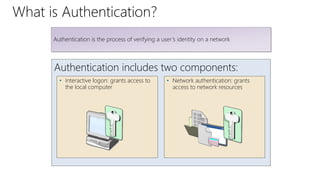
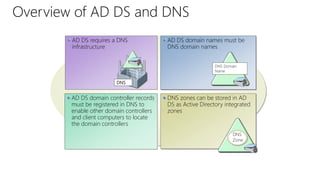
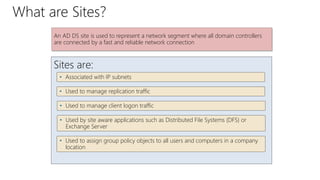
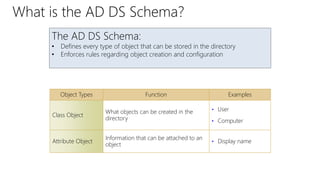
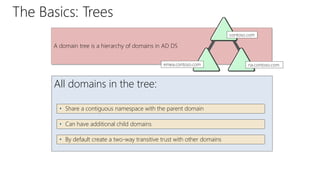
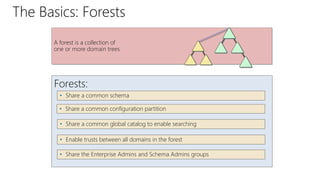
This document provides an overview of Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS). It discusses both the physical and logical components of AD DS, including domain controllers, global catalog servers, the data store, replication, sites, domains, trees, forests, organizational units, trusts, and common AD DS objects. The key takeaway is that AD DS provides centralized management of users, computers, and other resources on a network through authentication, authorization, and directory services.