This document discusses acute CNS infections such as acute pyogenic meningitis, meningoencephalitis, and tuberculous meningitis (TBM). It covers the etiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of these conditions. Common causes of acute pyogenic meningitis in children include Group B streptococcus, pneumococcus, meningococcus, and HIB. Meningoencephalitis can be caused by enteroviruses, arboviruses, or herpes viruses. TBM most often affects children ages 6 months to 4 years and has distinct prodromal, abrupt, and coma stages. Lumbar puncture and CSF analysis are important for diagnosing these infections


![Significance
• Significant morbidity & mortality in
children [1.2m cases worldwide]
• Diagnosis, challenging in young children
• High incidence of sequalae](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecnsinfection-170209084743/85/Acute-cns-infection-3-320.jpg)


![Etiology
• < 2months
• Maternal flora; NICU/PNW flora;
• GBS, GDS, gram-ve, listeria, HIB,
• 2m-12m
• Pneumococci, meningococci, HIB[now less]
• Pseudomonos, staph.aureus, CONS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecnsinfection-170209084743/85/Acute-cns-infection-7-320.jpg)
![Reasons for infection
• Less immunity
• Contact with people with invasive disease
• Occult bacteremia [infants]
• Immunodeficiency
• Splenic dysfunction
• CSF leak ,Meningomyelocele
• CSF shunt infection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecnsinfection-170209084743/85/Acute-cns-infection-8-320.jpg)






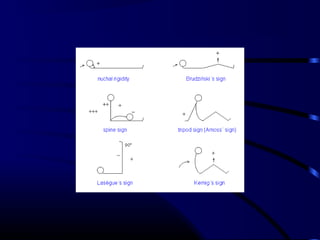
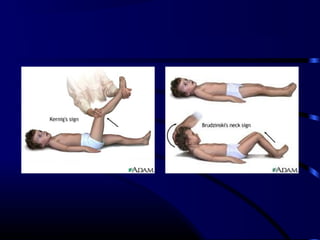
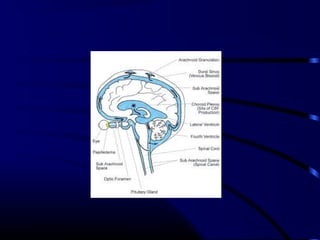
![ICT signs
Headache,vomiting,
Fits
Ptosis, squint,
AF bulge, widened sutures
Hypertension, bradycardia
Stupor, coma
Abnormal posturing
Papilloedema [only in chronic ICT]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecnsinfection-170209084743/85/Acute-cns-infection-17-320.jpg)
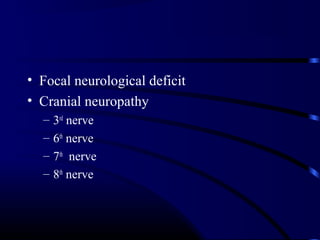
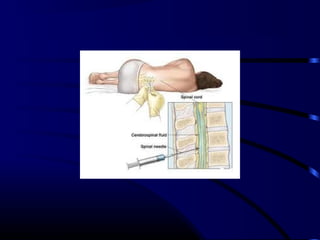
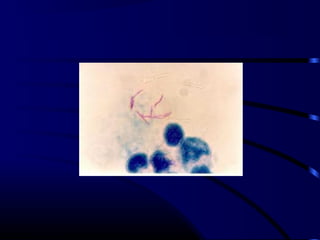
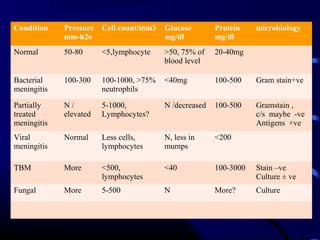
![Diagnosis
• LP & CSF analysis
– Gram stain
– Culture
– Cell count
– Glucose, protein
– [Contraindications for LP]
• Blood culture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecnsinfection-170209084743/85/Acute-cns-infection-19-320.jpg)



![Treatment
• Rapidly progressive [ ~24h]
LP antibiotics
ICT , FND CTbrain & antibiotics
Manage shock, ARDS
• Subacute course [4-7d]
• Assess for ICT, FND
• Antibiotics CT LP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecnsinfection-170209084743/85/Acute-cns-infection-29-320.jpg)


![Duration of therapy
Pneumococci : 7-10 days
Menigococci: 5-7 days
HIB; 7-10 days
E.coli,Pseudomonos ; 3 weeks
Antibiotics started before LP [partially
treated meningitis] ; ceftrioxone 7-10 days.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecnsinfection-170209084743/85/Acute-cns-infection-32-320.jpg)



![Prognosis
• Mortality >10% [more in pneumococci]
• Prognosis poor in
– Infants
– Fits >4days
– Coma, FND on presentation
• Neurological sequalae 20%
– Behavior changes 50%
– Deafness [pneumo,HIB],visual loss
– MR,fits,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecnsinfection-170209084743/85/Acute-cns-infection-36-320.jpg)
![Prevention
• Meningococci
– Rifampacin for close contacts [10mg/kg/day q12h for
2days]
– Quadrivalent vaccine for high risk children
• HIB
– Rifampacin for contacts for 4days
– Conjugate vaccine
• Pneumococci
– Heptavalent conjugate vaccine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecnsinfection-170209084743/85/Acute-cns-infection-37-320.jpg)










![Clinical features
• Depends on parenchymal involvement
• Preceding mild febrile illness & exantheme
• Acute onset of high fever, headache,
irritability,lethargy,nausea,myalgia
• Convulsions,stupor,coma
• Fluctuating FND,emotional outburst
• Ant.horn cell injuryflaccid paralysis [west
nile,entero virus]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecnsinfection-170209084743/85/Acute-cns-infection-48-320.jpg)

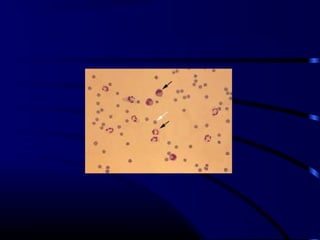
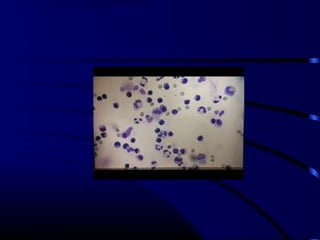
![Diagnosis
• CSF: lymphocytic predominance
– Protein: normal,high in HSV
– Glucose: normal,low in mumps
– Culture of organism [entero V]
– Viral antigen by PCR
– Culture from Npswab,feces,urine
• EEG: focal seizures [temporal];HSV
• CT/MRI: swollen brain parenchyma](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecnsinfection-170209084743/85/Acute-cns-infection-50-320.jpg)
