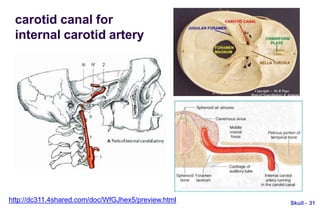
This document provides an overview of the bones that make up the human skull. It discusses the neurocranium, which includes the cranial vault bones of the frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital and sphenoid bones. It also covers the viscerocranium, which includes the facial skeleton bones such as the maxilla, zygomatic, nasal and lacrimal bones. It describes the various parts of these bones and their roles in forming the cranial fossae and facial structures like the orbits, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses and oral cavity. Openings on the bones that transmit nerves, vessels and canals are also detailed.



















![Dural sinuses in Posterior cranial fossa
groove for transverse sinus; confluence of the sinus - internal
occipital protuberance
tentorium cerebelli: separating occipital lobe from cerebellum
internal occipital crest [- falx cerebelli]
Skull - 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/boneskull-230112082903-88d71e57/85/Bone_Skull-pptx-20-320.jpg)






![Inner surface of Occipital bone, Temporal bone
Occipital bone: Basilar part, [clivus]; Lateral parts;
Squamous part (squama occipitalis)
Temporal bone: Squamous part; Petrous part; (Mastoid
part; Sytloid process)
Skull - 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/boneskull-230112082903-88d71e57/85/Bone_Skull-pptx-27-320.jpg)