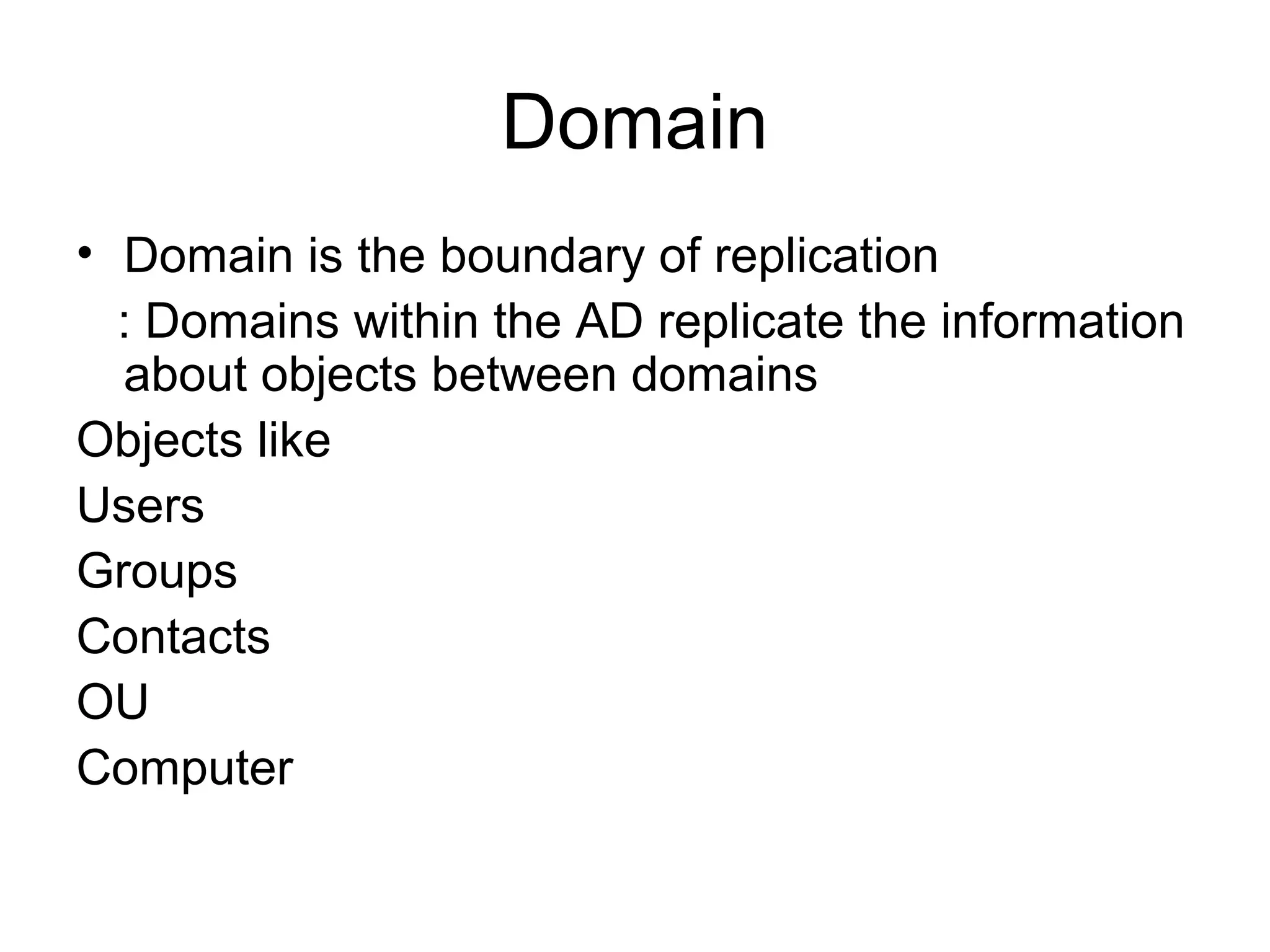
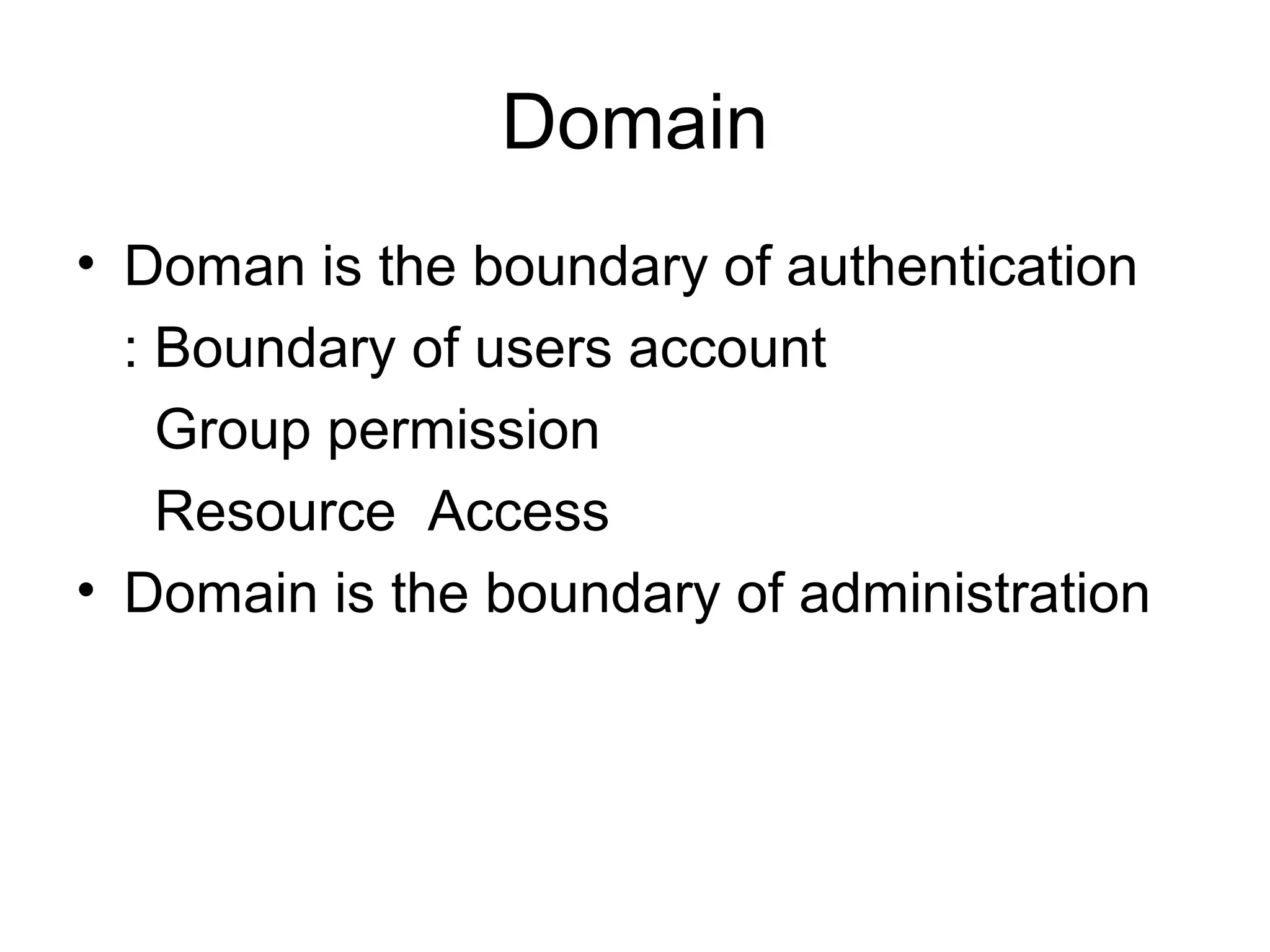
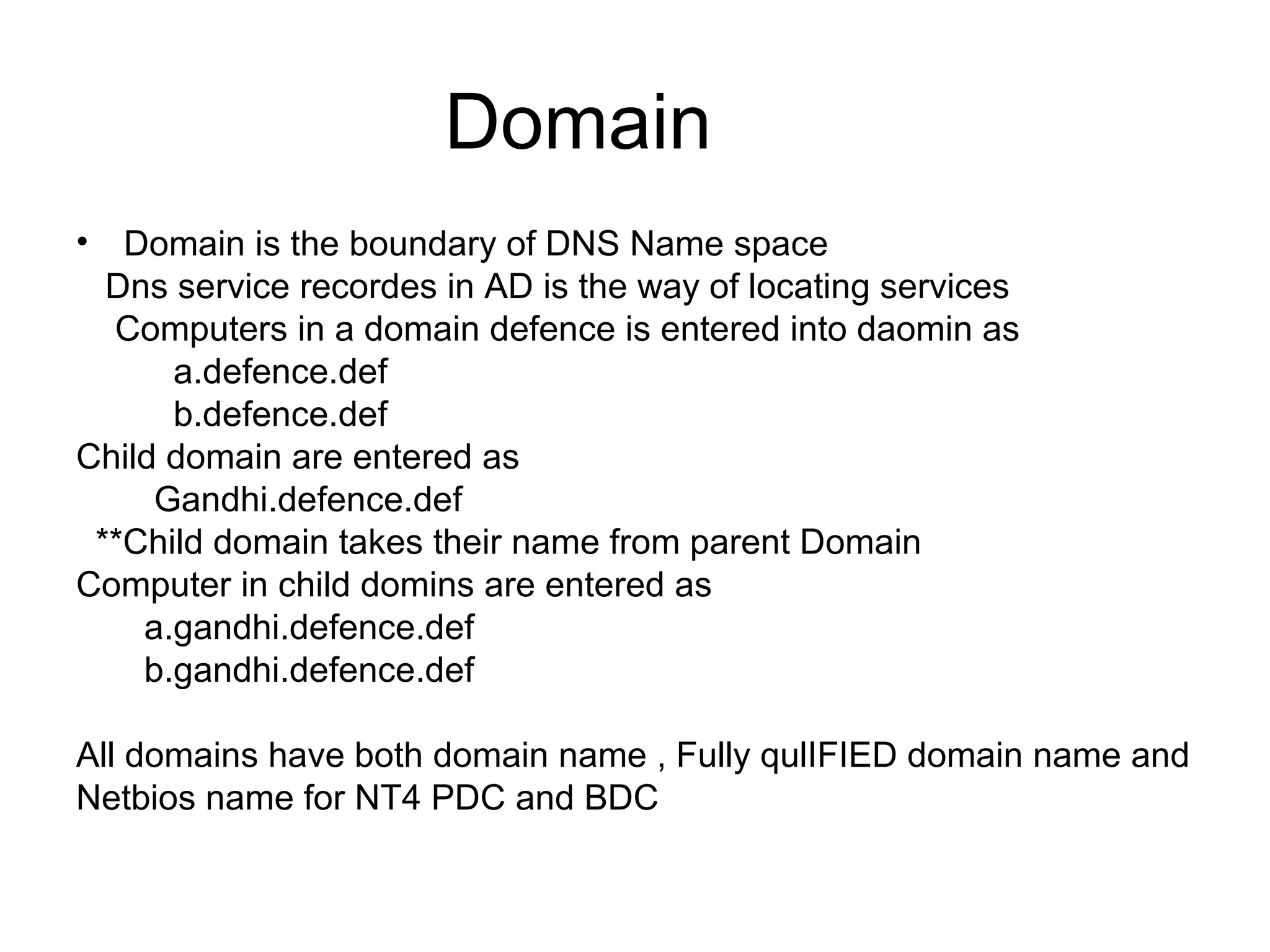
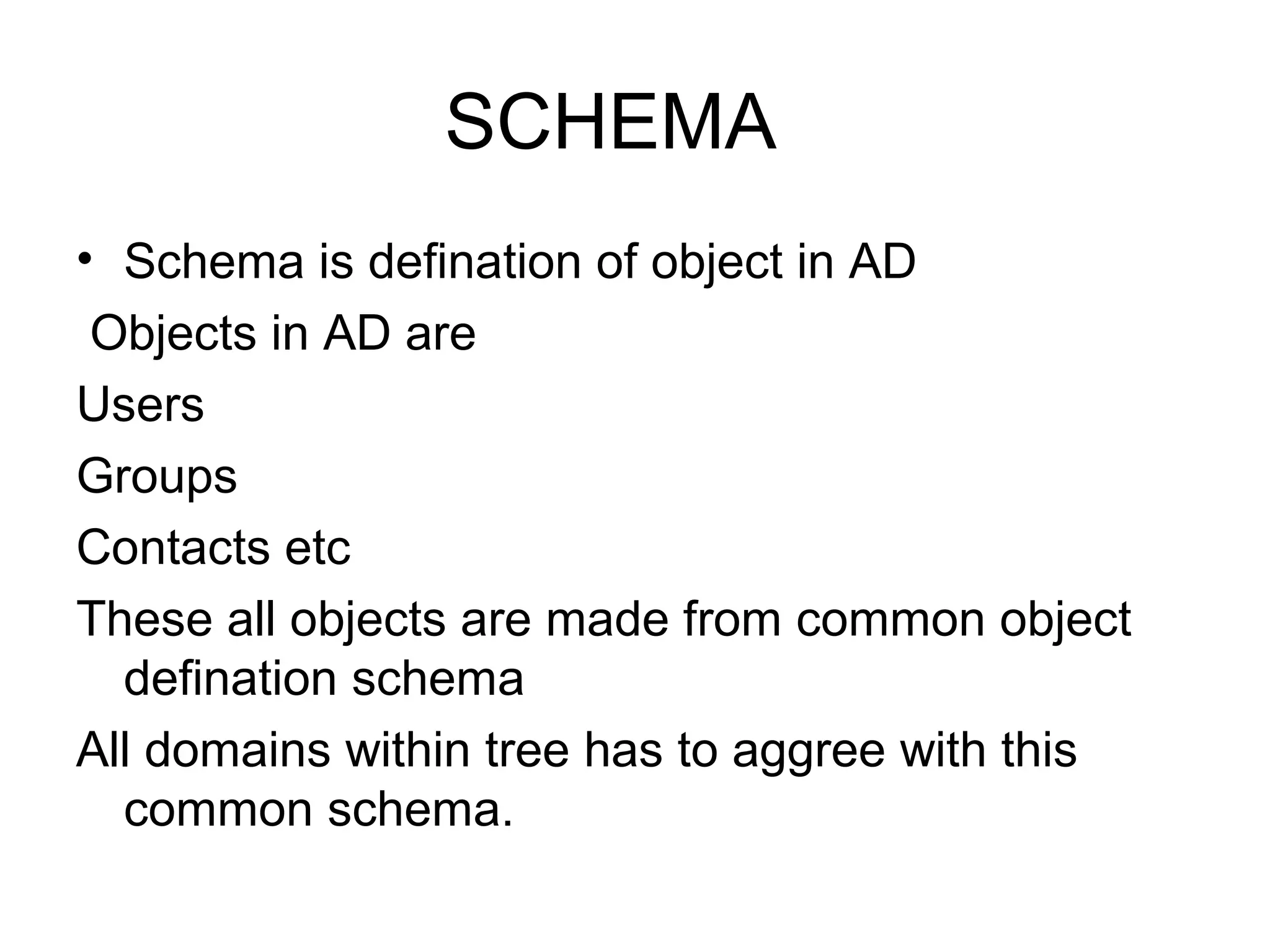
Active Directory (AD) is a centralized directory service that provides a single point of access for network resources. It utilizes standards like LDAP and DNS to organize users, groups, computers, policies and other objects in a hierarchical structure. Key components of AD include domains, trees, forests, organizational units, and sites. Domains define the boundaries for authentication, administration and replication. Trees and forests connect related domains. Organizational units help organize objects. Sites represent physical network locations and define replication scopes.