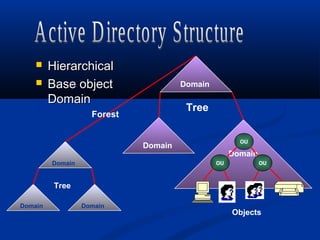
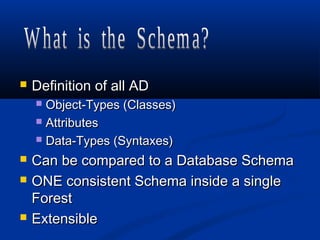
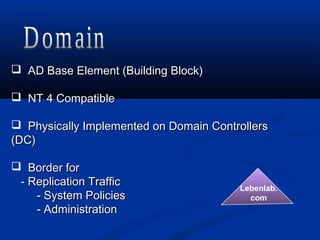
A directory service stores and organizes information about a computer network's users and resources. Active Directory is Microsoft's implementation of an LDAP directory service that allows administrators to define and manage objects like users, printers, and servers across an organization. It provides authentication, authorization, and other services to users and applications. Active Directory replicates information across domain controllers to provide redundancy and high availability.