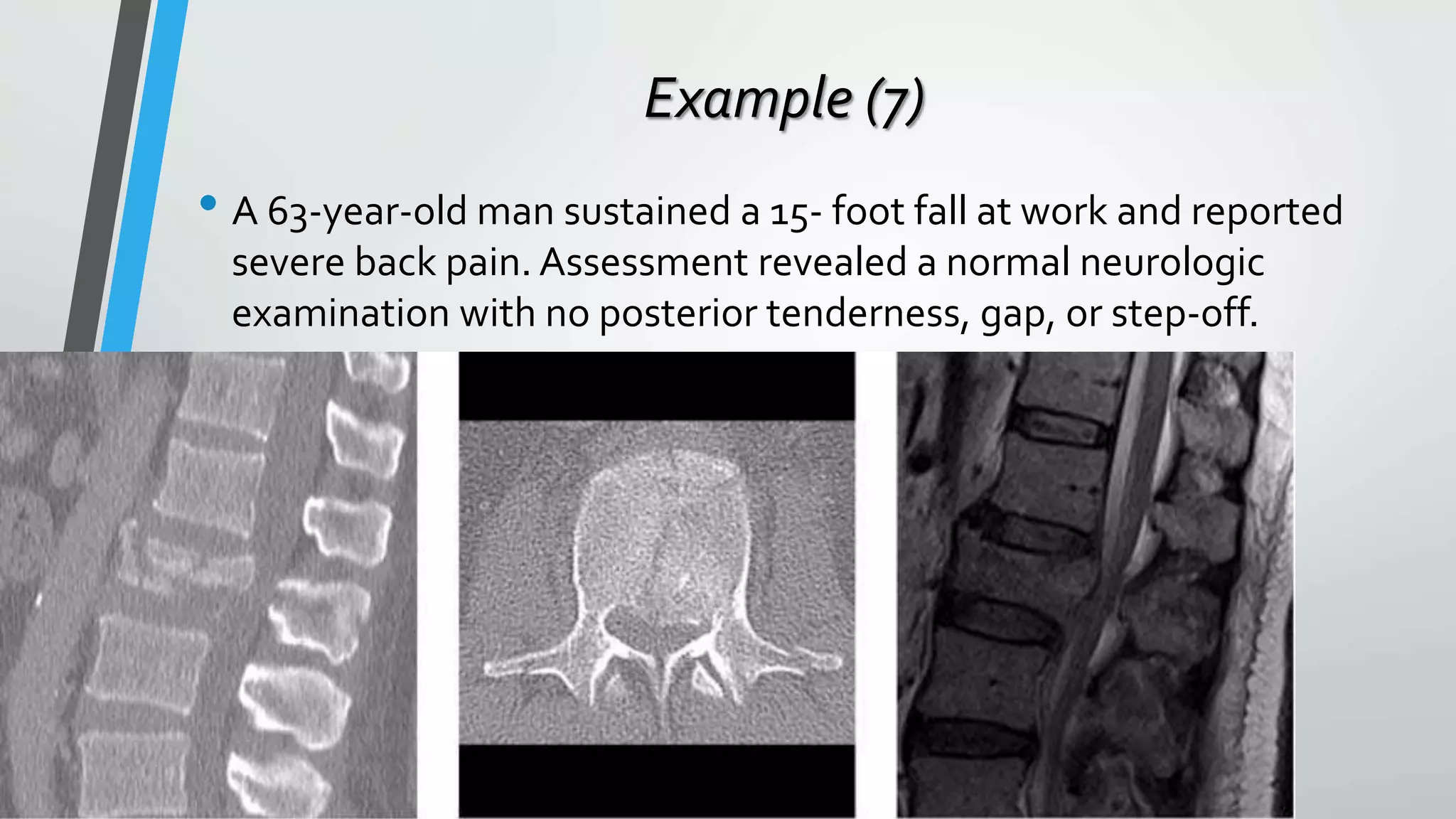
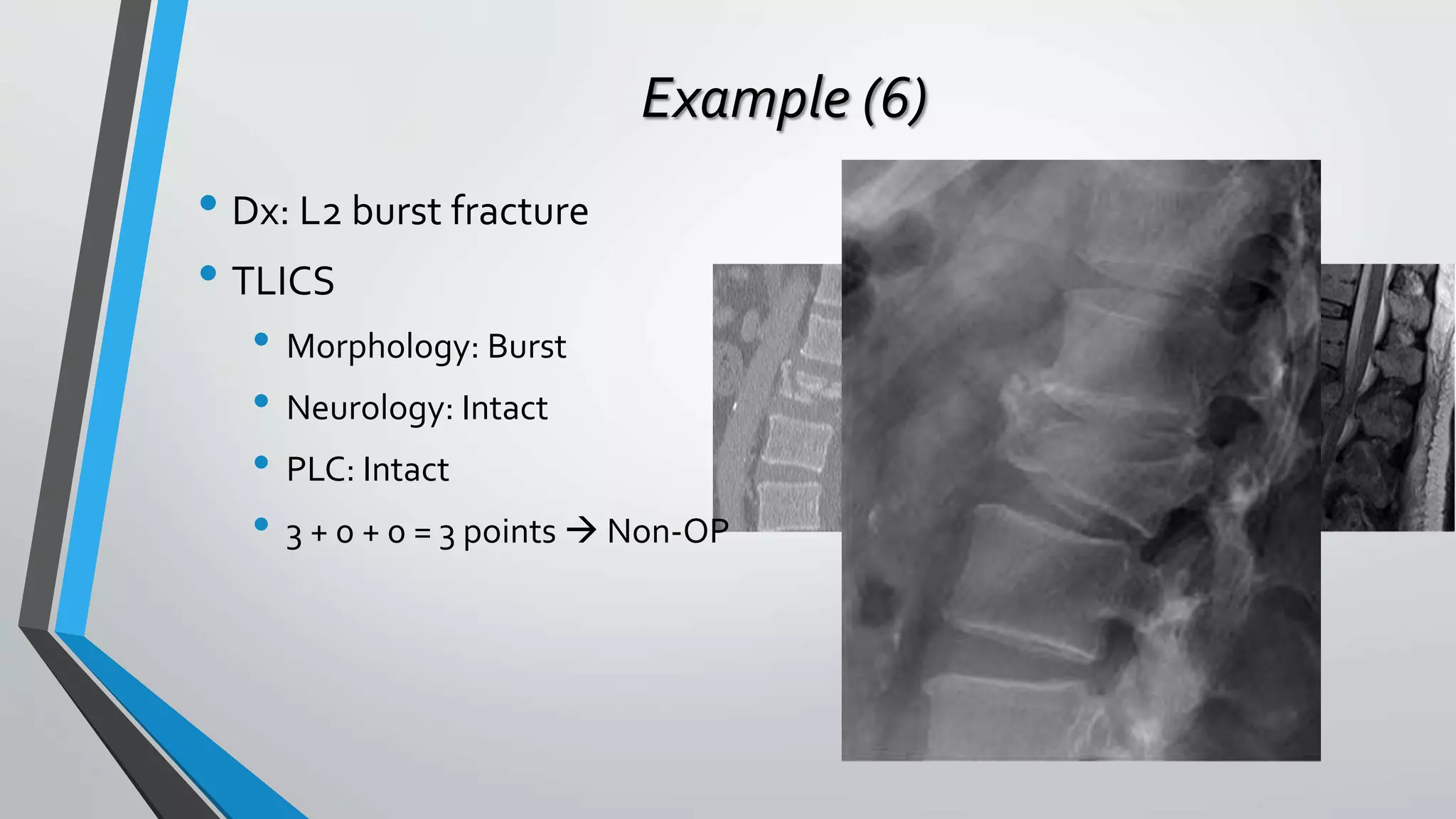
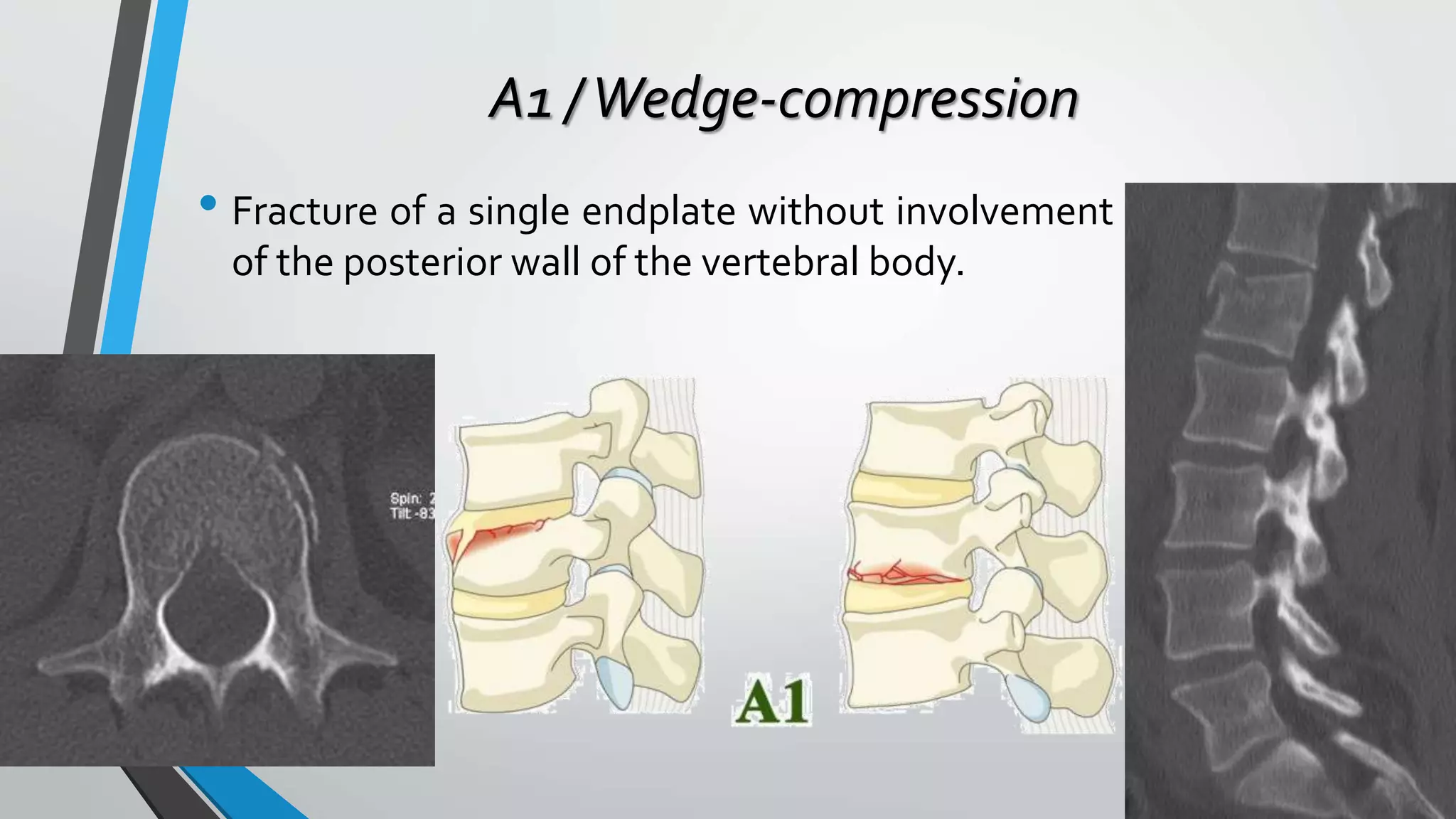
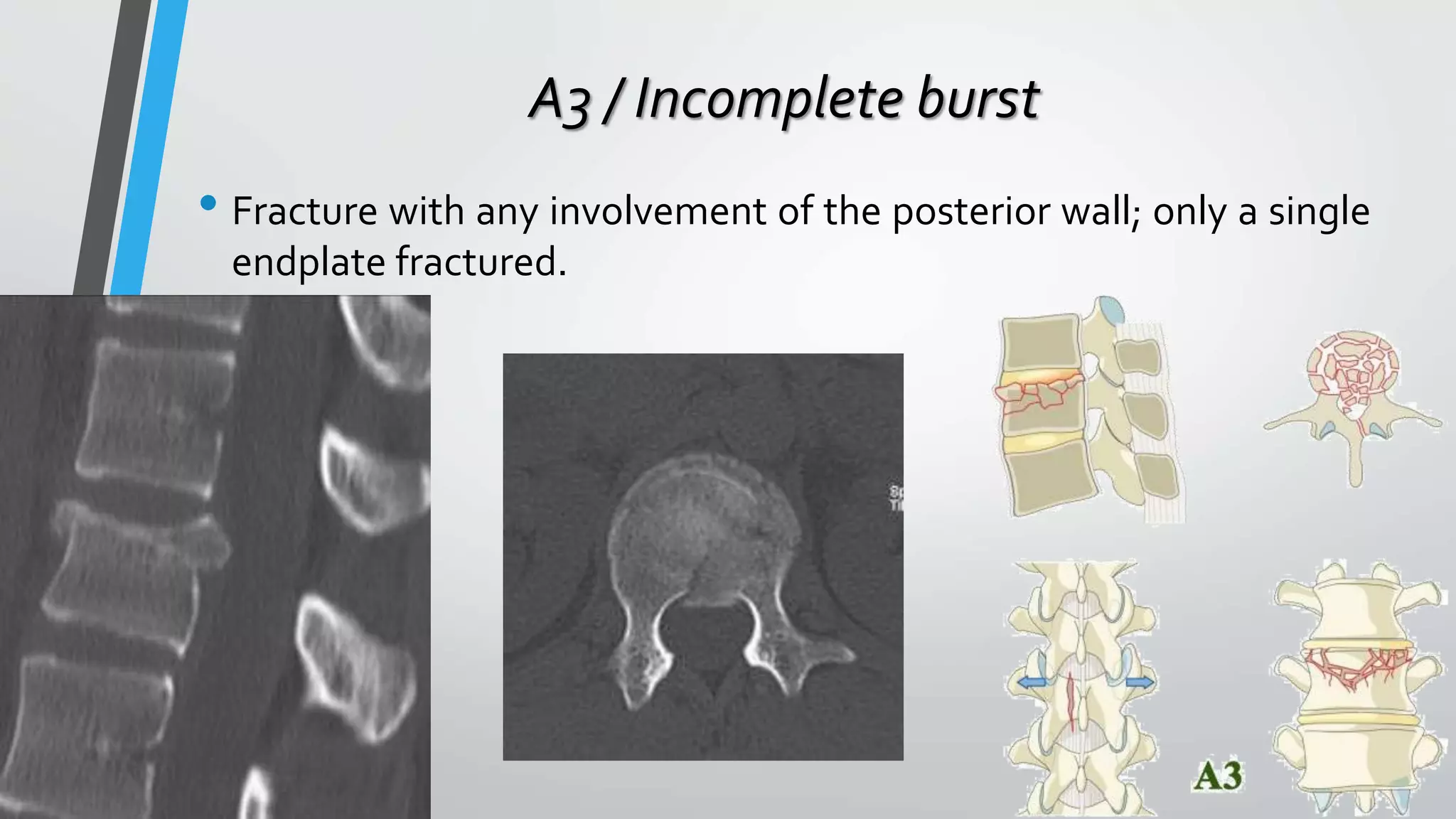
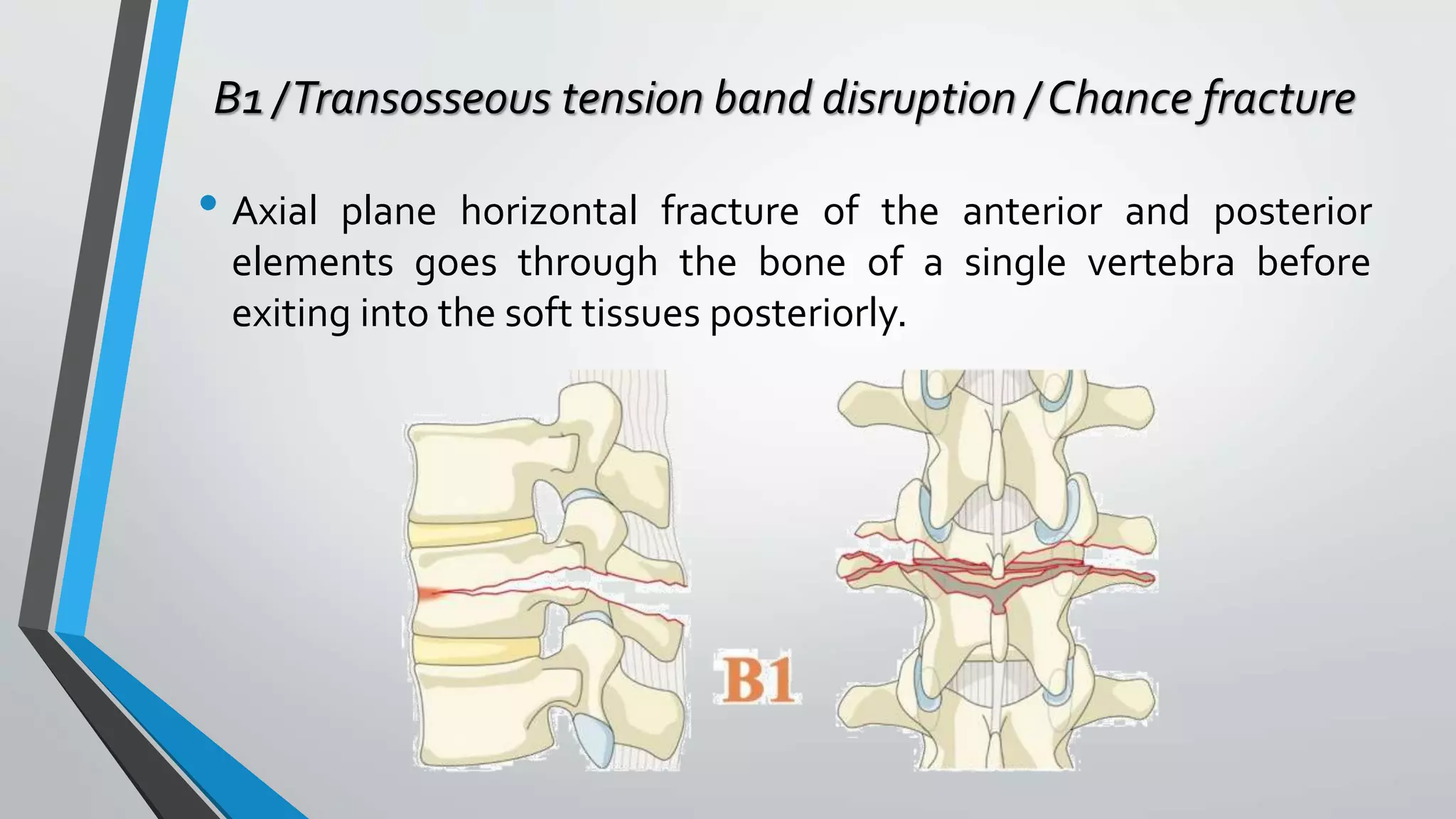
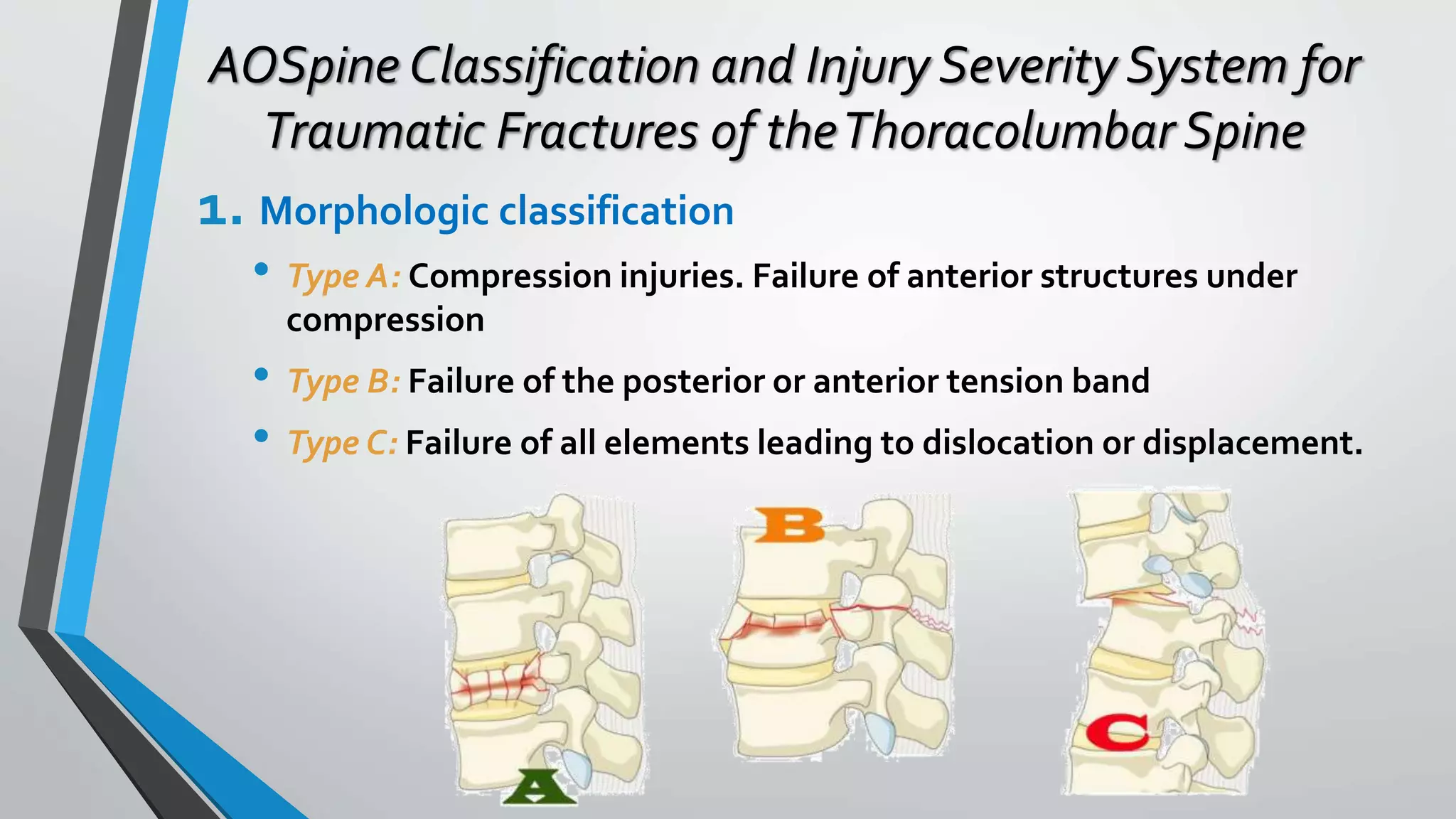
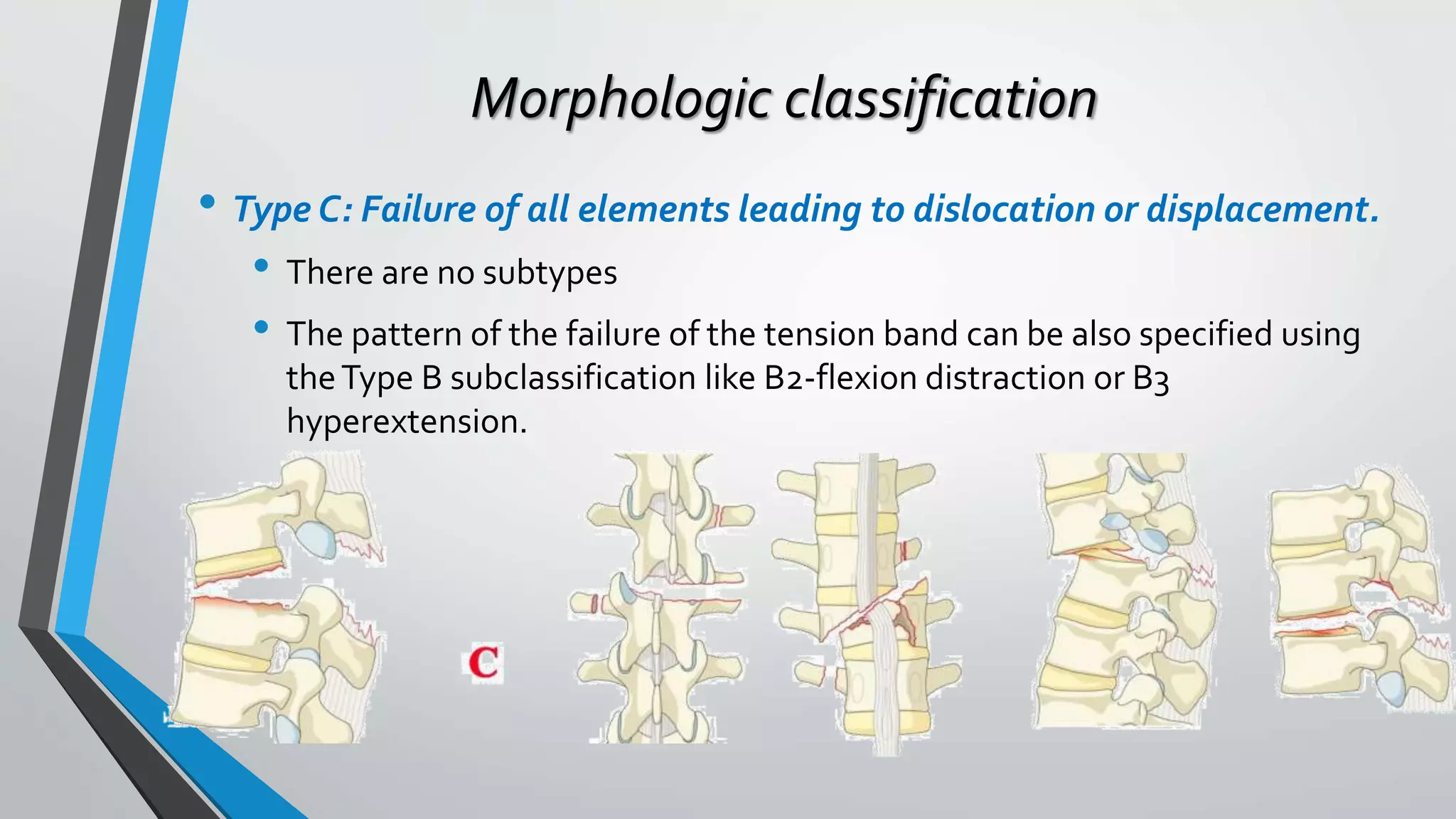
This document provides an overview of different classification systems for thoracolumbar fractures. It discusses early anatomic classifications including the 2-column theory and 3-column theory. It then summarizes the Denis classification and Load-Sharing classification. The AO classification and Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity Score (TLICS) are also described. The document concludes by outlining a new AOSpine Classification and Injury Severity System for Traumatic Fractures of the Thoracolumbar Spine which is based on the morphological classification of the fracture, neurologic injury status, and clinical modifiers.