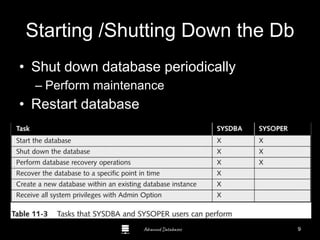
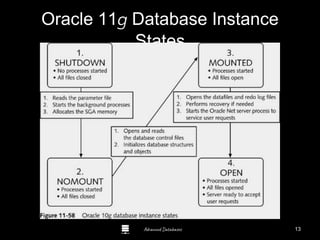
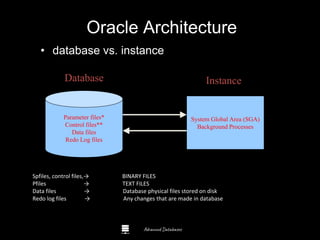
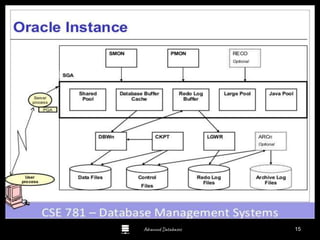
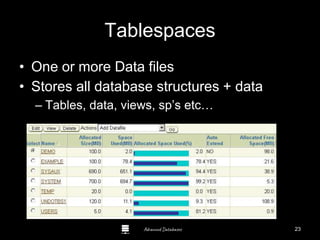
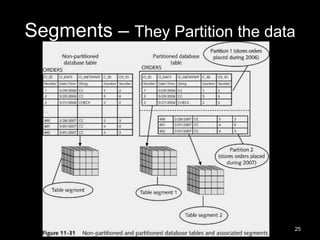
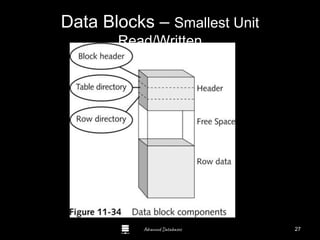
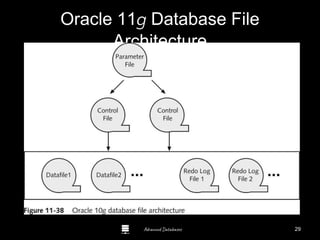
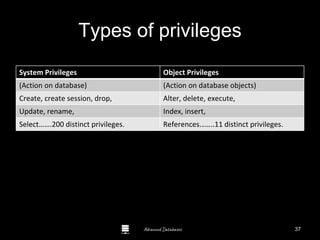
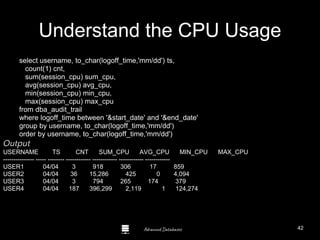
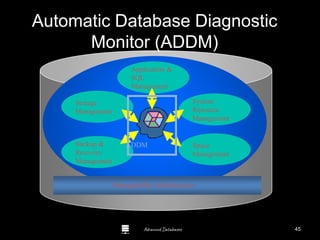
The document is a comprehensive guide to database administration, specifically focusing on Oracle 10g and 11g, covering tasks, tools, and user account management. It details the roles and responsibilities of a Database Administrator (DBA), performance management, security, and usage of Oracle Enterprise Manager for database operations. Furthermore, it explains data storage structures, including tablespaces and data files, and highlights additional DBA activities such as backups, recovery, and auditing.